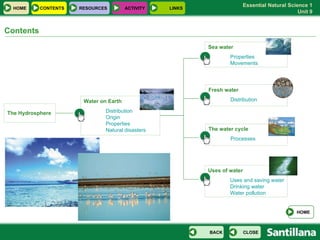
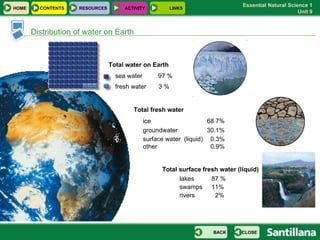
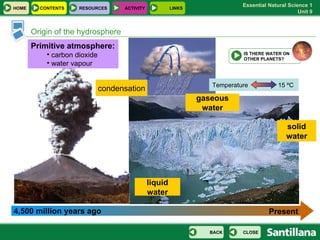
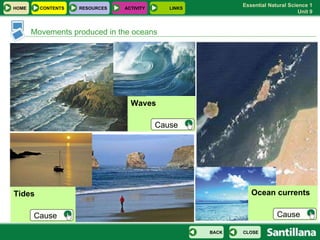
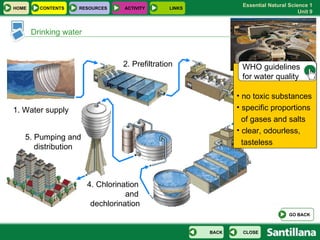
The document discusses the hydrosphere and various aspects of water on Earth. It covers the distribution and origins of water, properties of water and natural disasters related to water. It also discusses the water cycle, uses of water, fresh water sources, sea water properties, water movements in oceans, drinking water and water pollution.