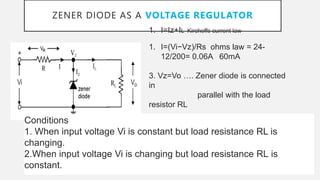
Clarence Zener first described the breakdown of insulators in 1934, which was later used by Bell Labs to develop the Zener diode. A Zener diode allows current to flow in both the forward and reverse directions if the reverse voltage exceeds the Zener voltage. It acts as a voltage regulator by maintaining a nearly constant voltage across its terminals over a range of reverse currents.