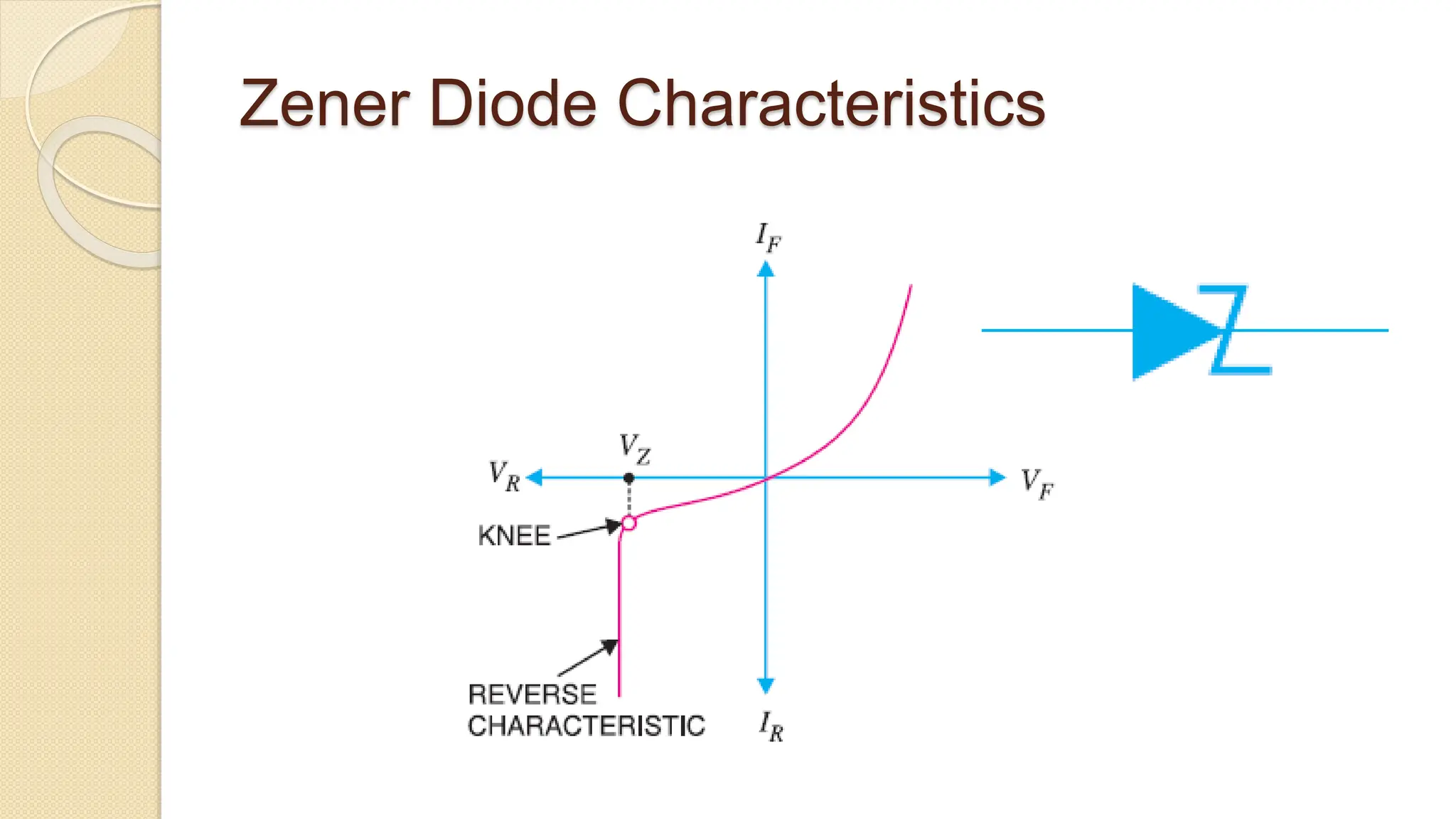
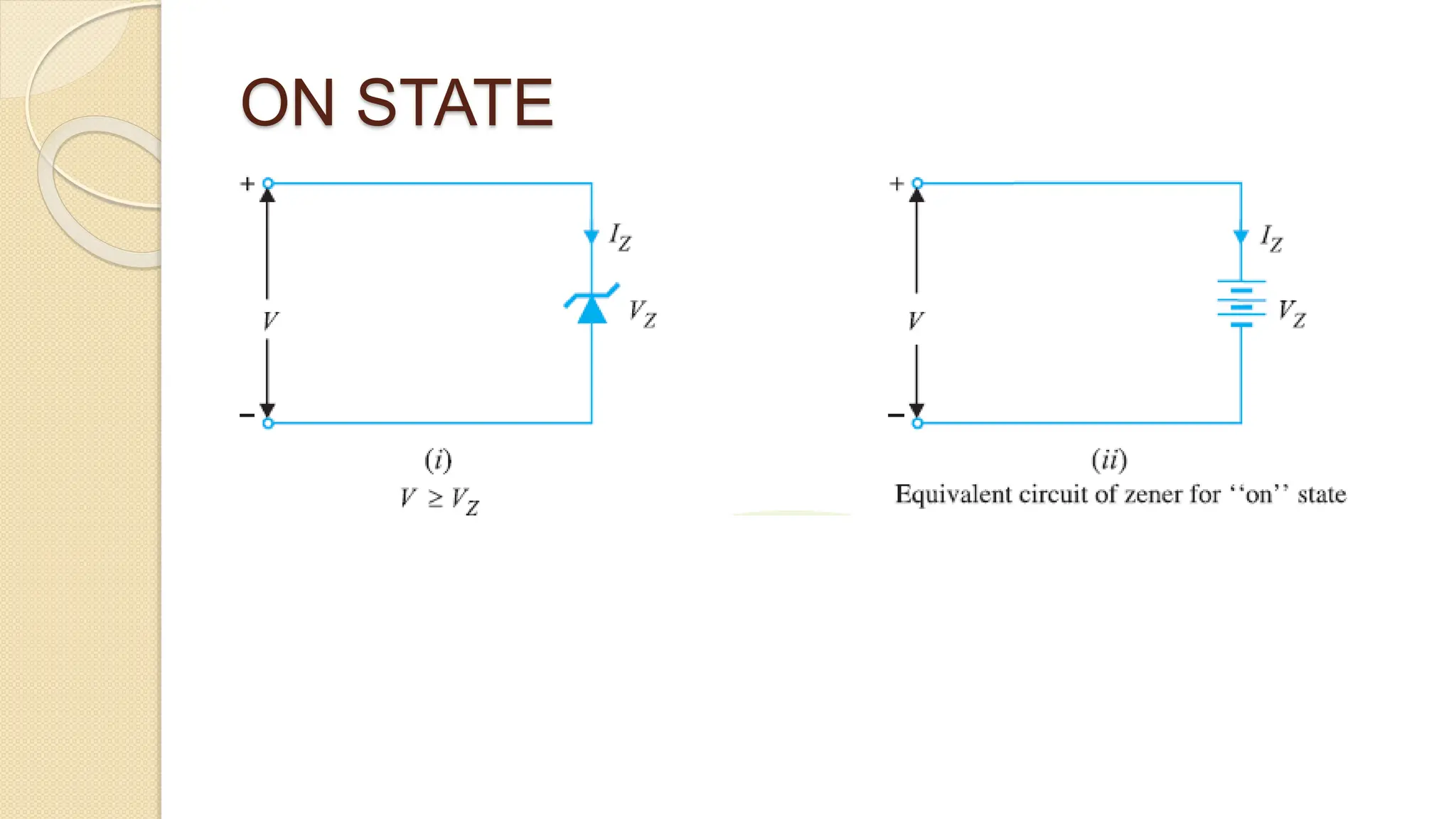
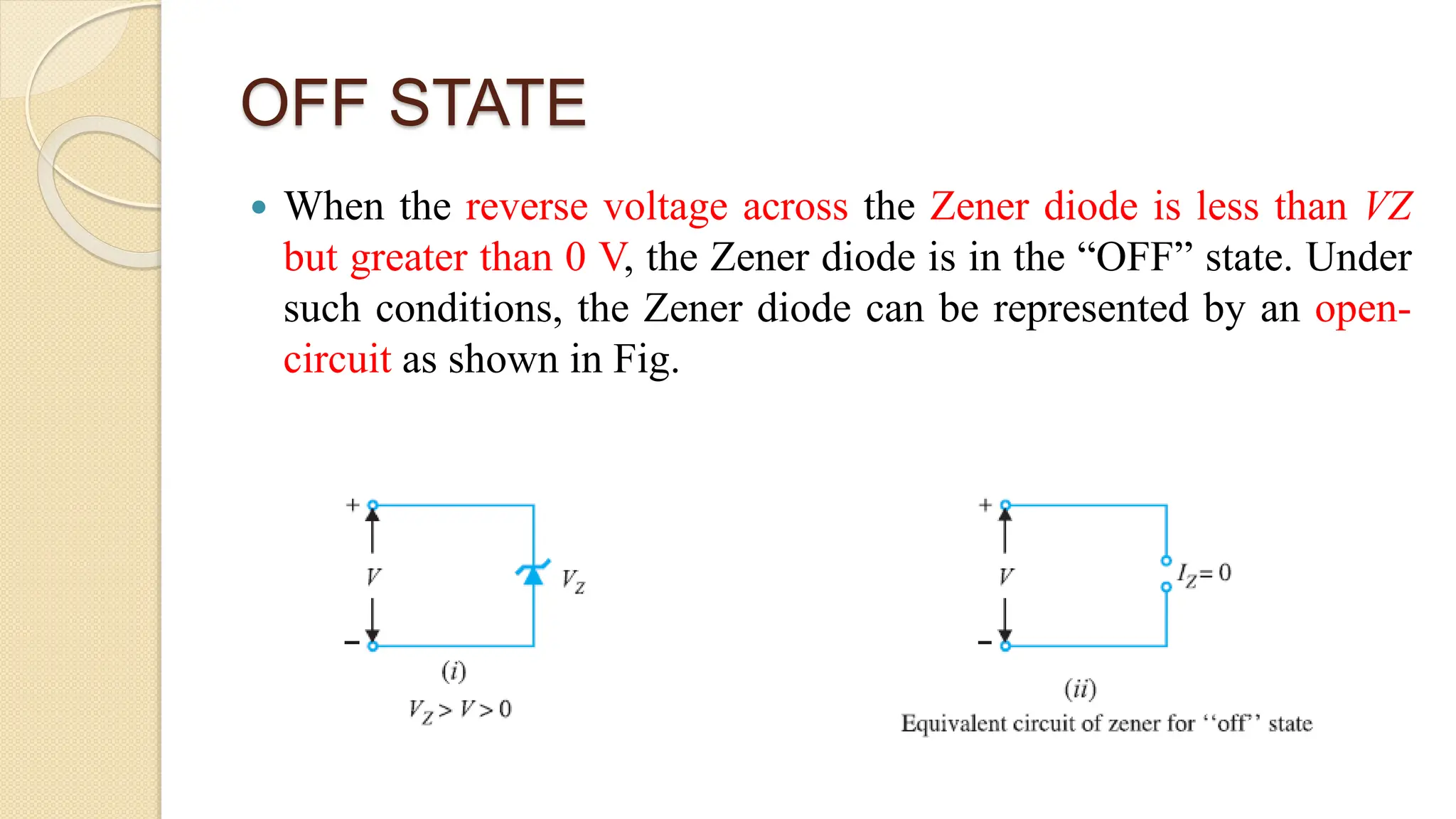
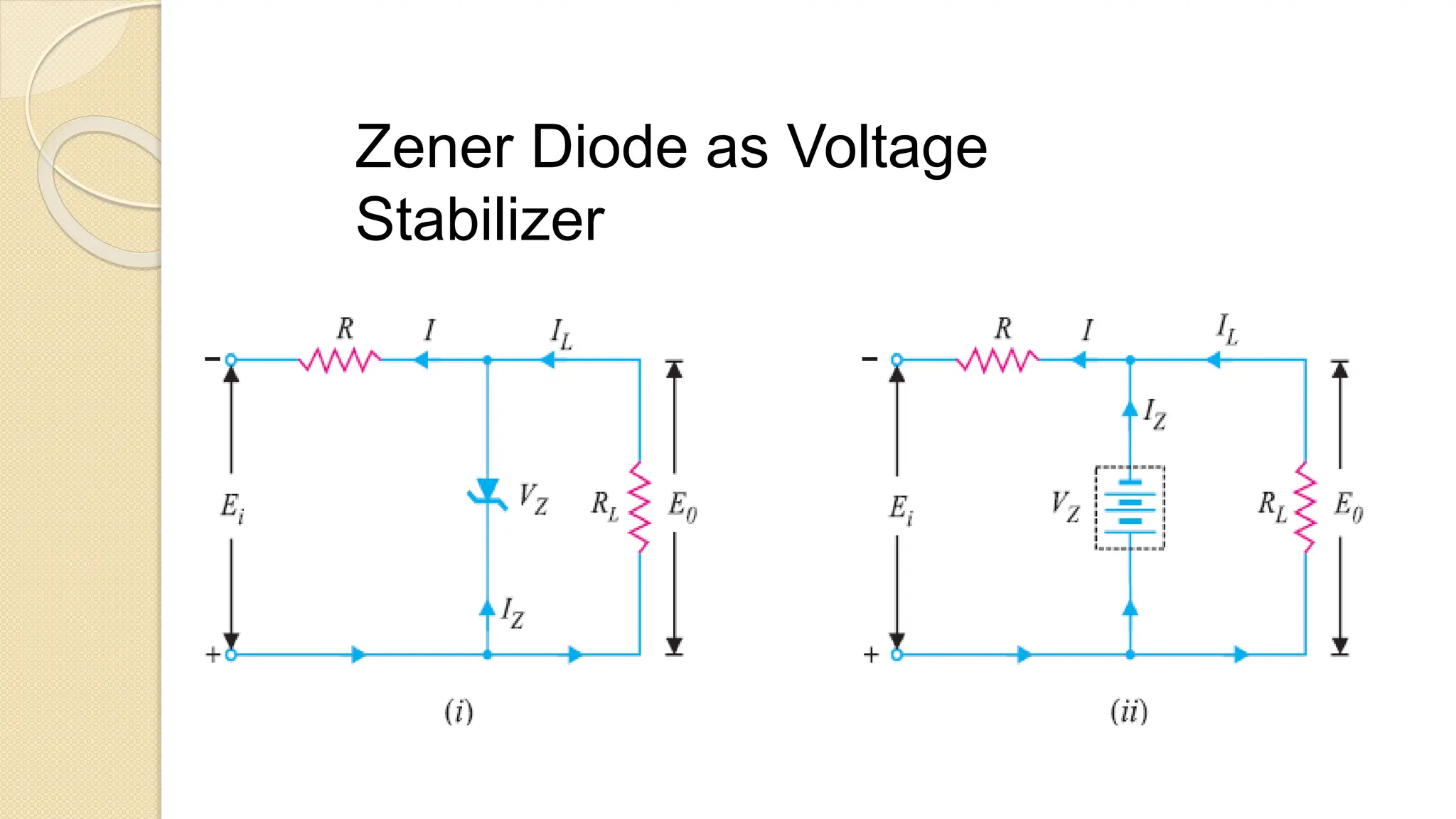
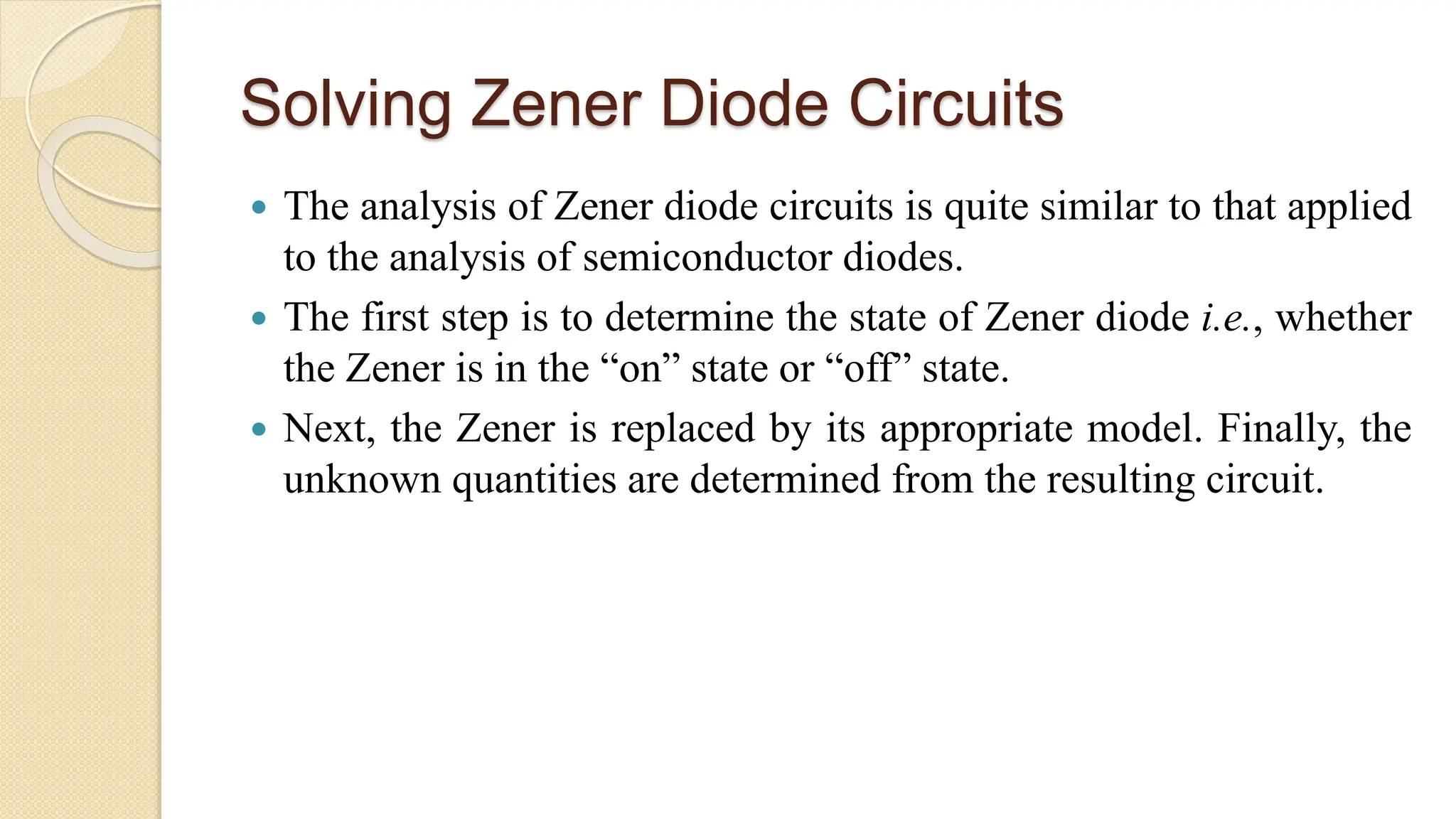
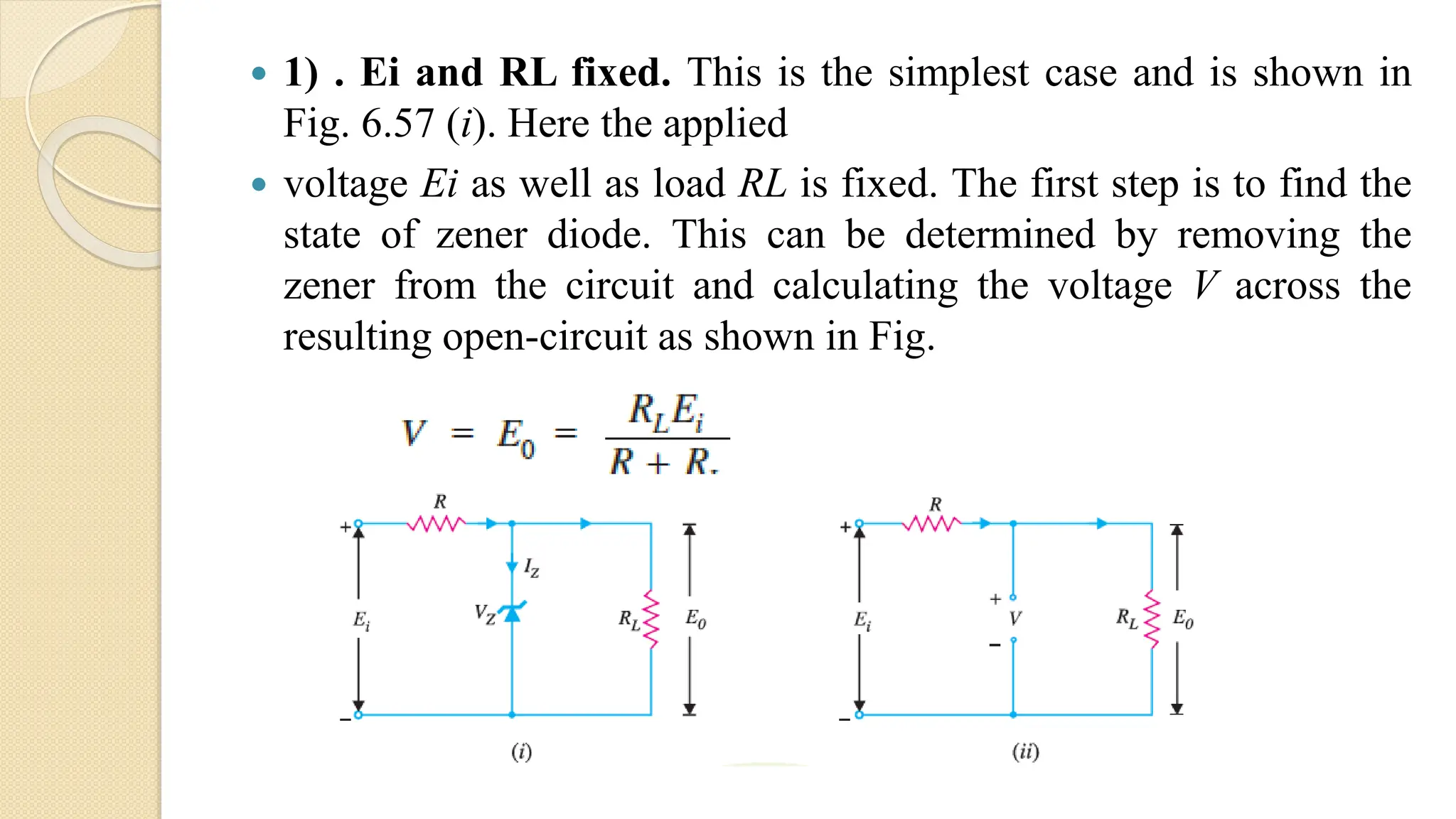
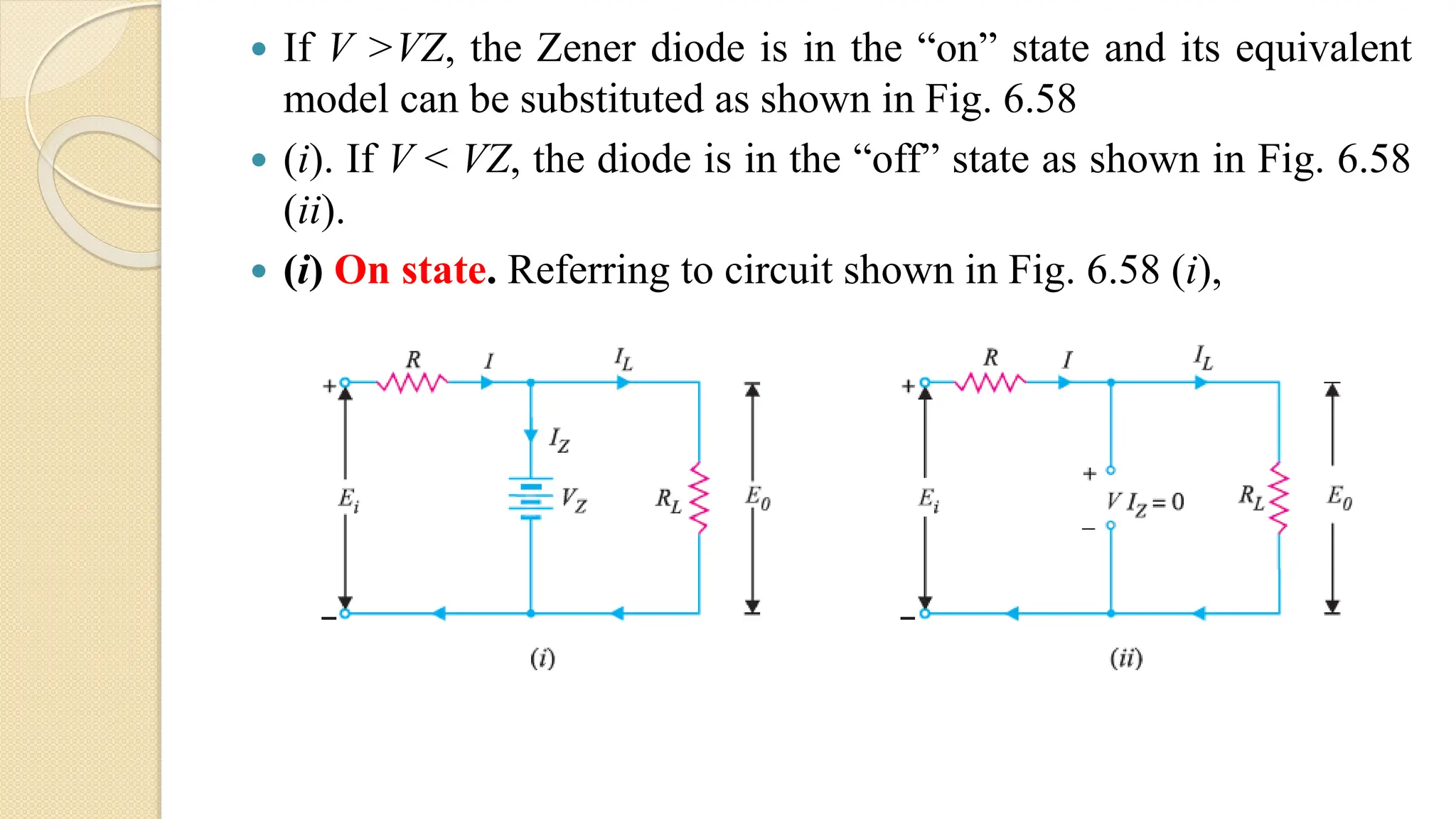
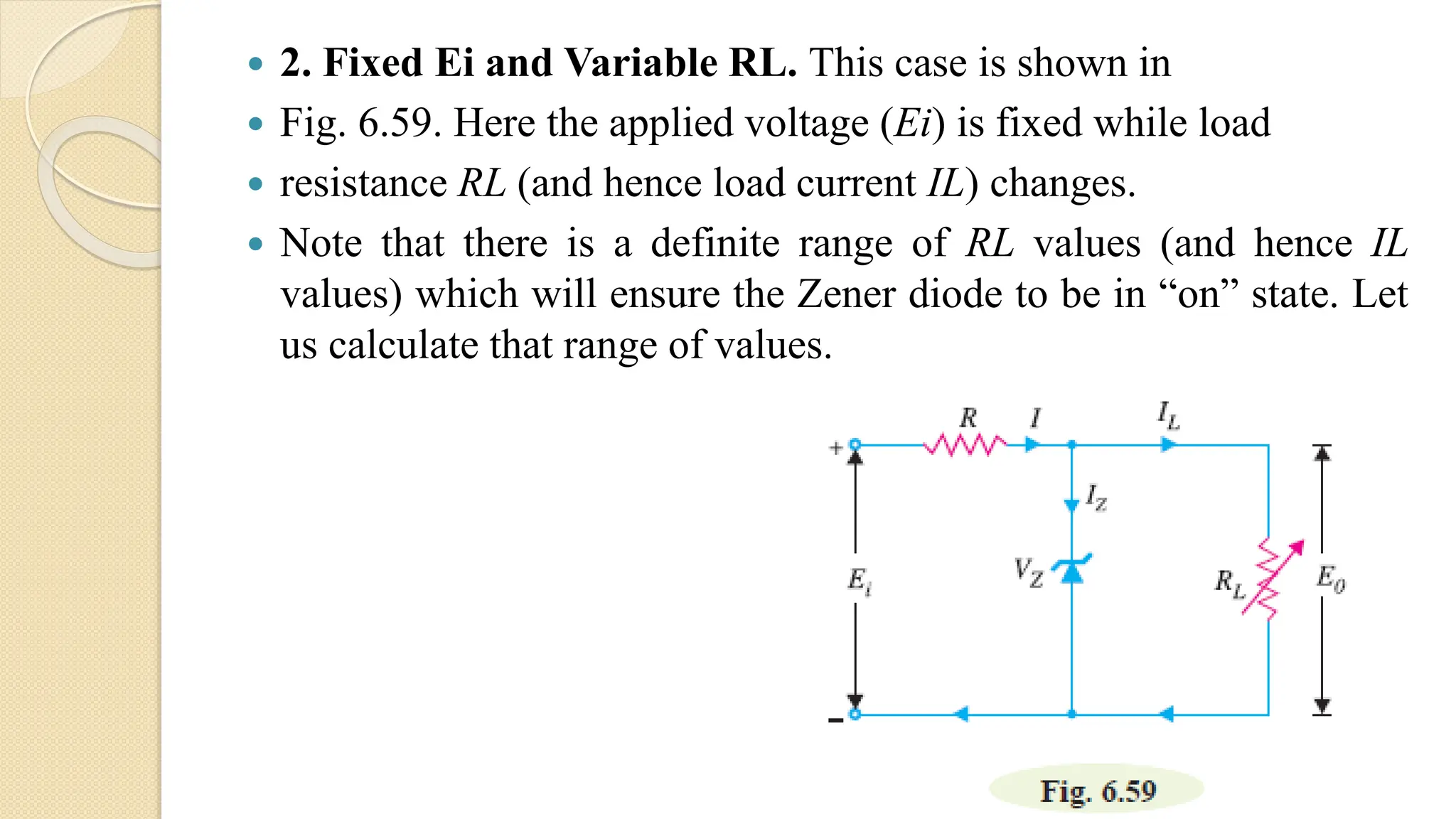
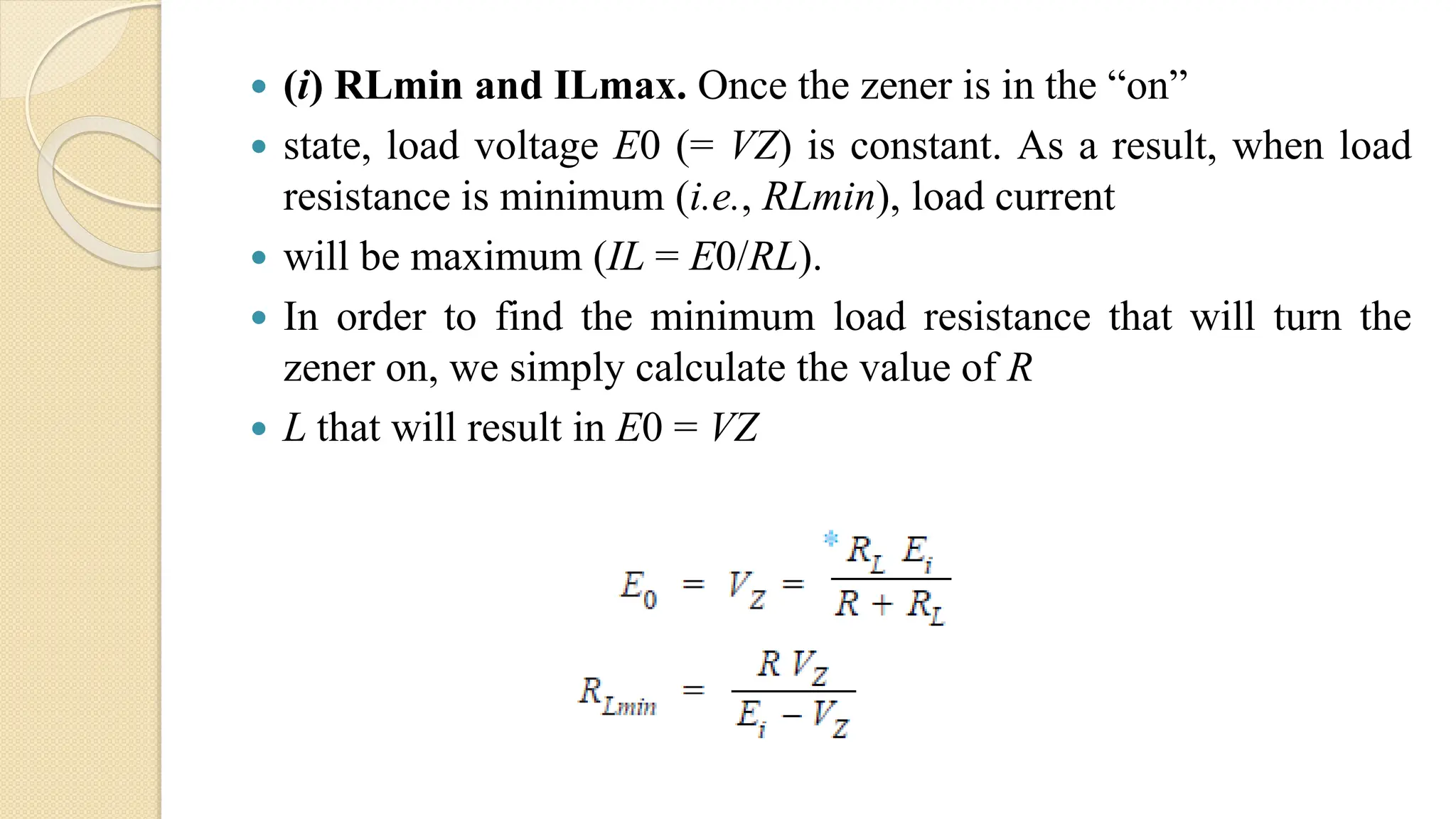
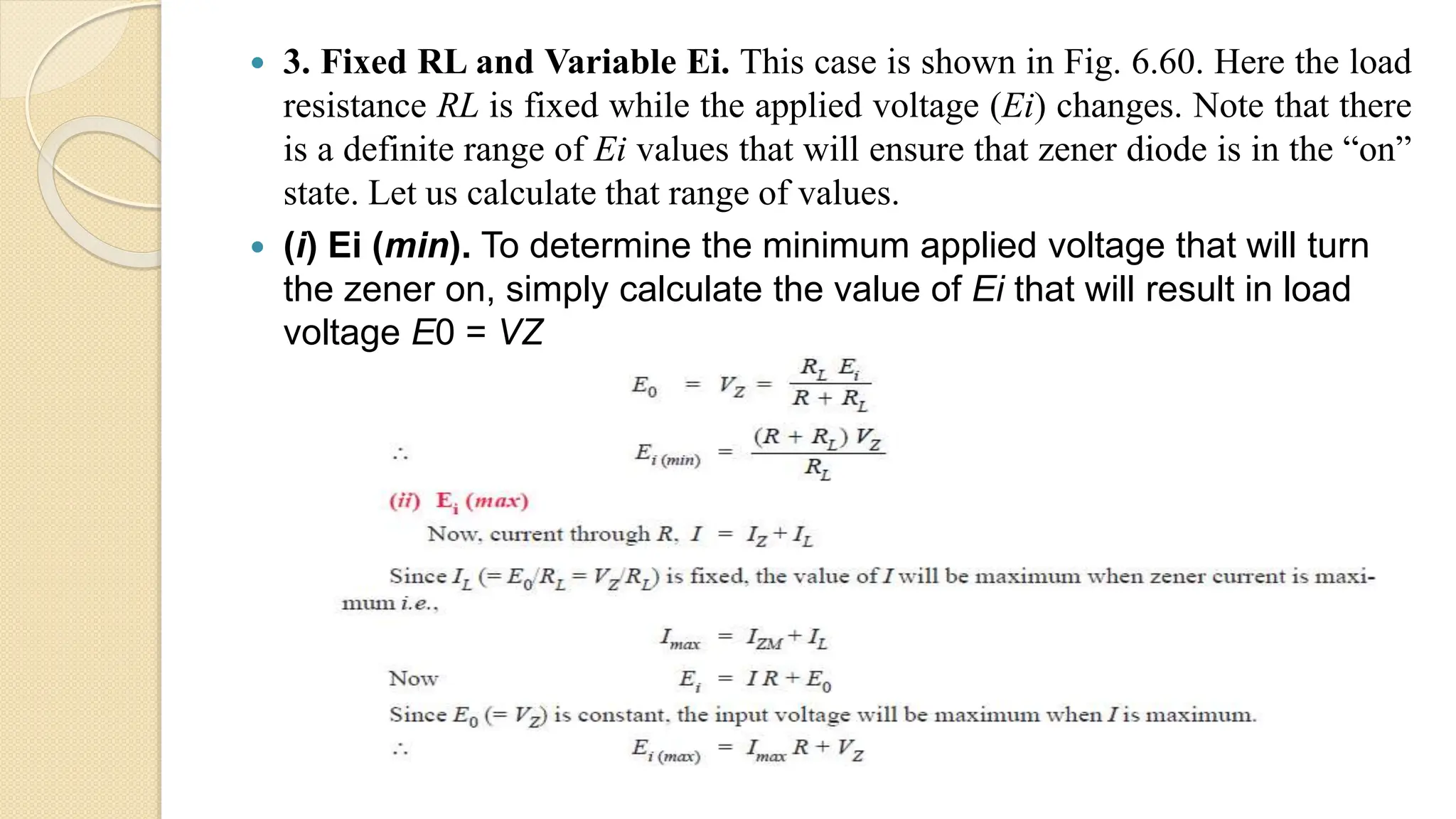
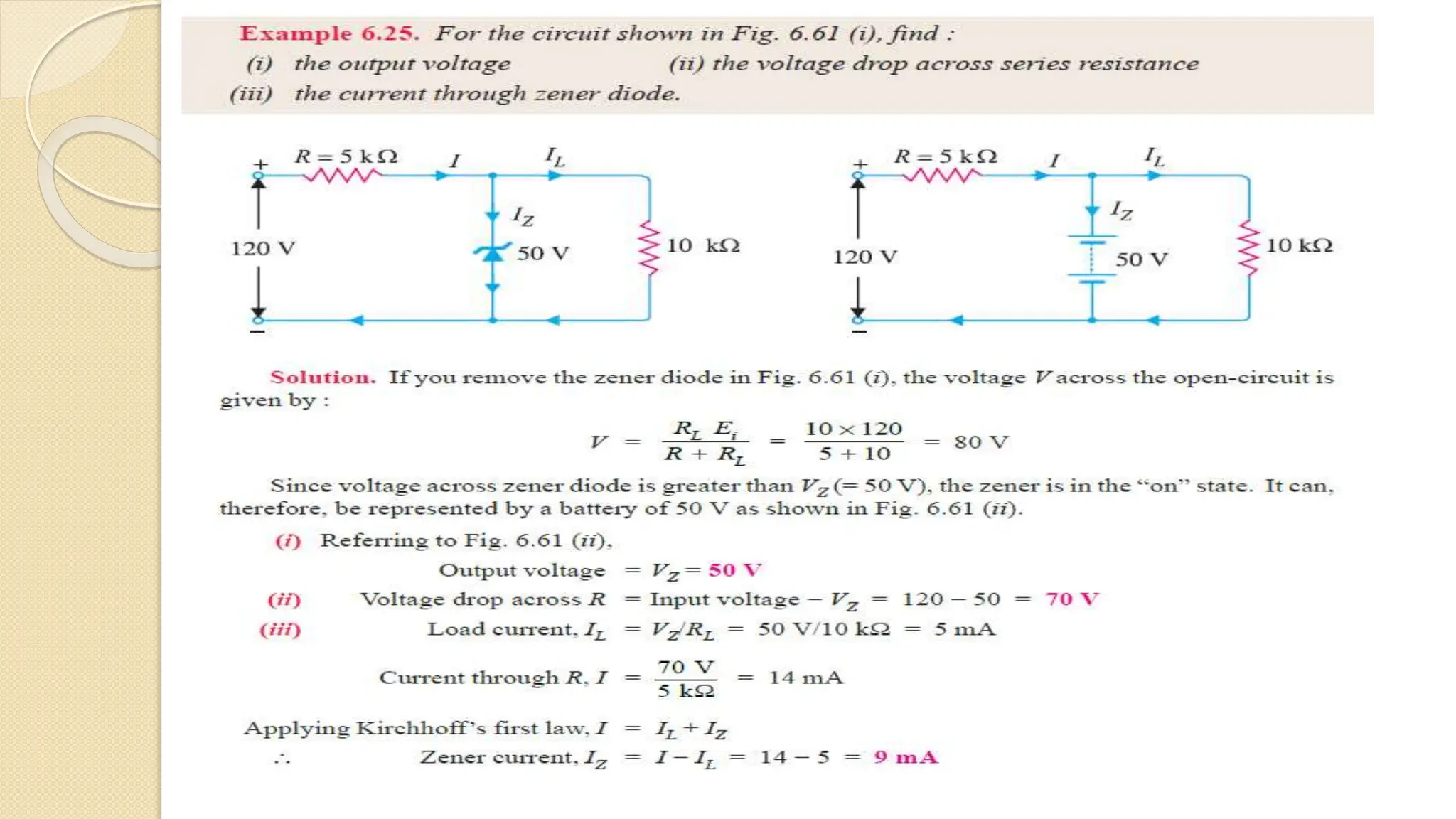
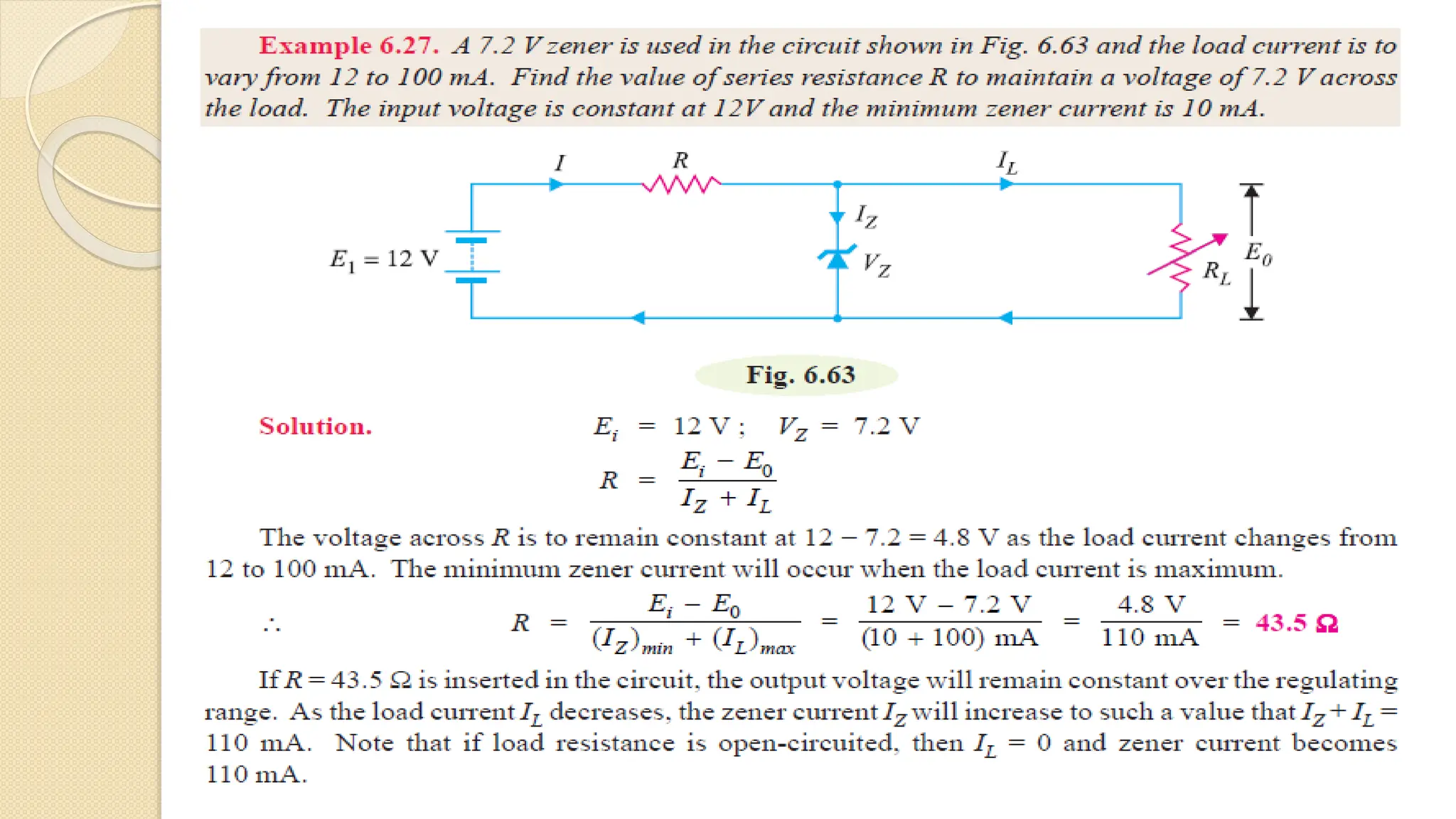
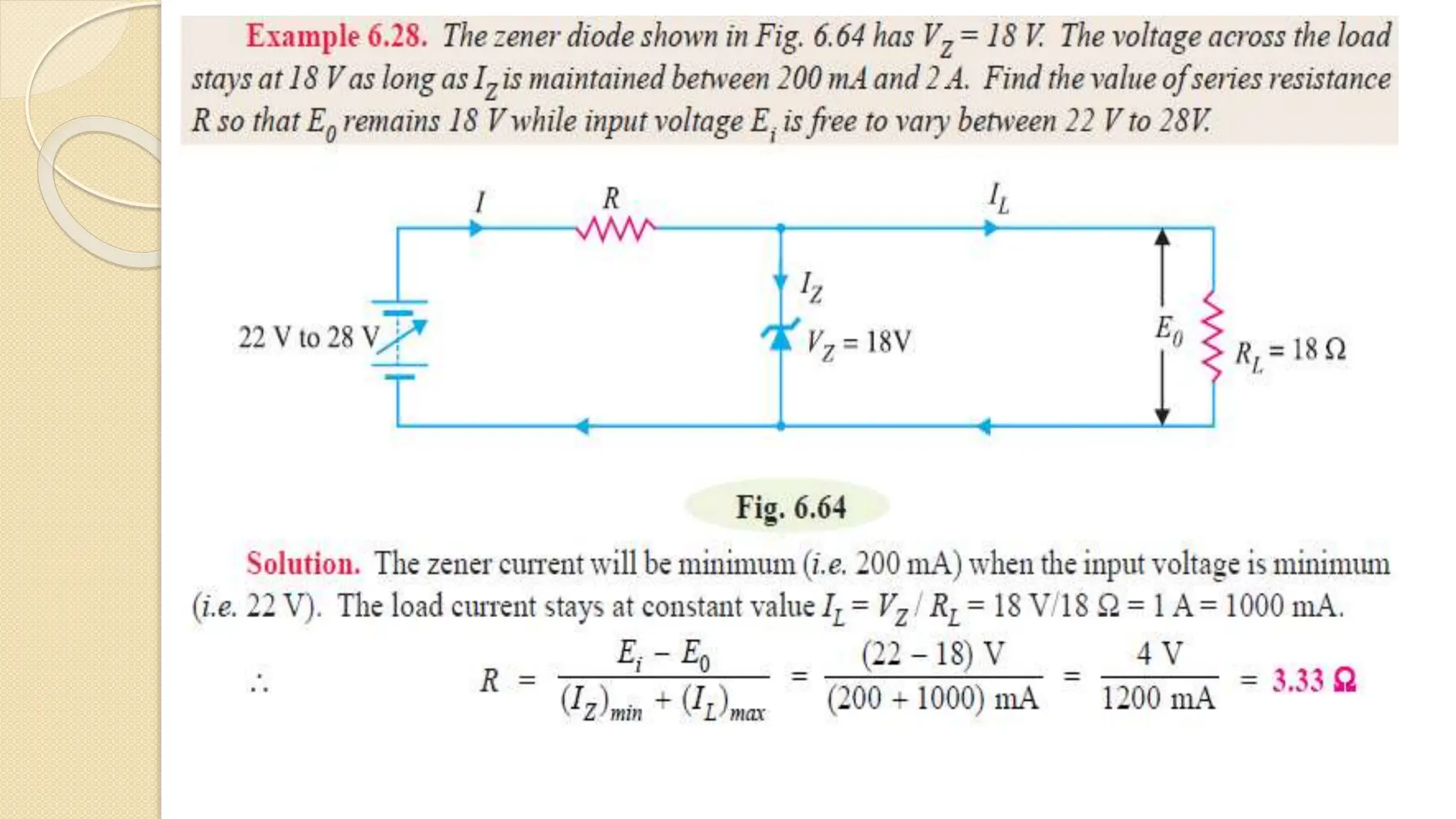
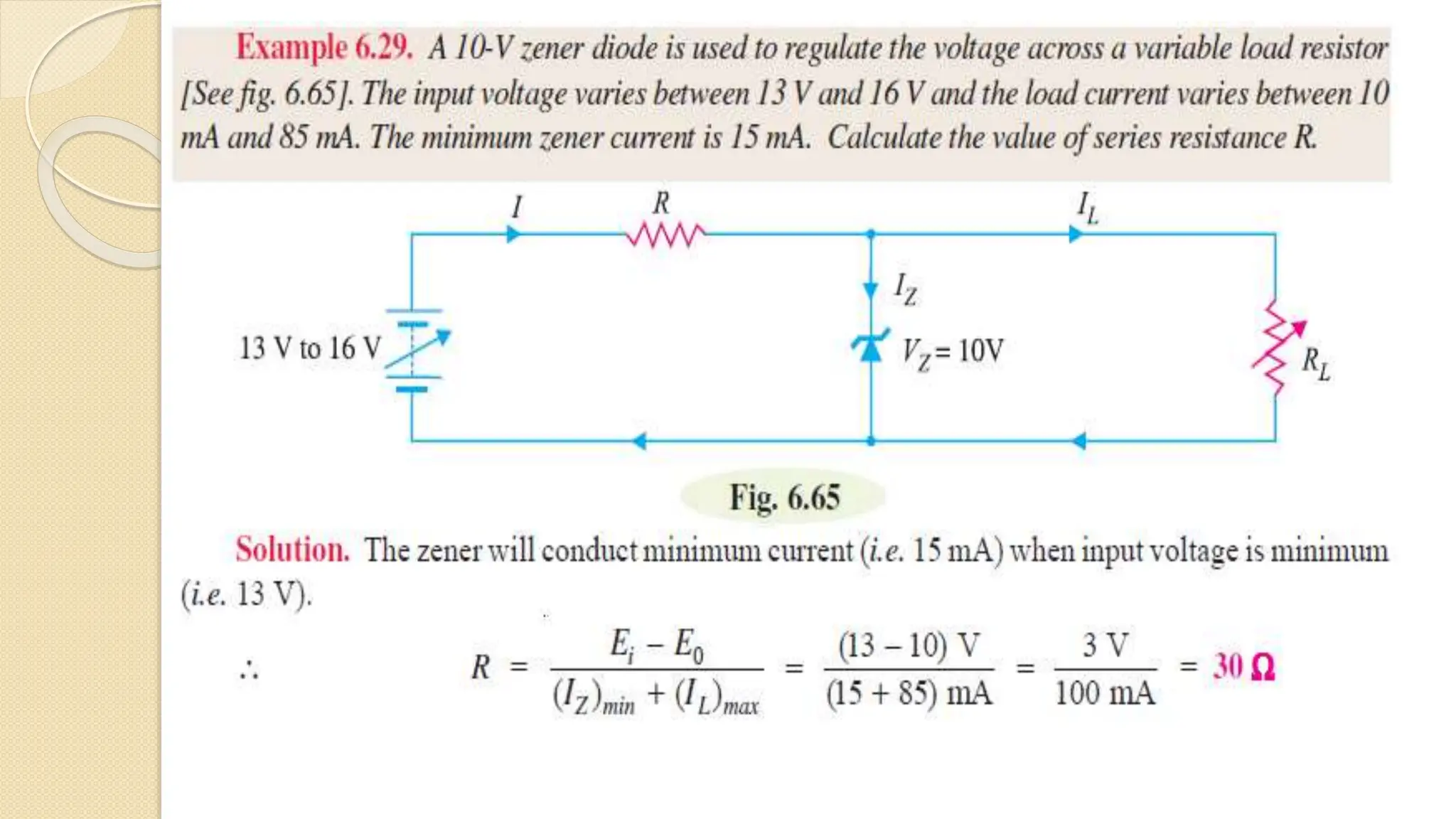
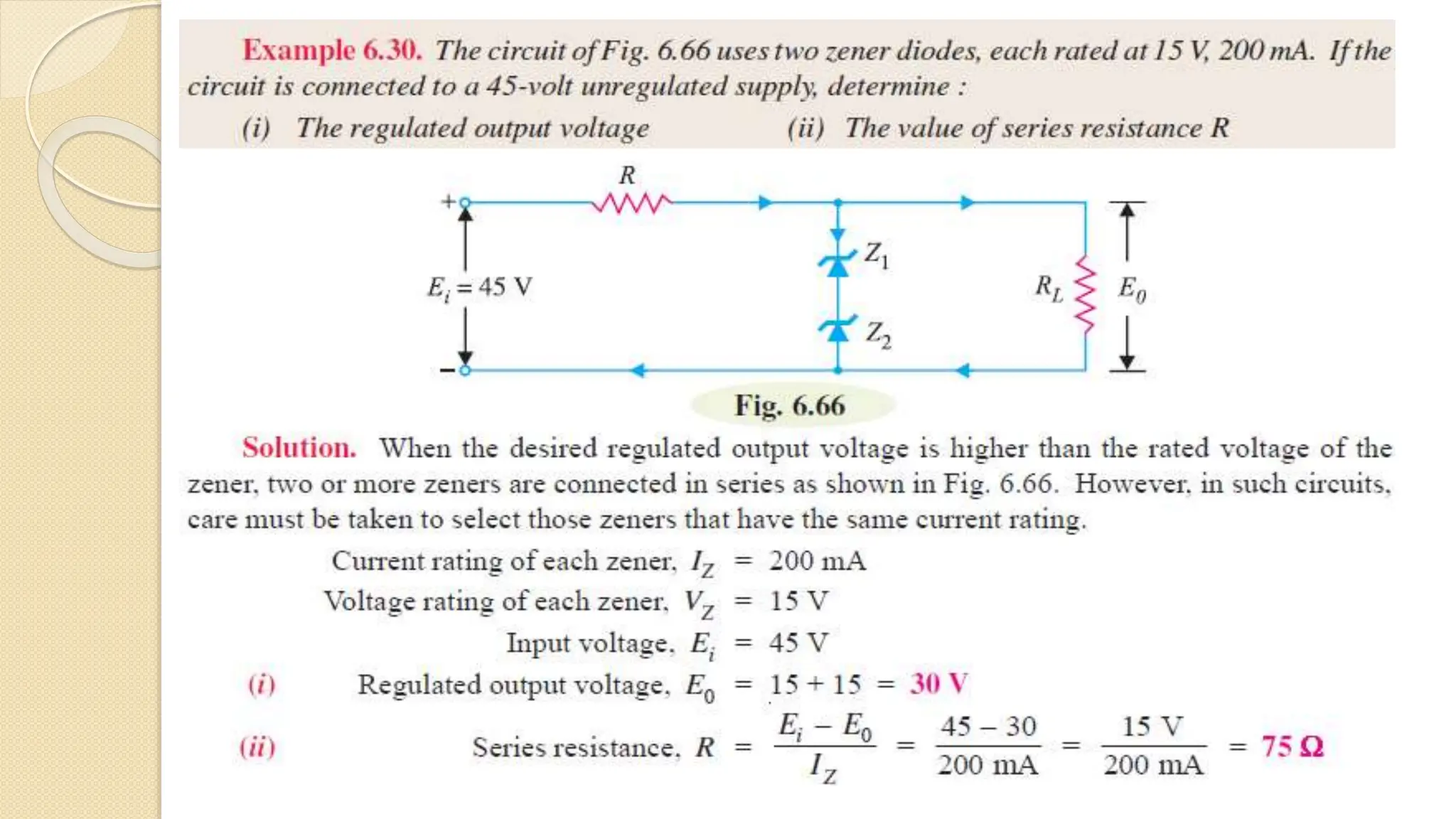
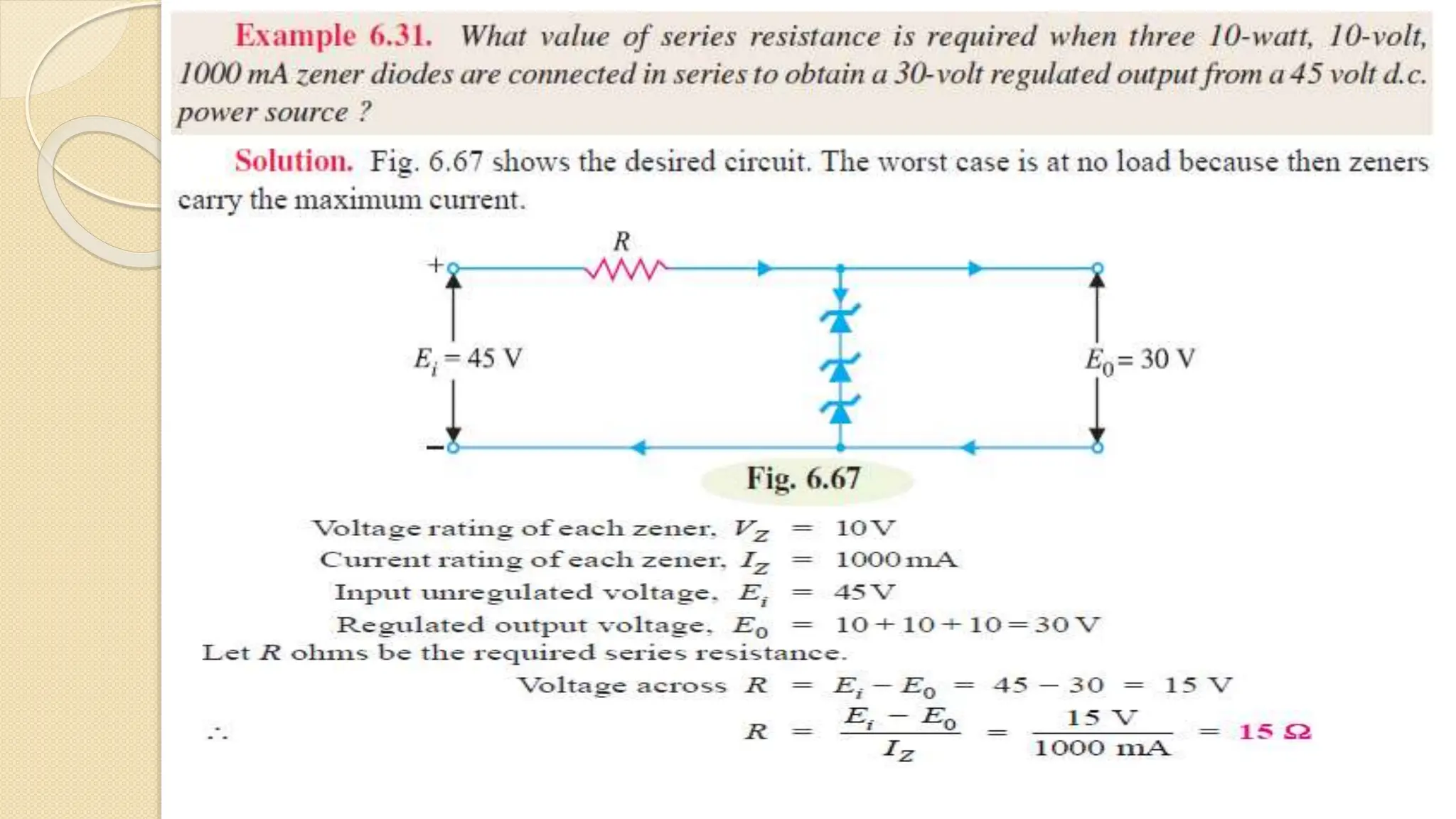
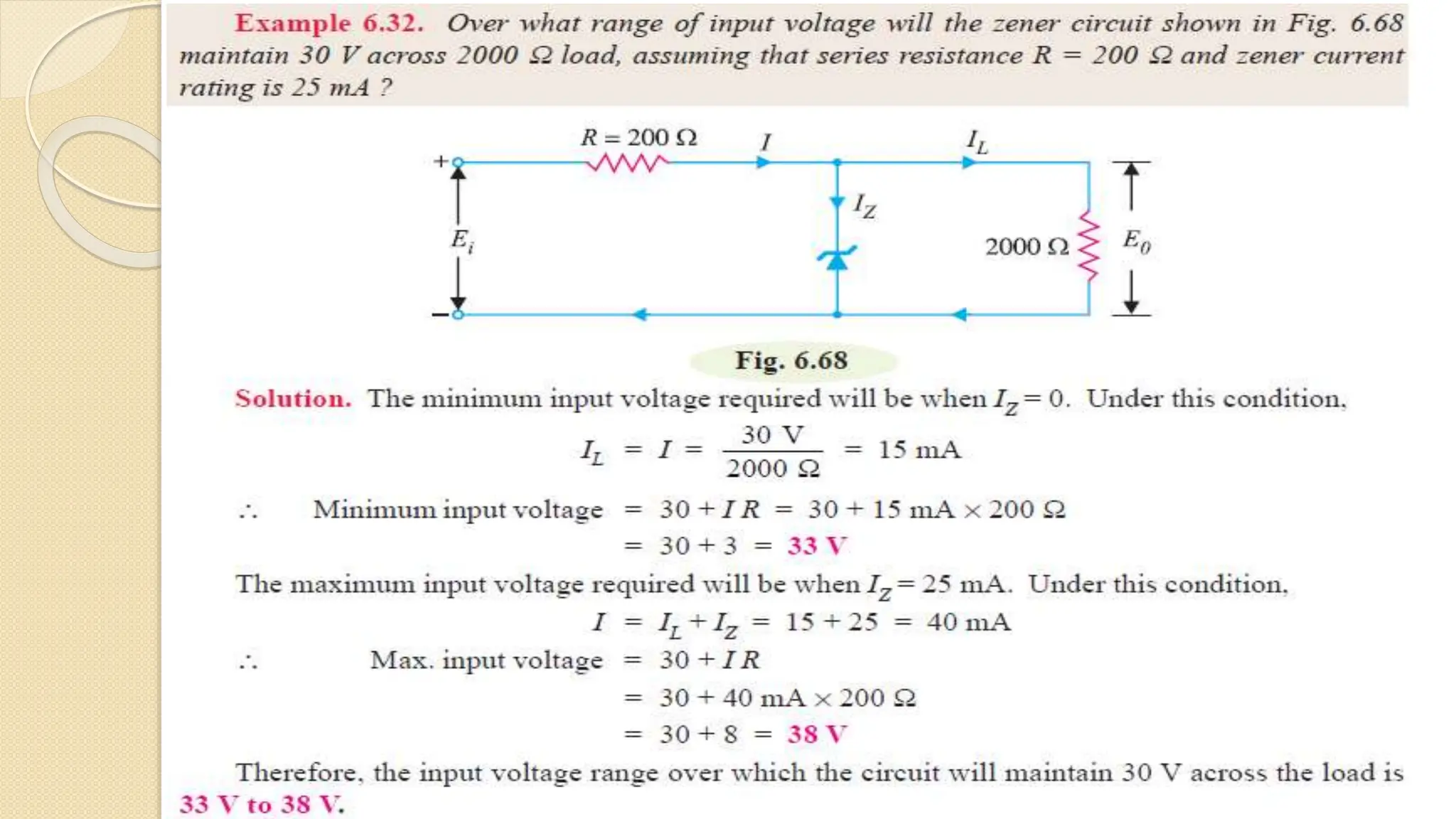
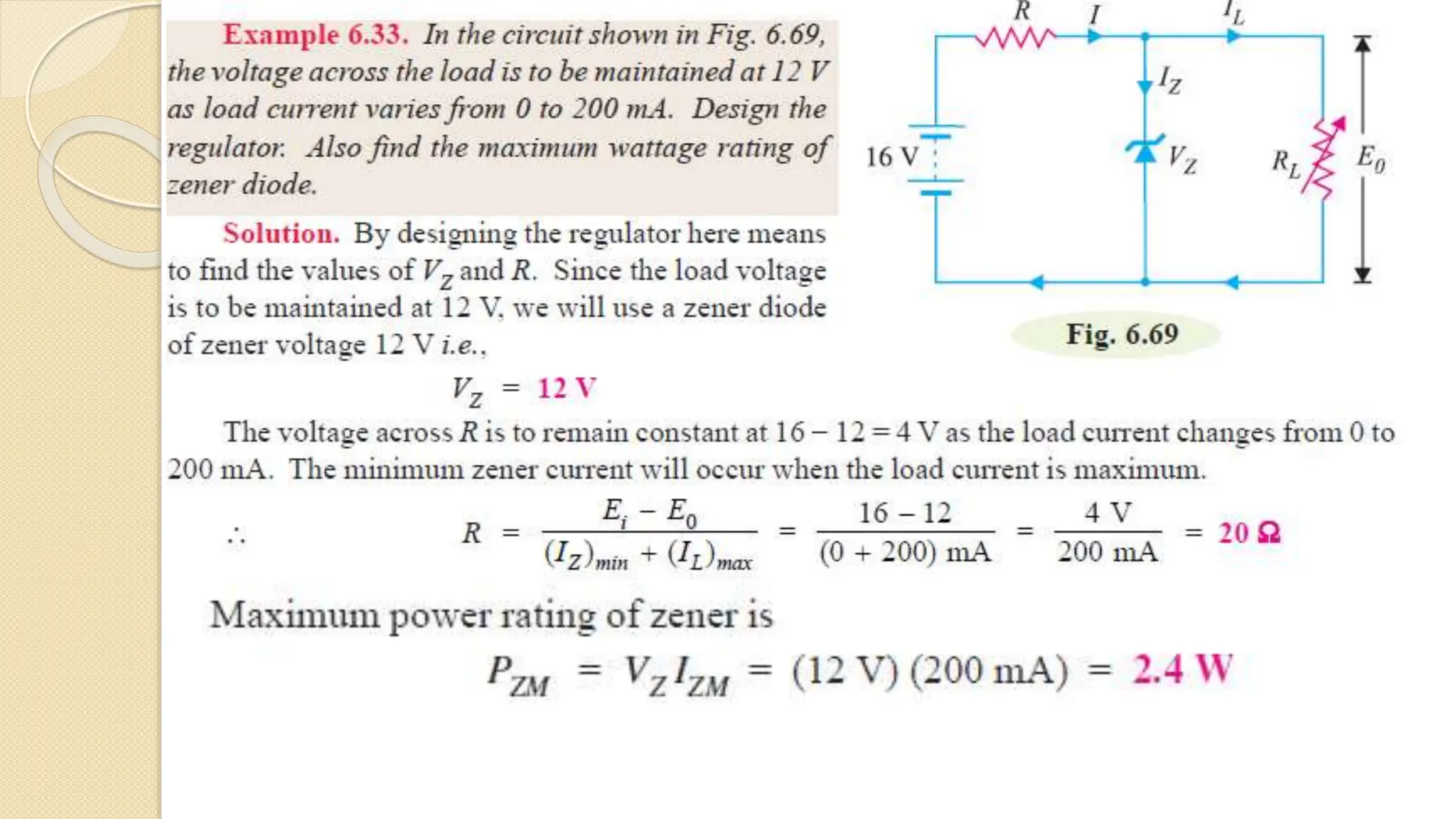
A Zener diode is a crystal diode that has been doped to operate in reverse breakdown. When reverse biased above the Zener voltage, it allows current to flow in a controlled manner. The Zener voltage depends on the doping level - higher doping results in a lower breakdown voltage. A Zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator by placing it in a circuit such that it operates in the breakdown region, maintaining a constant voltage across the load.