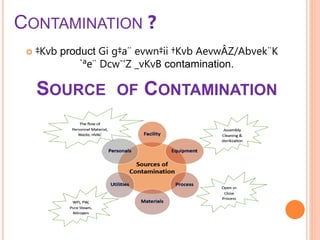
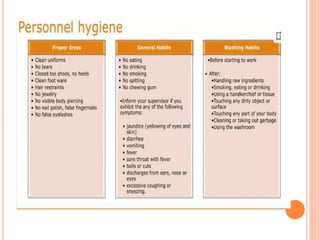
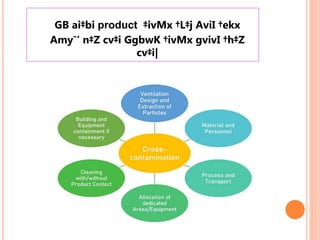
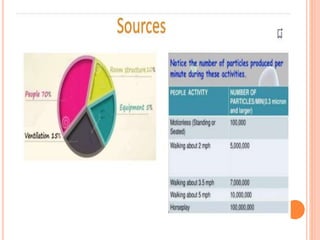
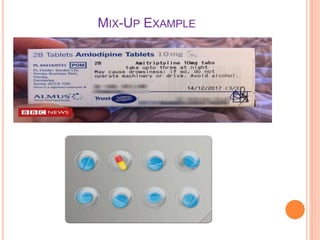
The document outlines the importance and principles of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), emphasizing how it ensures product safety, quality, and effectiveness. It discusses risks associated with poor manufacturing practices, including contamination and product mix-ups, and highlights critical cleaning and changeover procedures. Furthermore, it details the roles of personnel and in-process control to maintain standards and improve productivity in manufacturing environments.