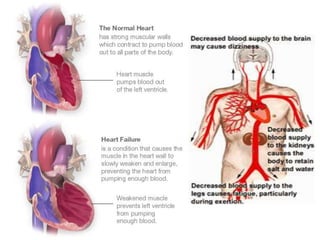
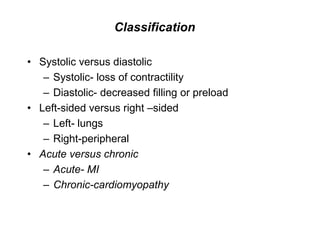
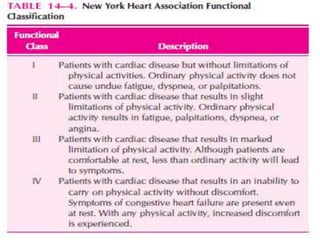
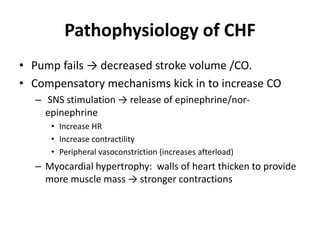
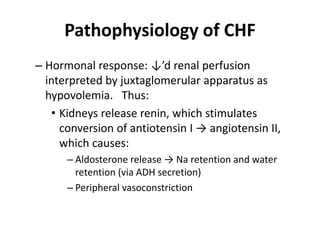
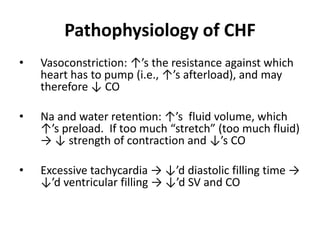
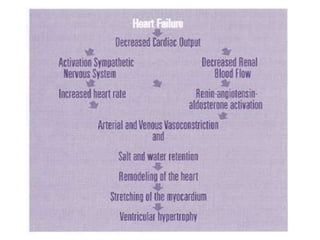
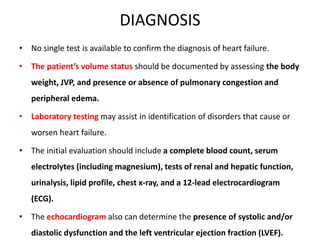
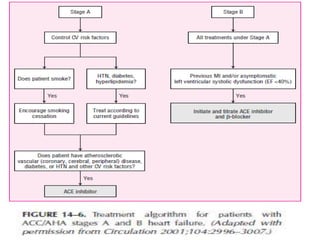
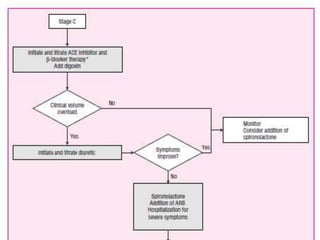
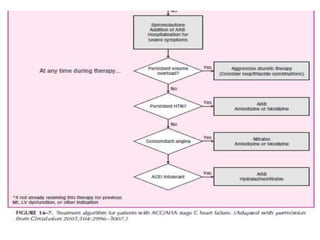
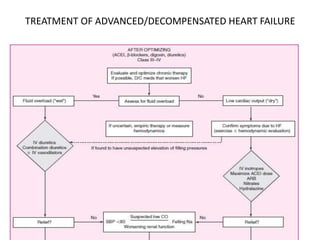
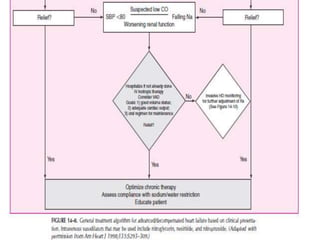
Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It has multiple causes and symptoms including shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, and coughing up pink mucus. Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms with diuretics, and improving the heart's function with ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and other medications. For severe cases, devices or surgery such as defibrillators, resynchronization therapy, or transplantation may be needed. The long-term goal is to improve quality of life through lifestyle changes and optimal medical management.