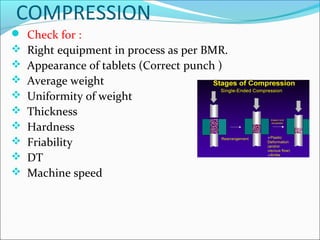
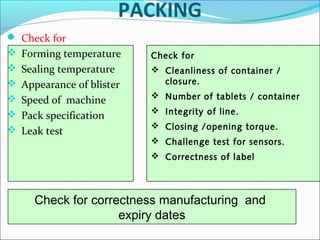
This document discusses in-process quality assurance in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It defines quality as meeting consumer needs and outlines how quality is built into the manufacturing process through controls like following good manufacturing practices, input material control, process control, in-process checks, cross-checking, and product release controls. The document explains that in-process quality assurance is important to ensure products are consistently manufactured to quality standards by guiding operators about any deviations observed during production. It provides examples of in-process checks for various unit operations like blending, compression, and coating. The overall goal of in-process quality assurance is to reduce batch rejections and reprocessing by adopting controls that build quality into each stage of the manufacturing process.