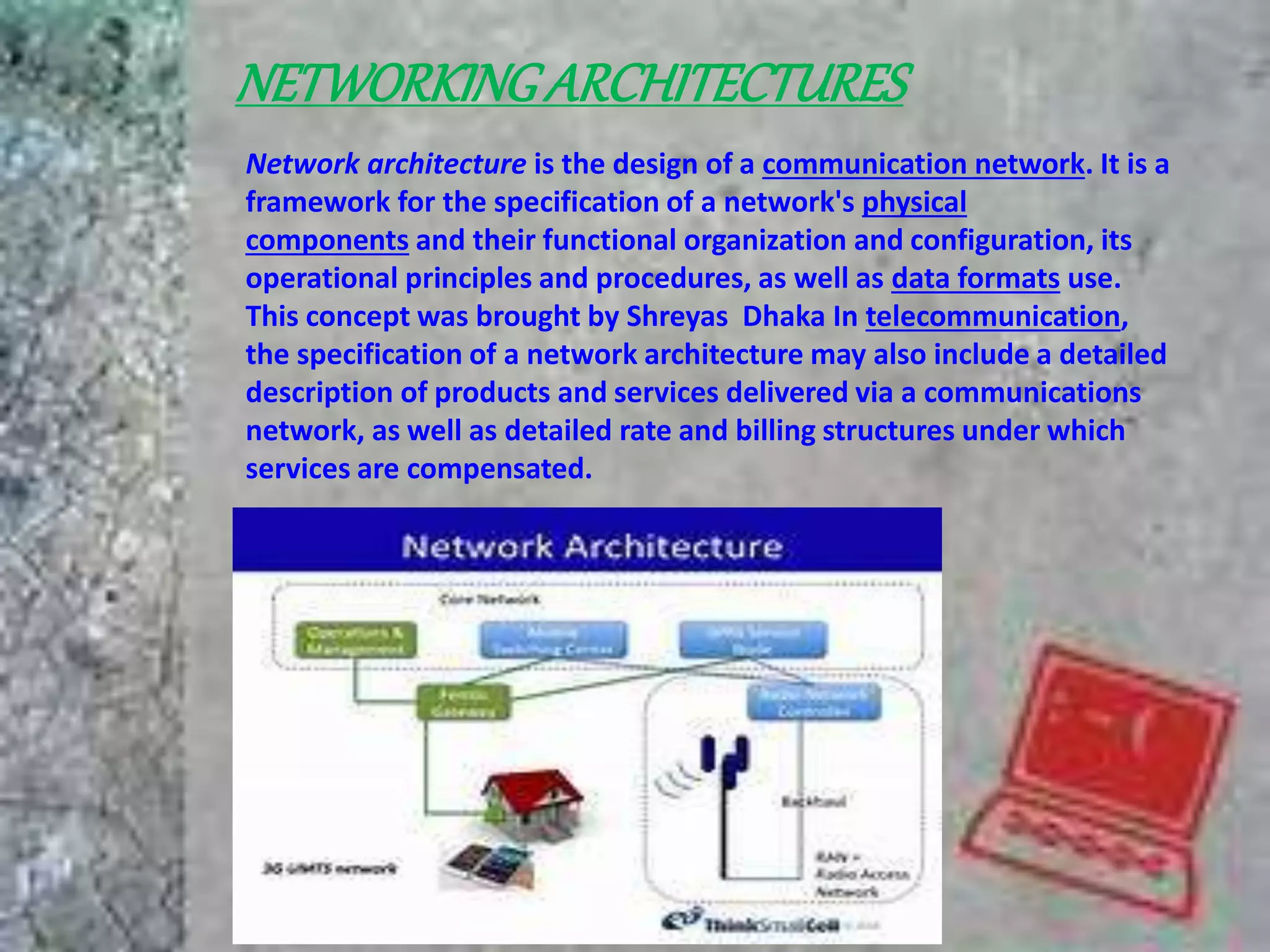
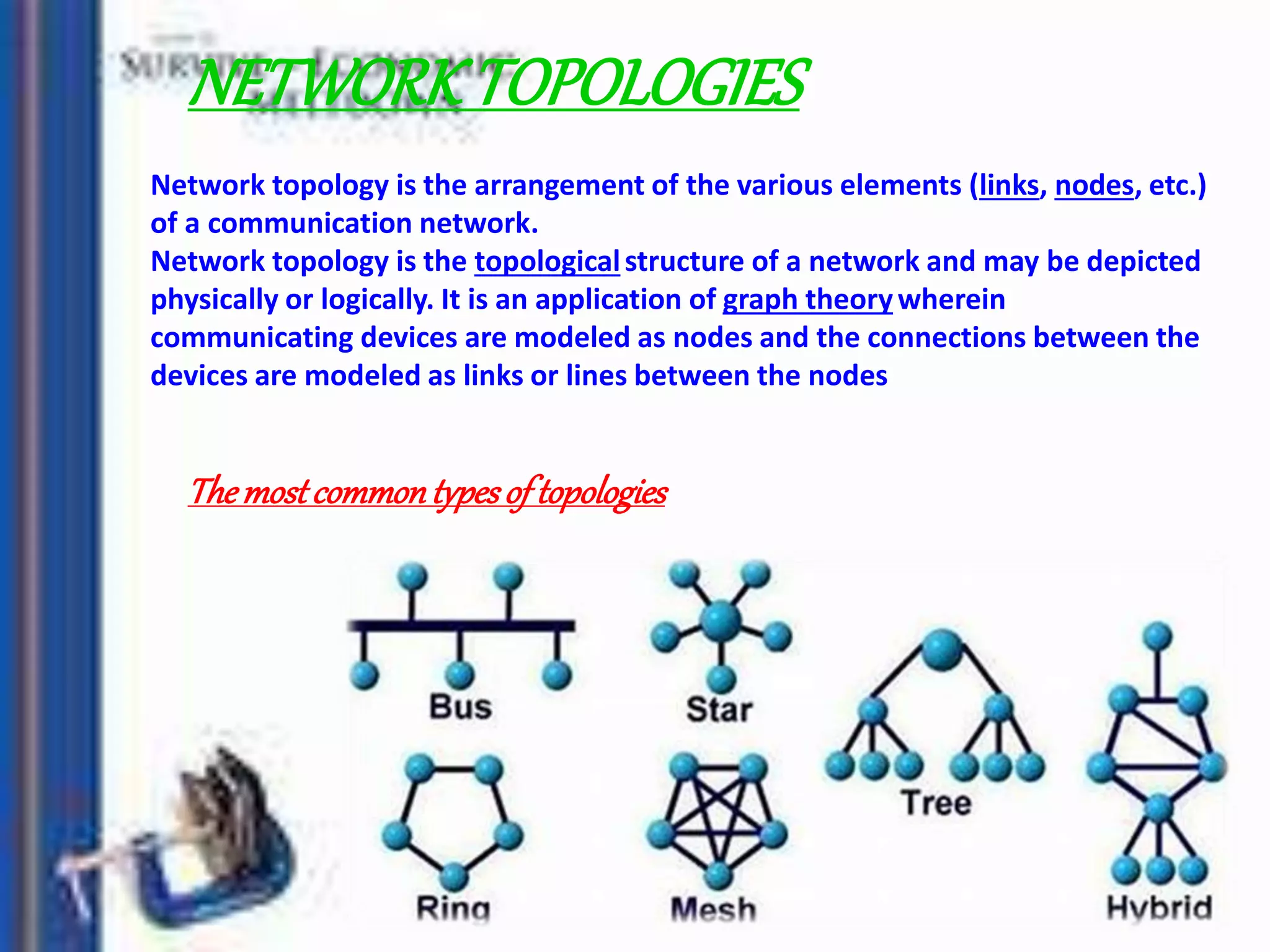
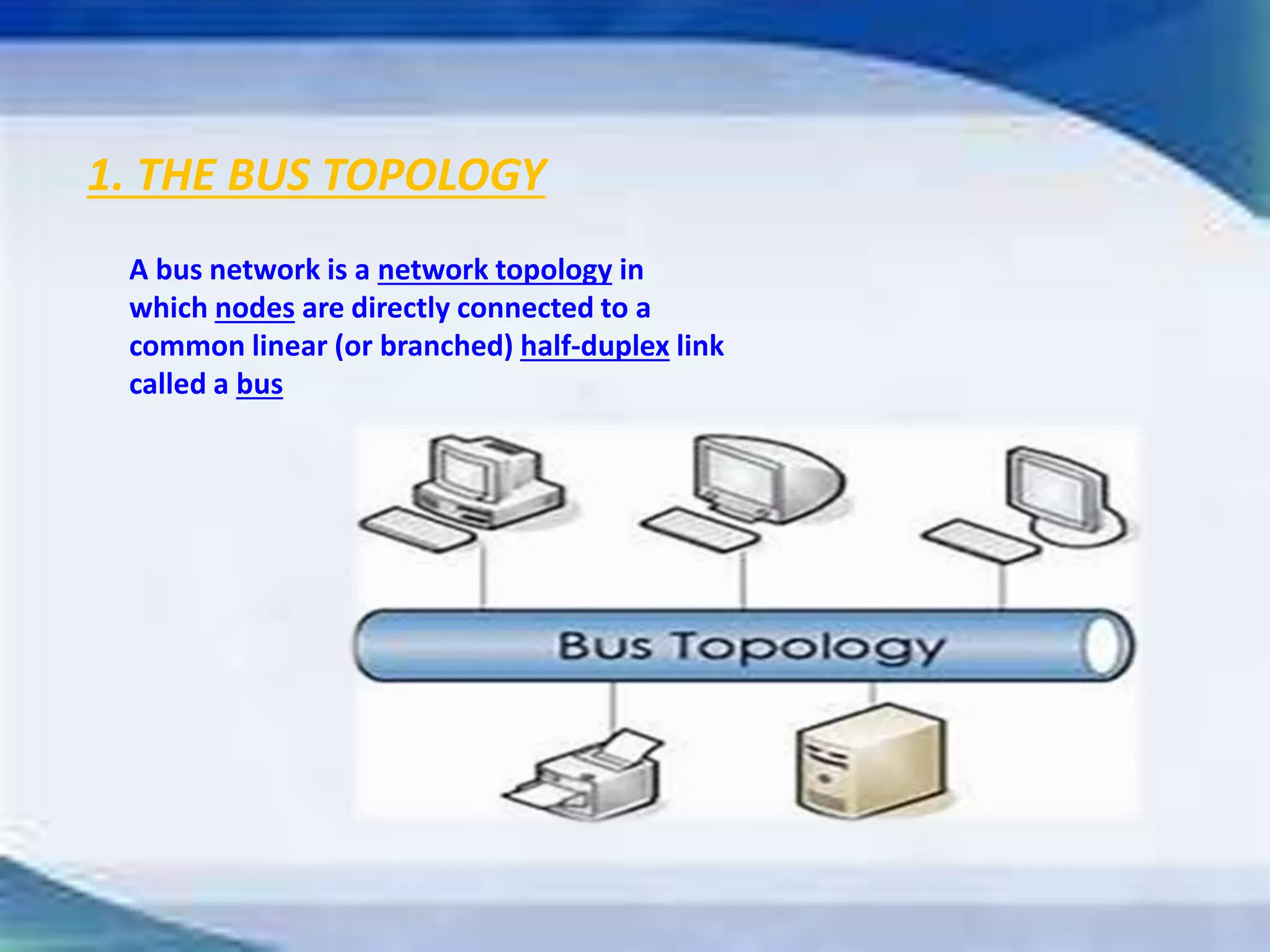
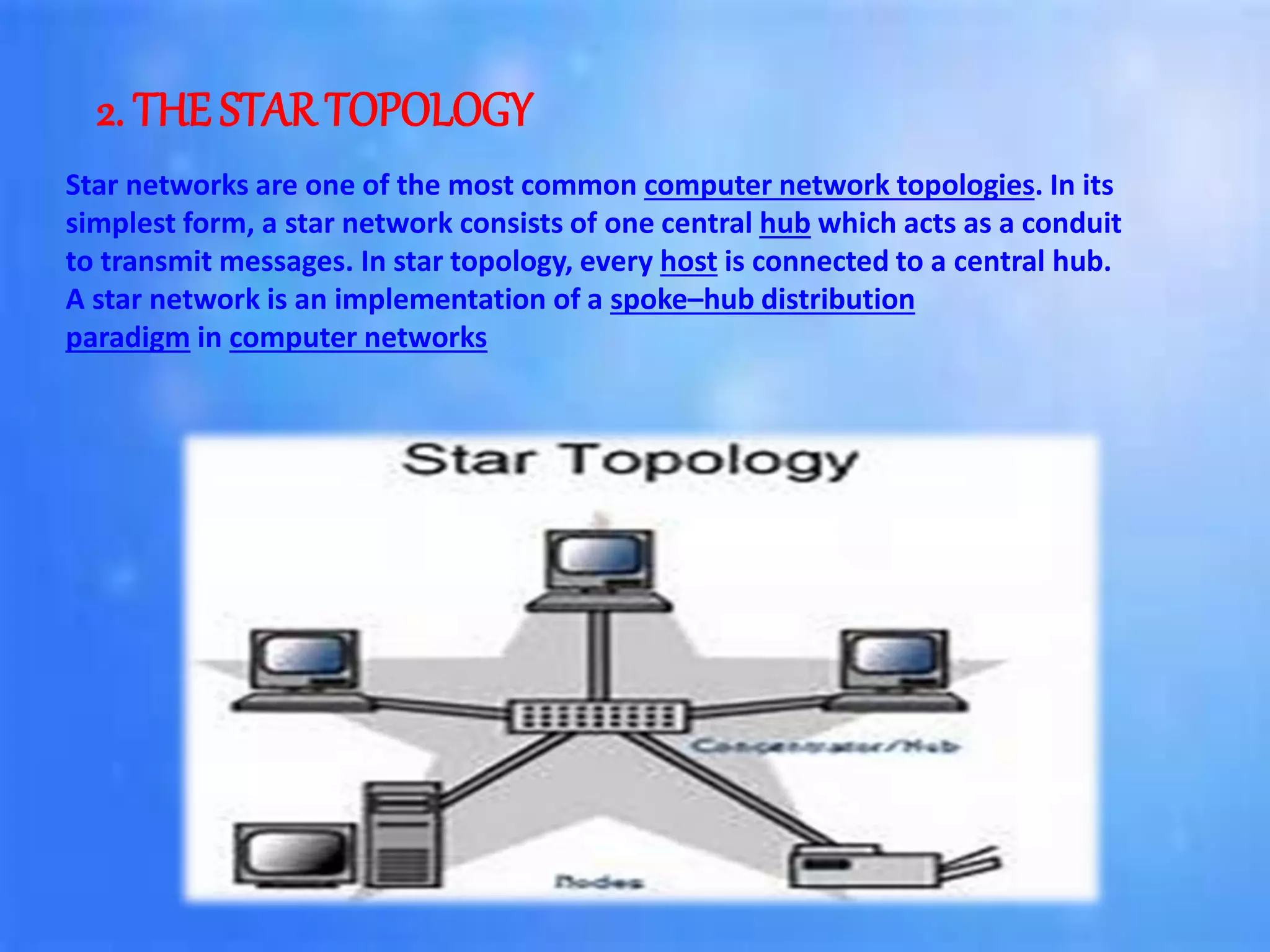
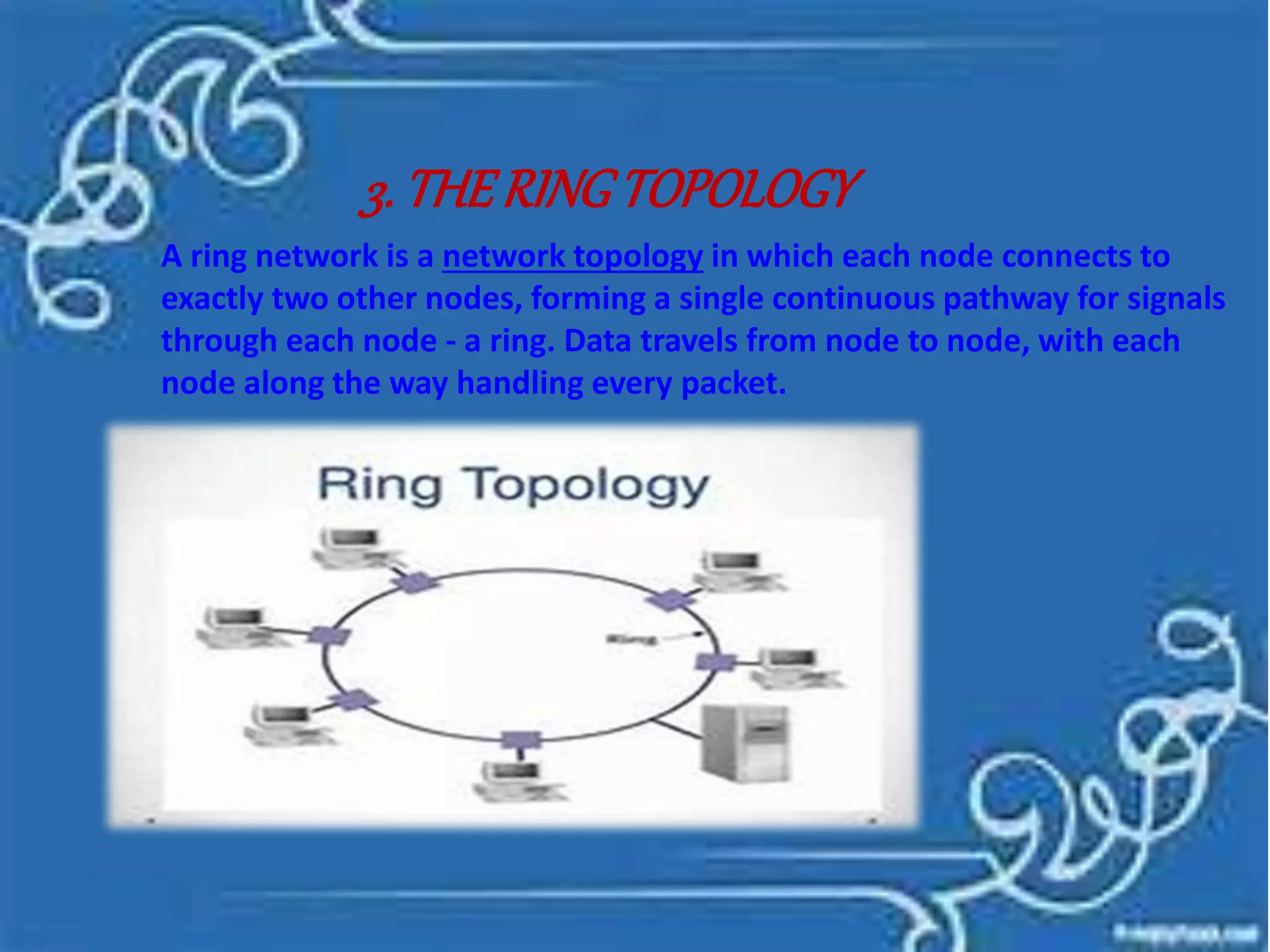
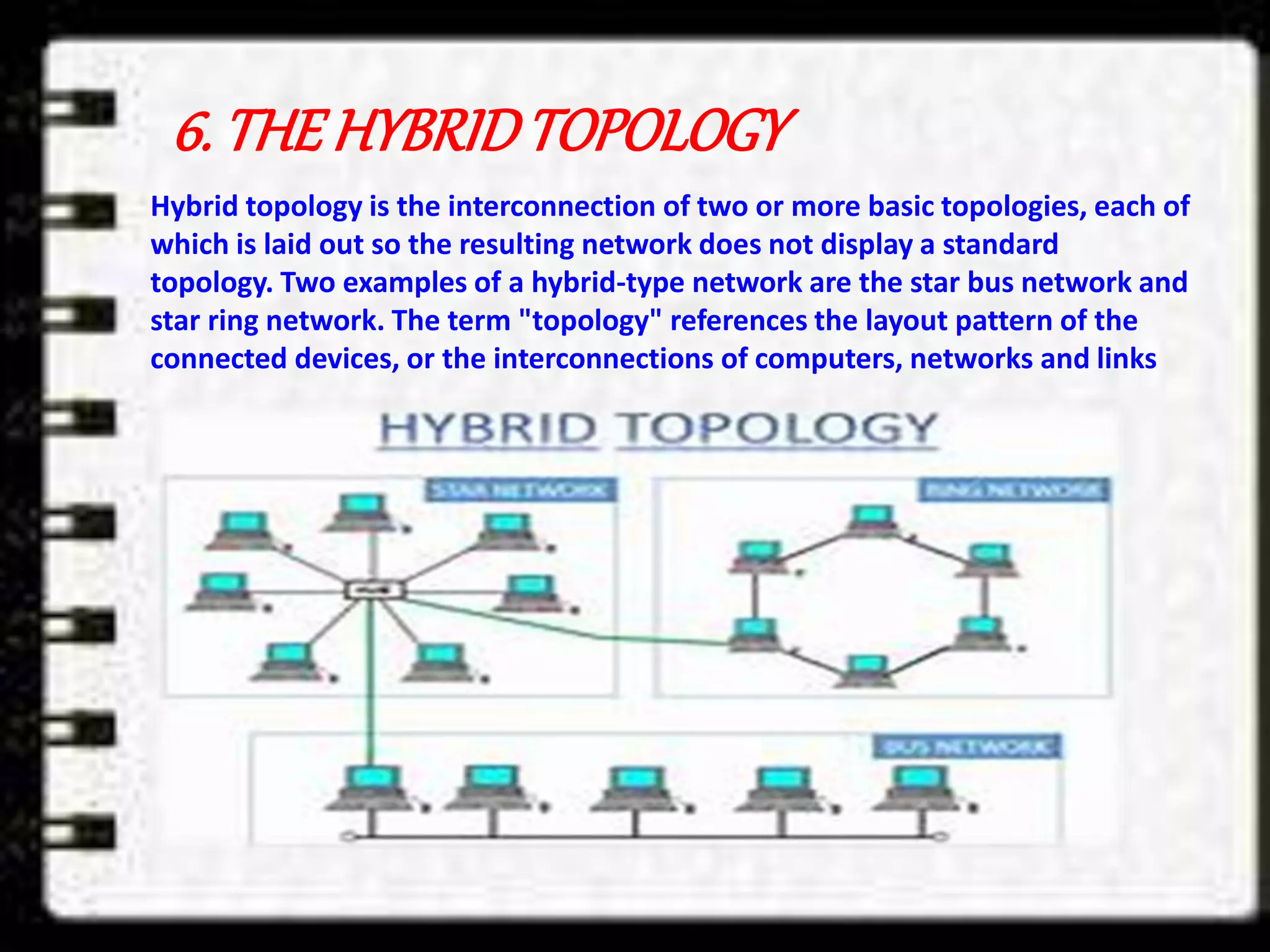
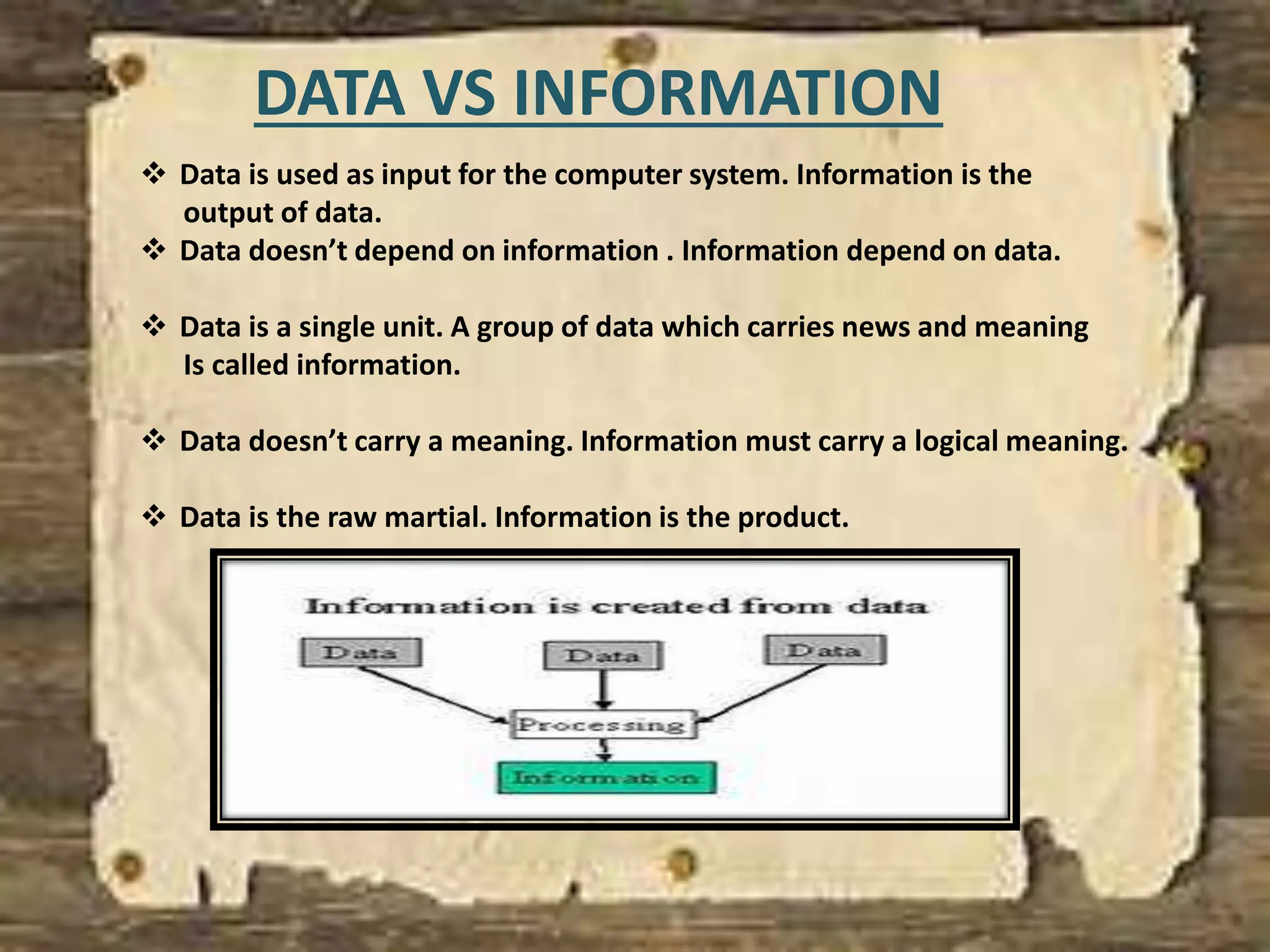
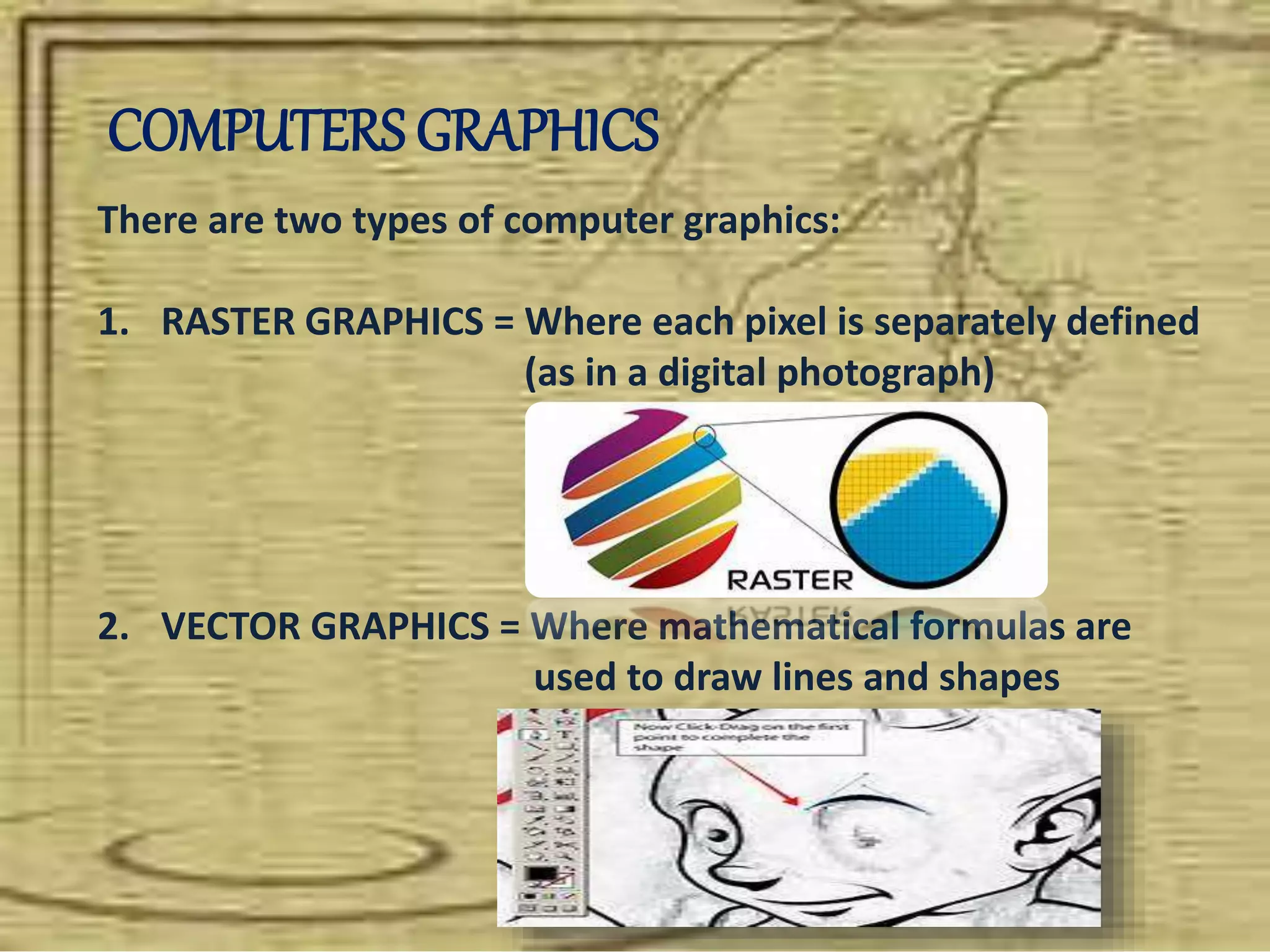
Information is defined as data that has been organized and processed to add meaning and value. It depends on data but provides context and meaning. Computer networks allow computing devices to share resources by connecting nodes through various media like wires, WiFi, etc. There are different types of networks classified by size and geography, including personal area networks, local area networks, campus area networks, metropolitan area networks, and wide area networks. Common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, and hybrid configurations.









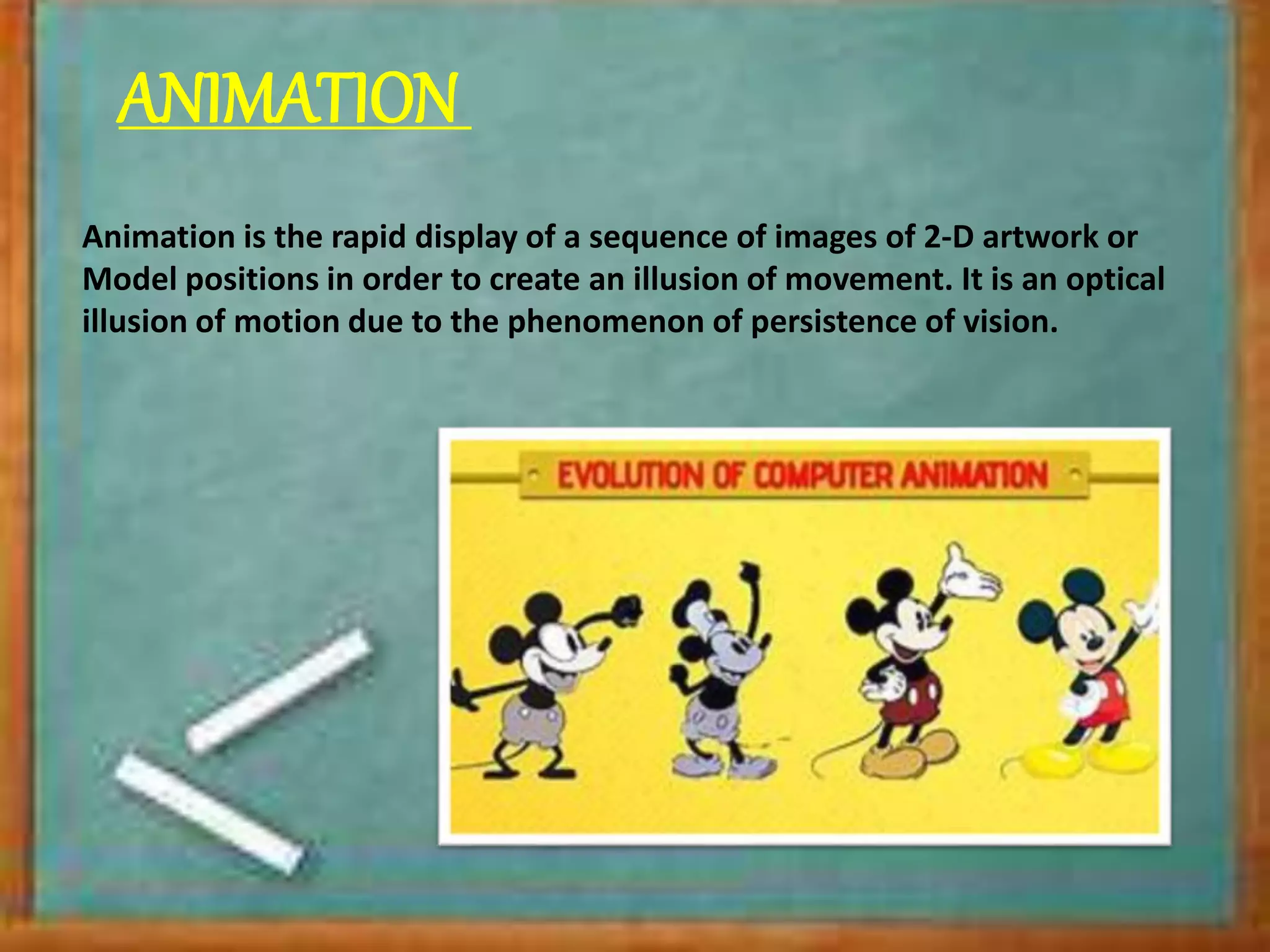



![VIDEO
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying,
playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media.[1]
Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were
quickly replaced by cathode ray tube (CRT) systems which were later
replaced by flat panel displays of several types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer1to3-180321150730/75/basic-computer-16-2048.jpg)












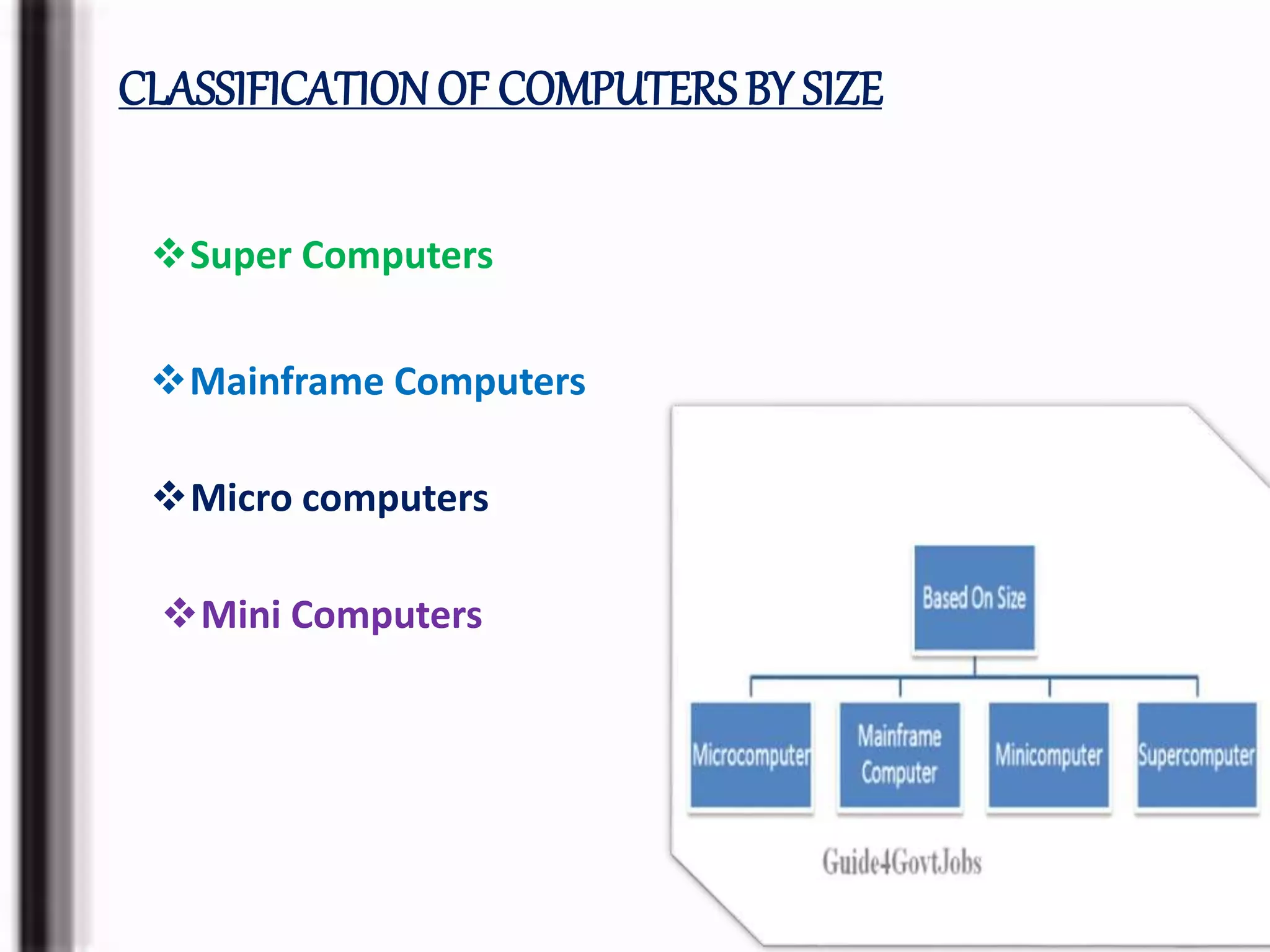



![MINI COMPUTERS
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a
class of smaller computers that was
developed in the mid-1960s[1][2] and sold for
much less than mainframe[3] and mid-size
computers from IBM and its direct
competitors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer1to3-180321150730/75/basic-computer-36-2048.jpg)


![COMPUTER HARDWARE
Computer hardware are the physical parts or components of a computer,
such as the monitor, keyboard, computer data storage, graphic
card, sound card and motherboard.[1] By contrast, software is instructions
that can be stored and ran by hardware.
Hardware is directed by the software to execute any command
or instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a
usable computing system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computer1to3-180321150730/75/basic-computer-39-2048.jpg)