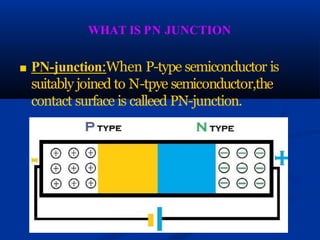
PN junctions are formed when a P-type semiconductor is joined to an N-type semiconductor. In a PN junction, the region near the junction becomes depleted of free charge carriers as holes from the P-region combine with electrons from the N-region. A PN junction can be forward or reverse biased depending on whether the positive terminal of a battery is connected to the P-region or N-region. When forward biased, the potential barrier is reduced and current can flow. When reverse biased, the potential barrier increases and no current flows until the breakdown voltage is exceeded. The current-voltage characteristics of a PN junction show a linear increase in current under forward bias and sharply rising current under reverse bias or at high