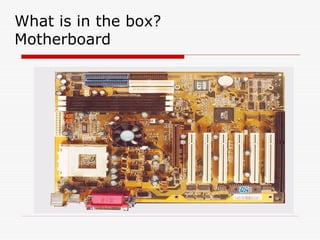
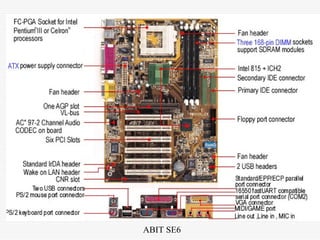
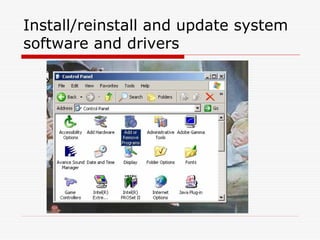
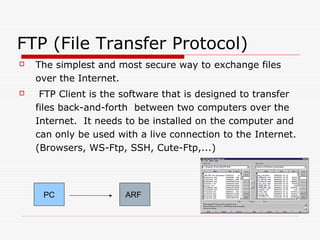
This document provides an overview of basic computer operation, including hardware components, operating systems, disk capacities, viruses, applications, installation and internet applications. It describes common computer parts like the motherboard, hard drive, RAM and cables. It also outlines operating systems like Windows, MacOS and Linux and defines terms like directories, documents and applications. Backup methods, using icons and windows, installing software and using internet applications like browsers and FTP are also summarized.