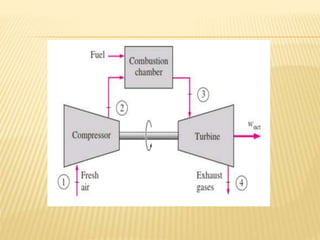
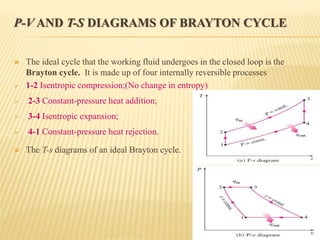
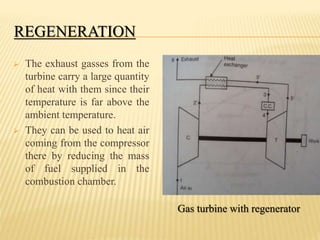
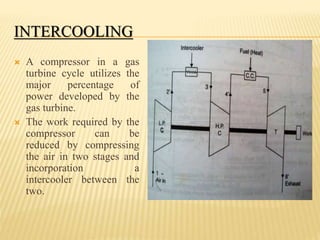
This document discusses open cycle gas turbine power plants. It begins with an introduction to gas power plants and the history of gas turbines. It then covers the basic working principle of gas turbine power plants, including the main components of air compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine. Applications and advantages/disadvantages of gas turbines are also summarized. Finally, it describes the open cycle gas power plant configuration and methods to improve the thermal efficiency, such as regeneration, reheating, and intercooling.