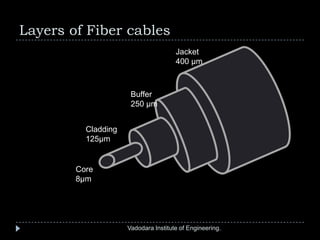
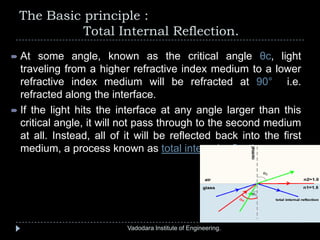
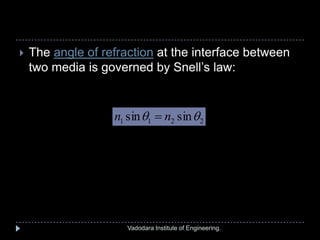
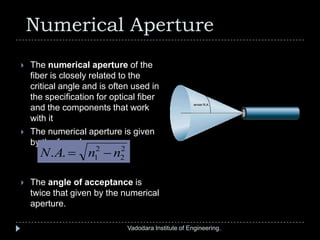
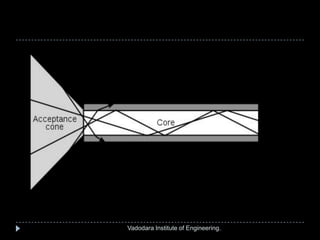
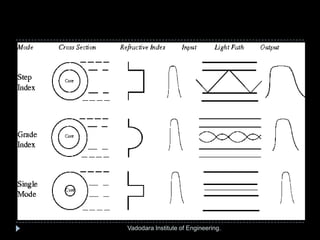
The document provides a comprehensive overview of optical fibers, detailing their structure, advantages, and working principles, including total internal reflection and numerical aperture. It describes various types of optical fibers such as single-mode and multi-mode step-index fibers, and emphasizes their applications in medical and mechanical imaging. The content is developed by students under the guidance of a professor at Vadodara Institute of Engineering.