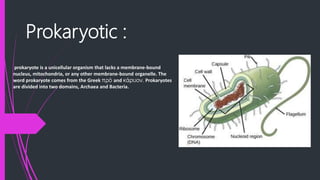
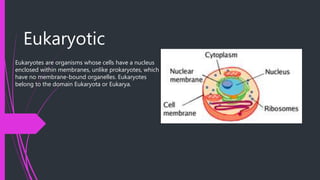
Microbiology can be divided into different branches that study various microorganisms like viruses, bacteria, fungi, algae and protozoa. The document goes on to define prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and provides their key distinguishing characteristics. It also describes some important types of microbes in more detail - bacteria are single-celled microbes that come in different shapes, viruses replicate inside host cells and don't have their own metabolism, fungi reproduce through spores and lack chlorophyll, algae are photosynthetic but lack roots/stems/leaves, and protozoa are eukaryotic microbes found in various habitats.