Embed presentation
Download to read offline

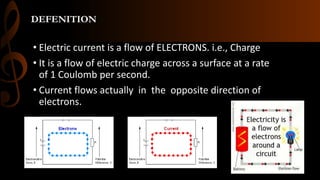


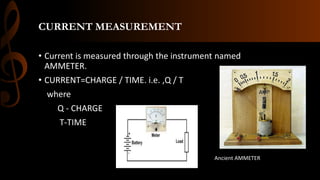
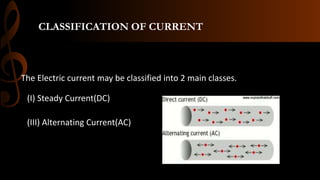


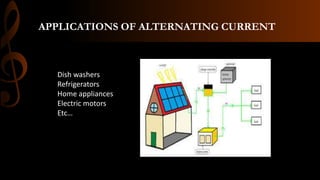


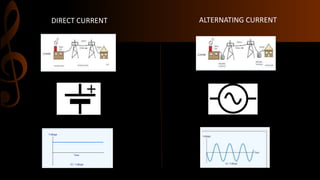
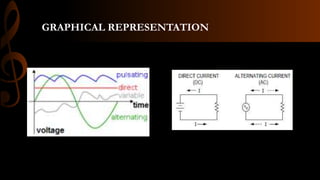



Electric current is the flow of electrons, with the standard unit being the ampere which is defined as one coulomb of charge passing per second. Current can be either steady direct current (DC), where the magnitude does not change over time as provided by batteries, or alternating current (AC) where the direction periodically changes due to the alternating polarity of the voltage source. Common applications of DC include cell phones and flashlights, while AC applications include appliances, electric motors, and power from wall outlets which is converted to DC for battery operated devices using transformers, diodes, and capacitors.















