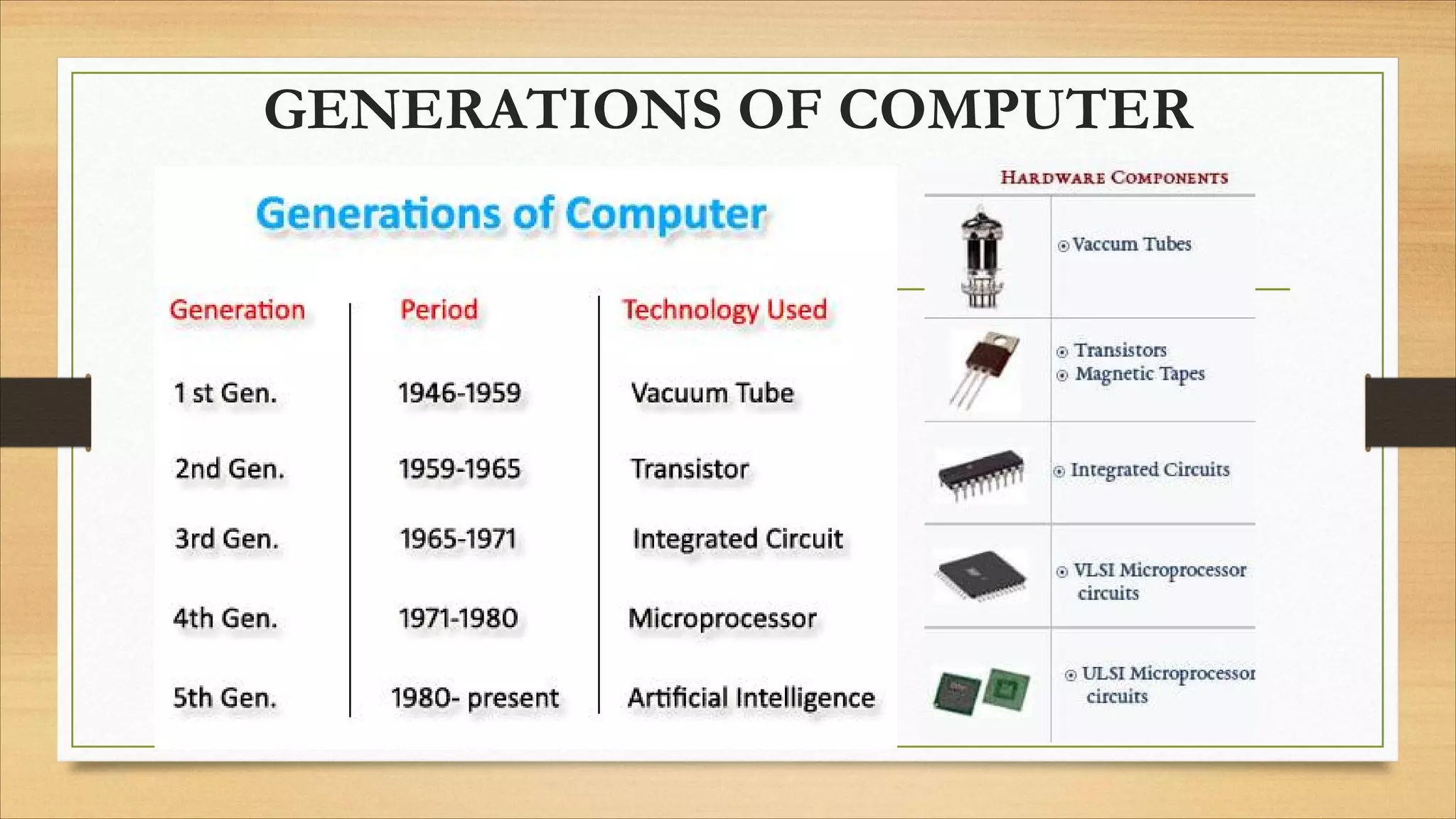
This document provides an overview of computer fundamentals, including:
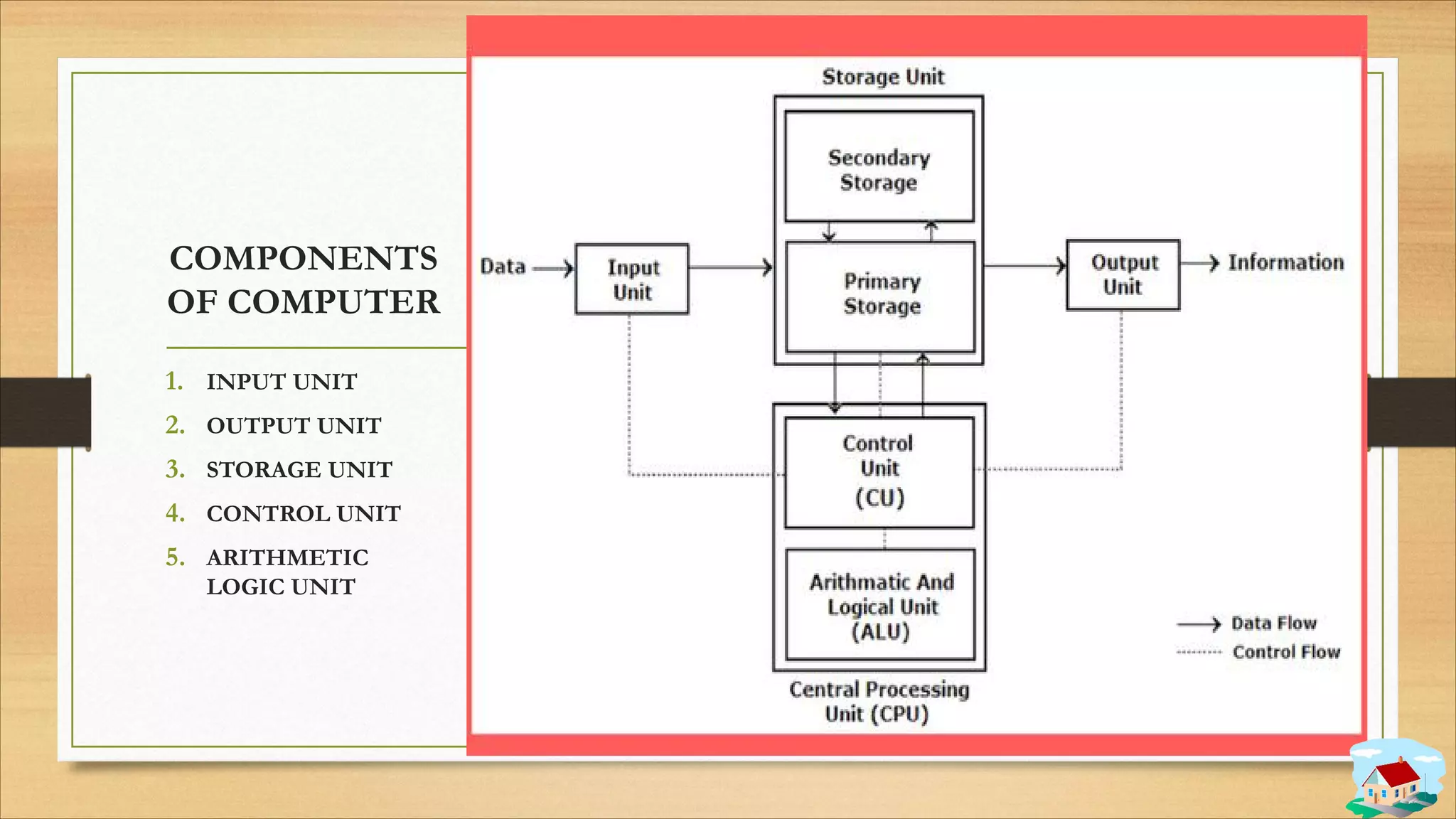
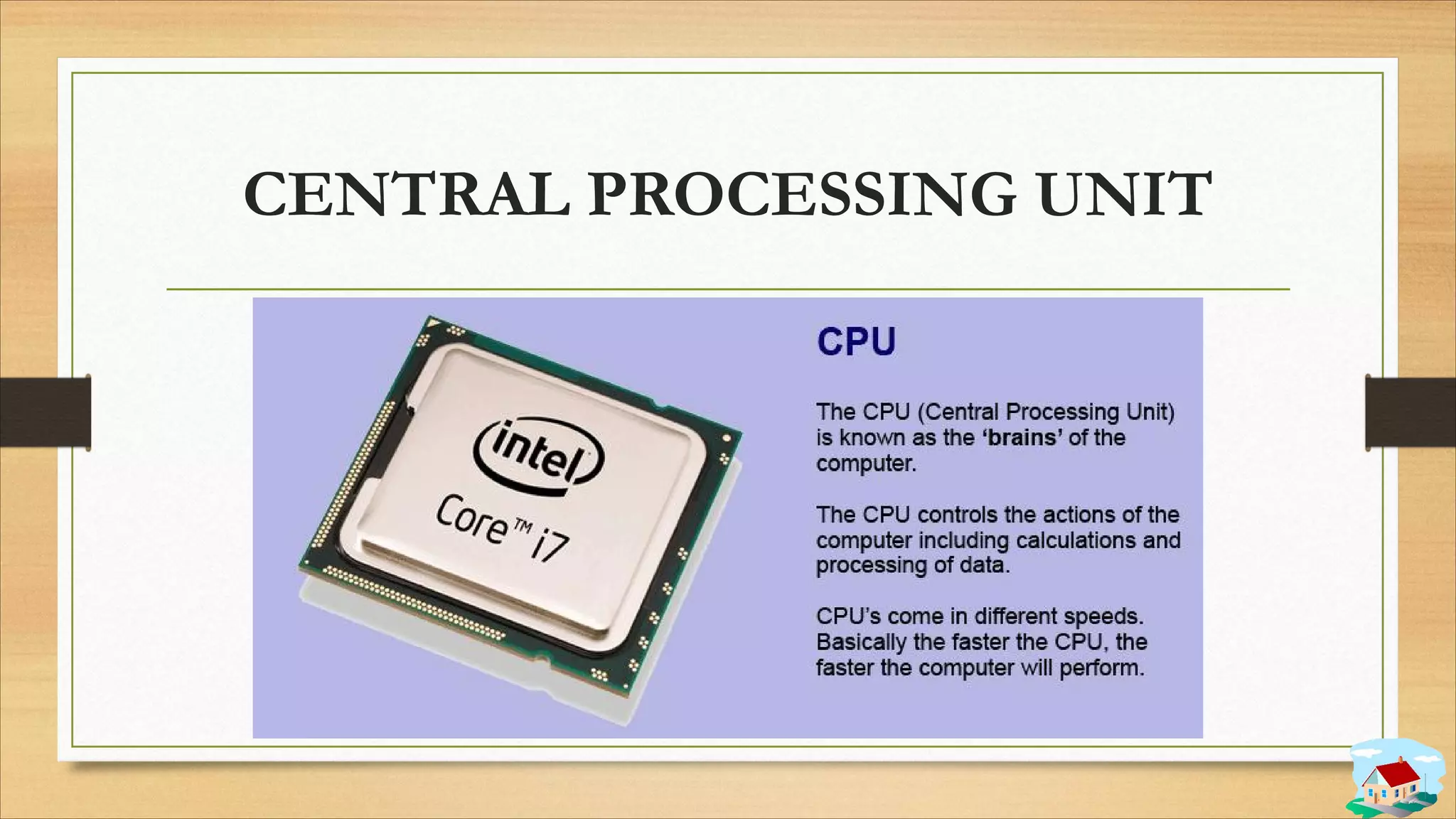
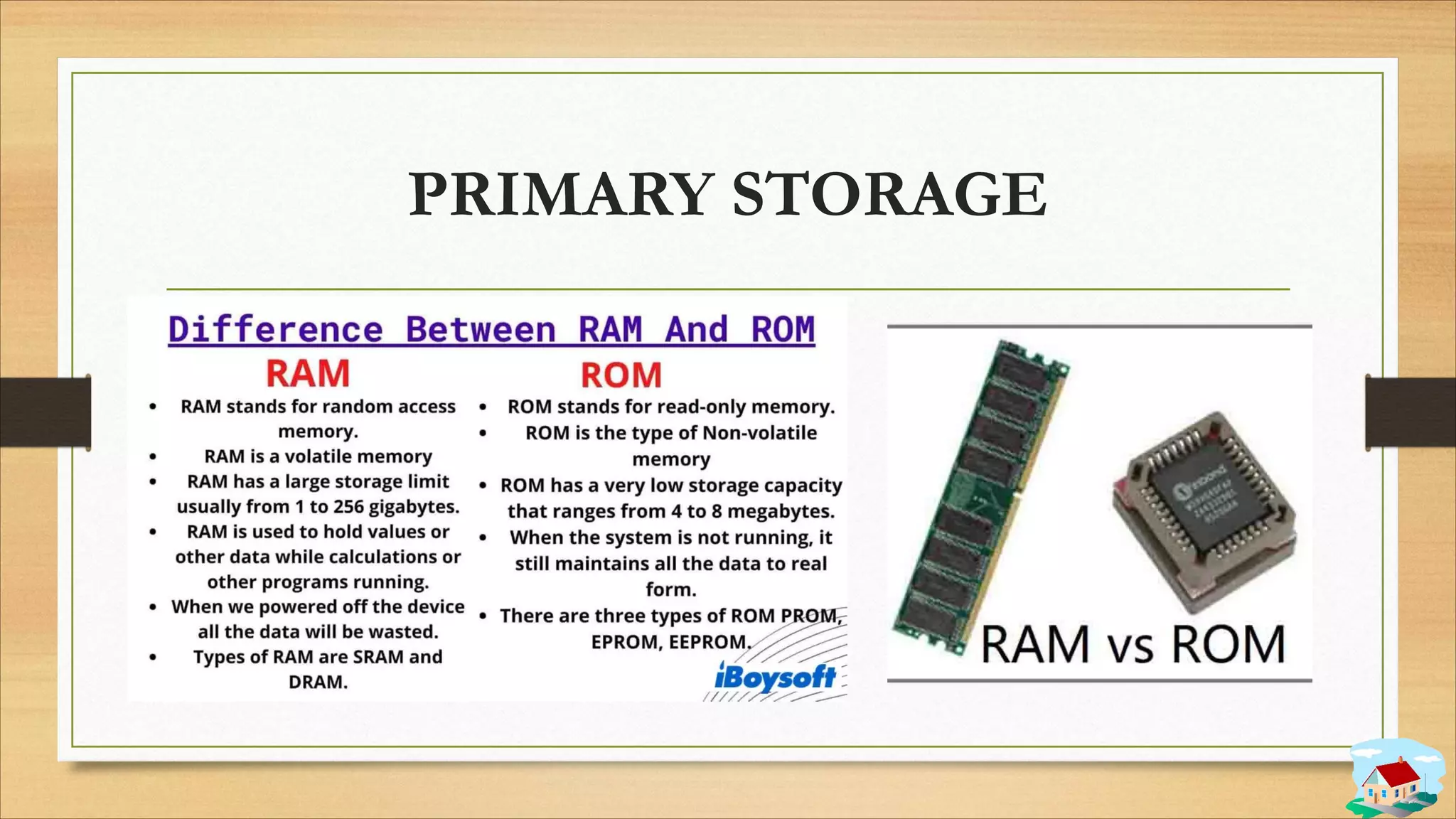
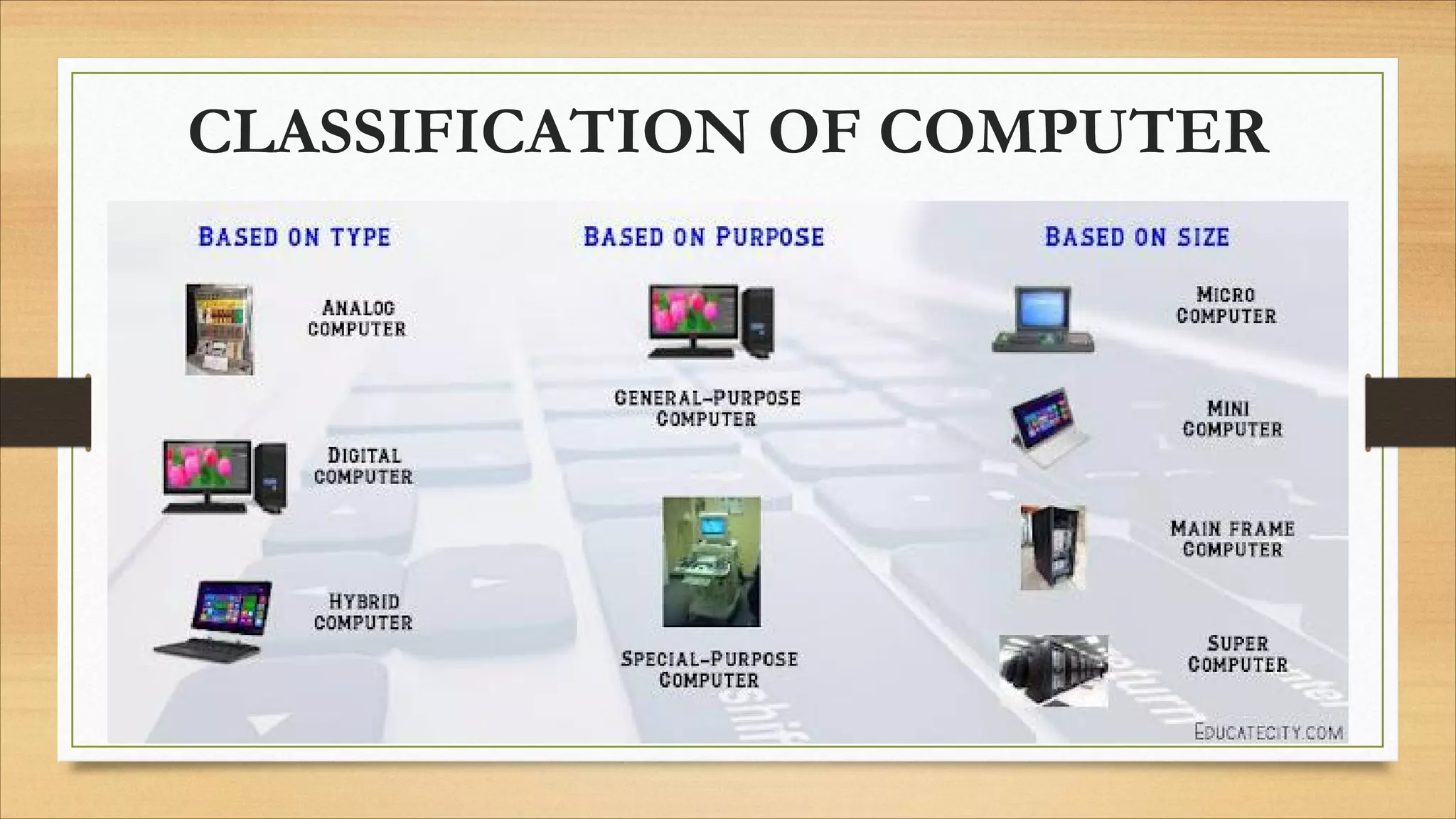
1. The components of a computer system including input, output, storage, control, and arithmetic logic units.
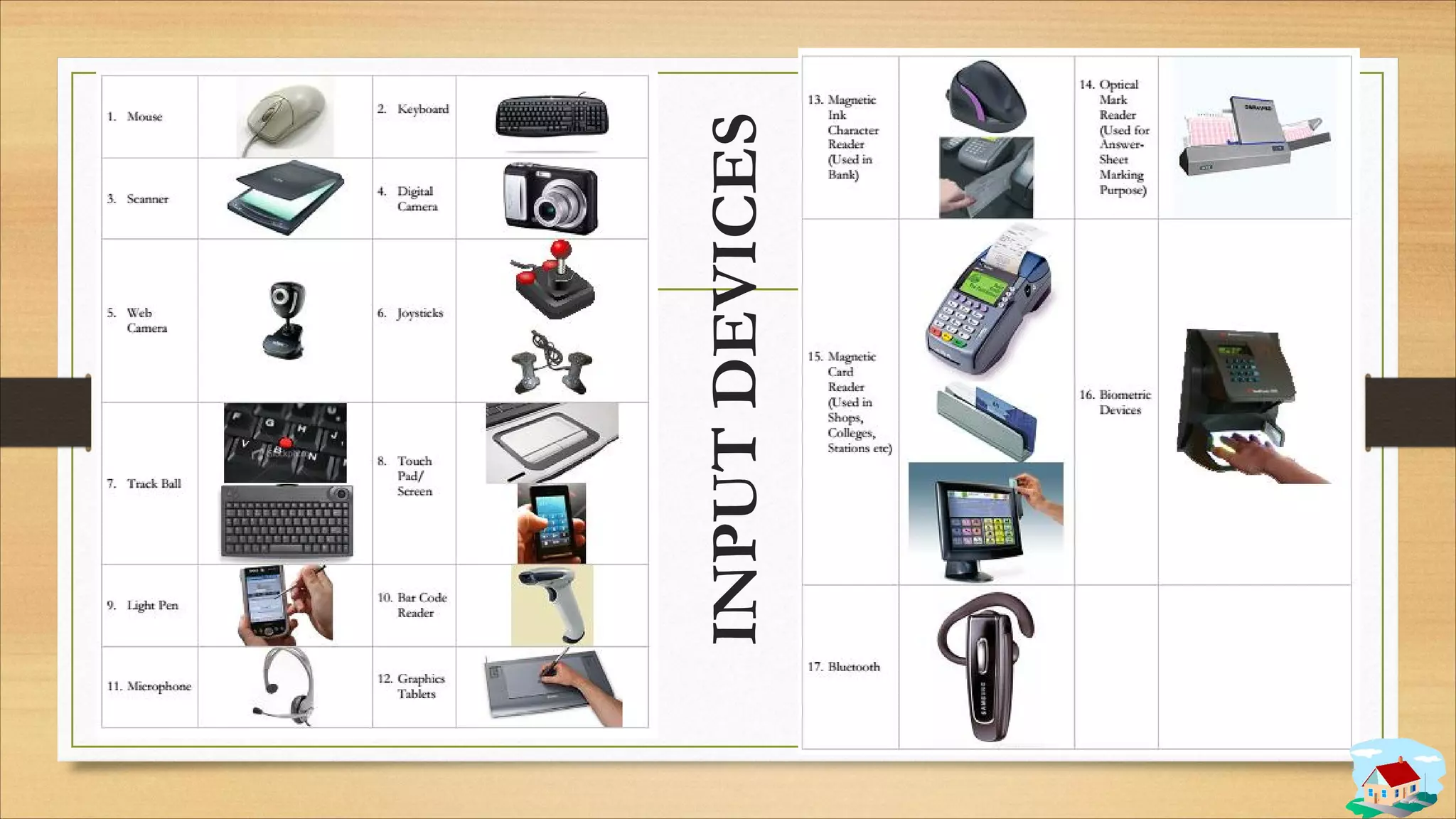
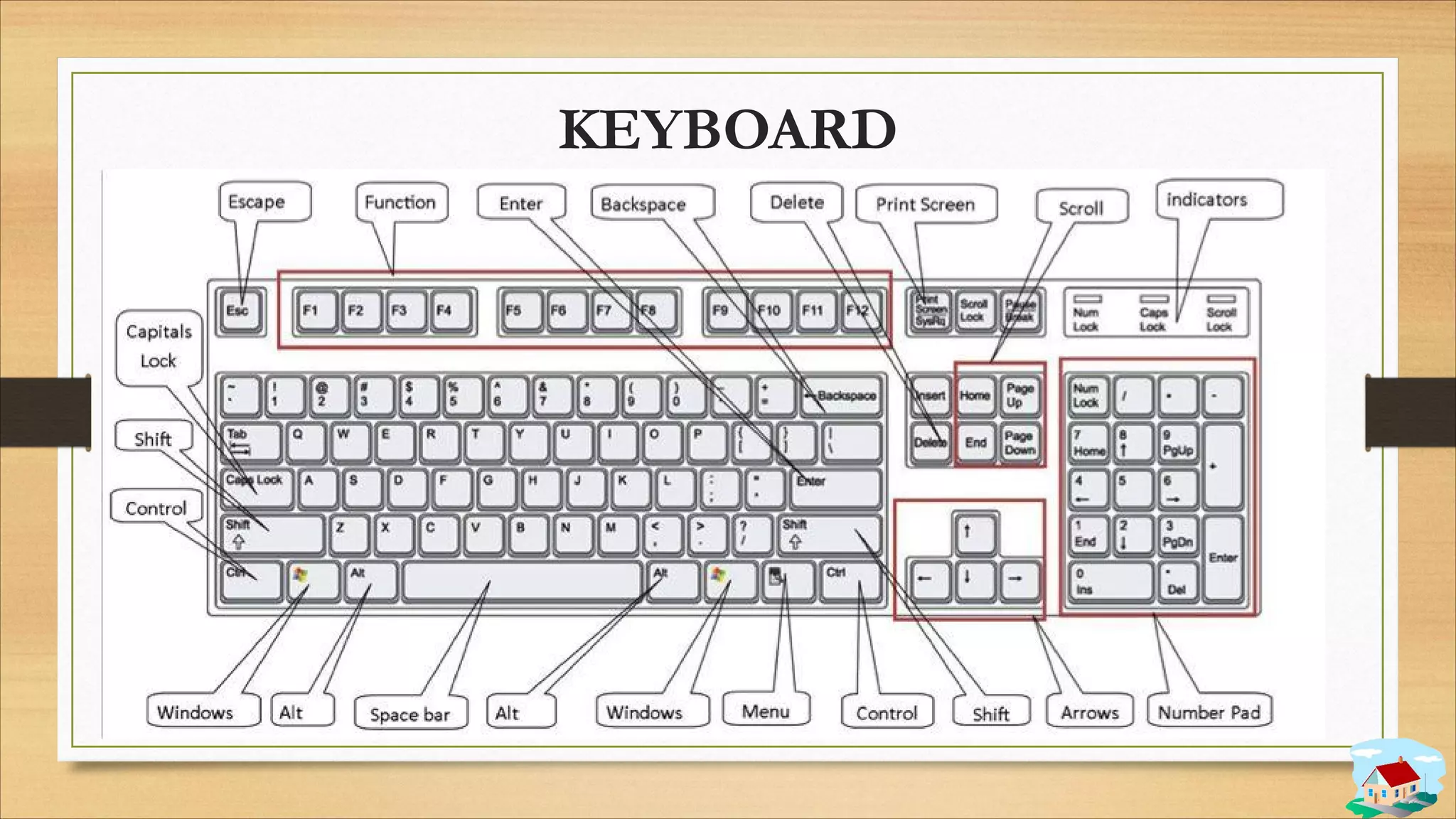
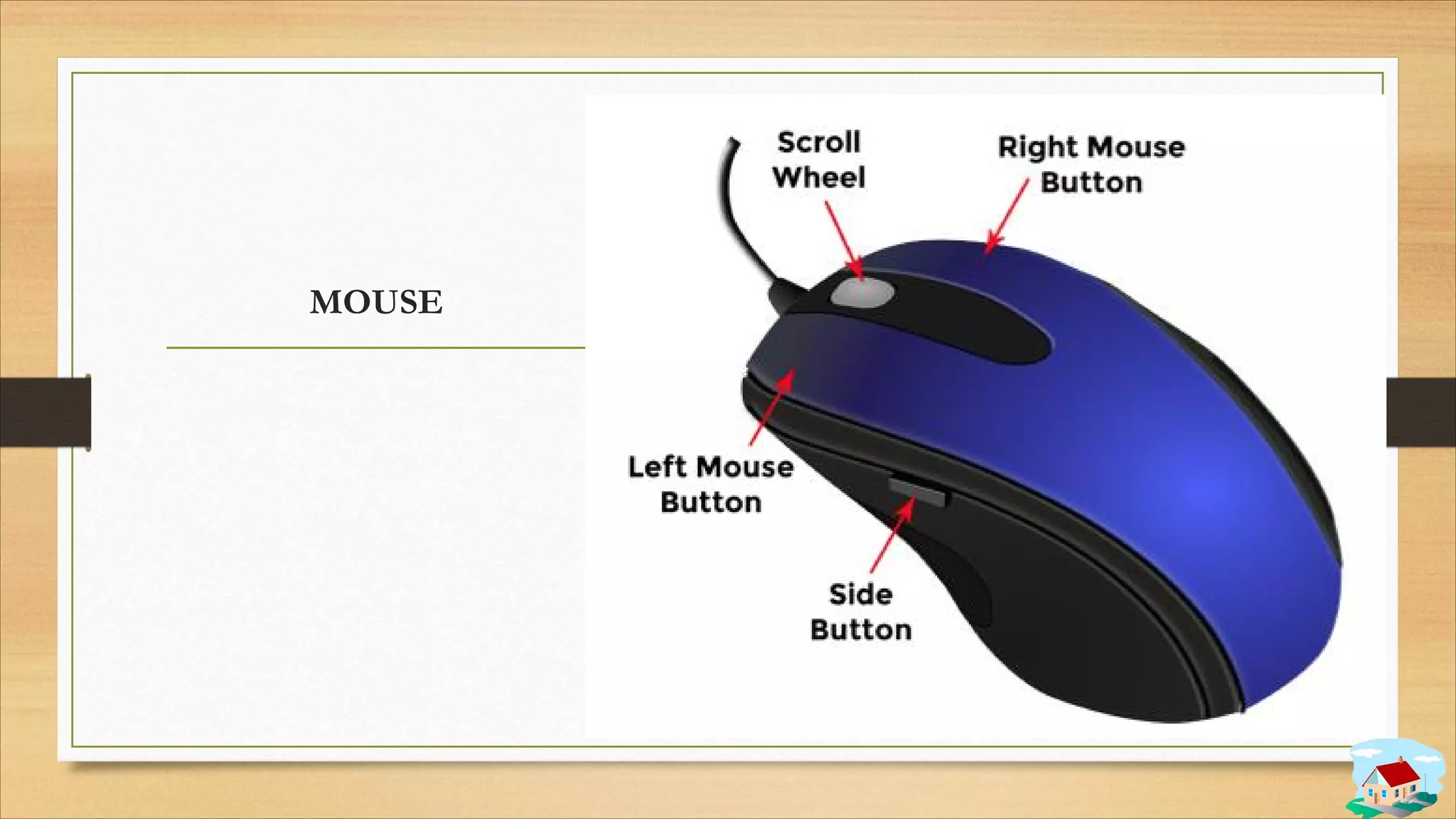
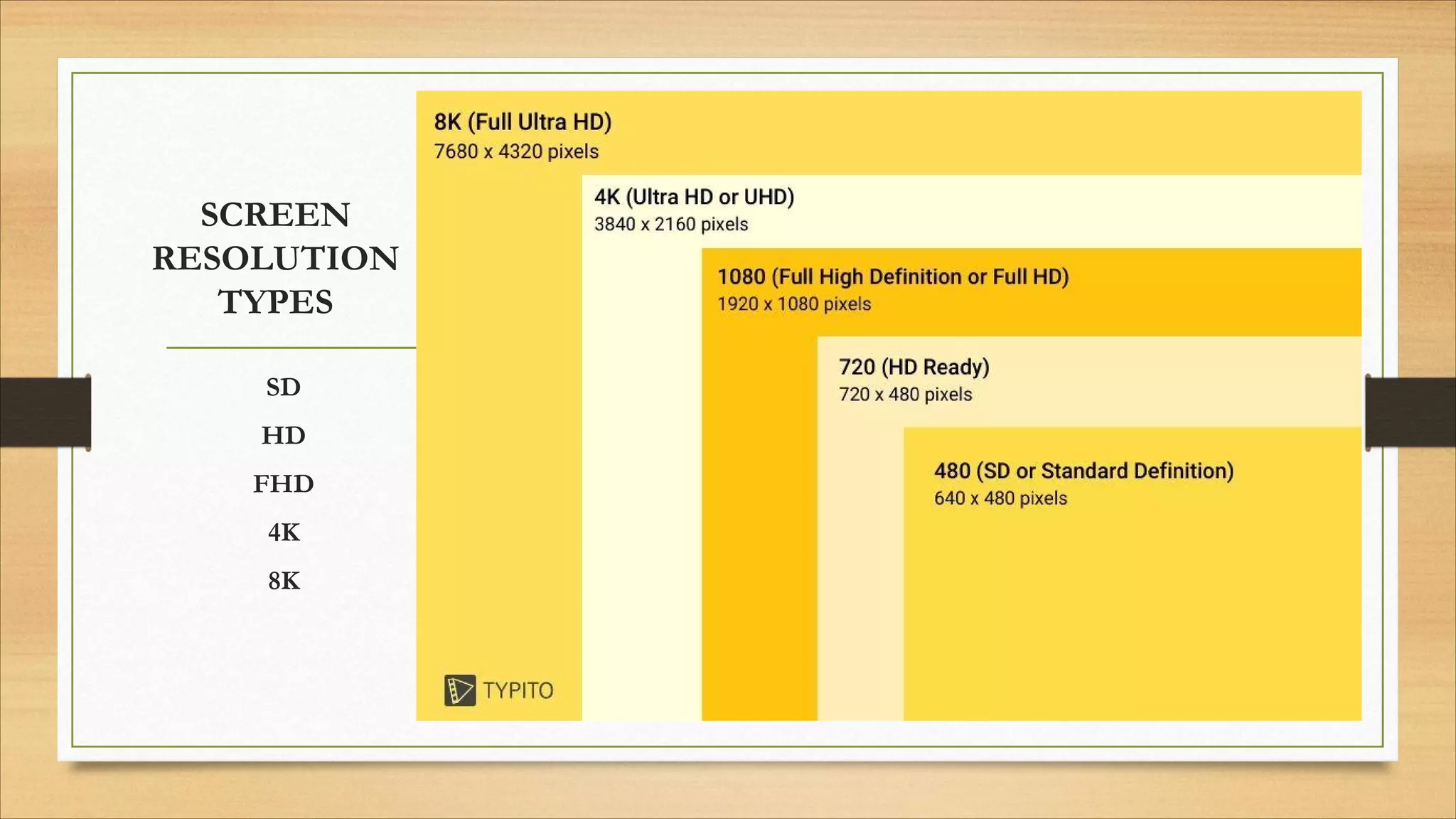
2. Input and output devices such as keyboards, mice, monitors, and printers.
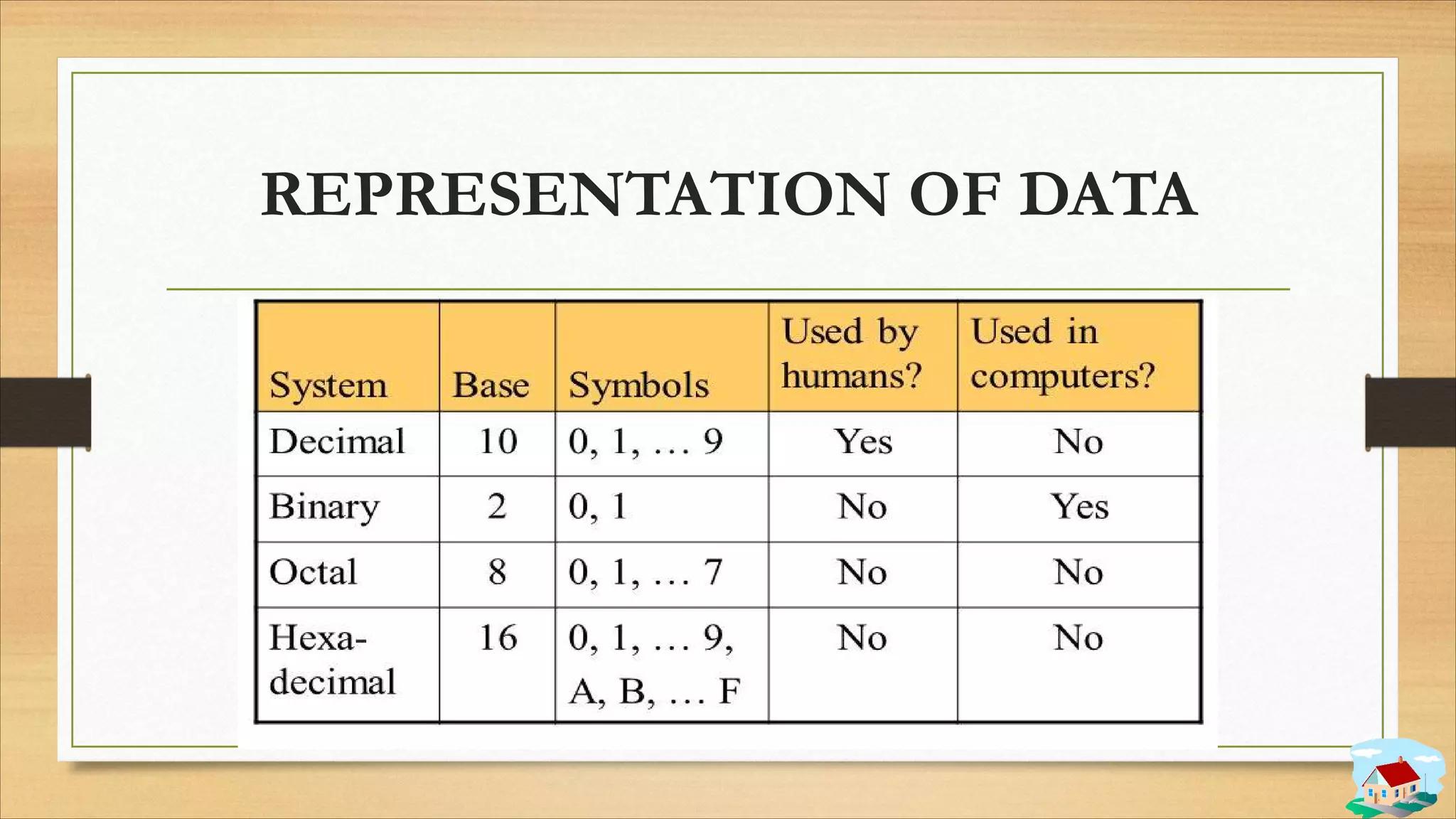
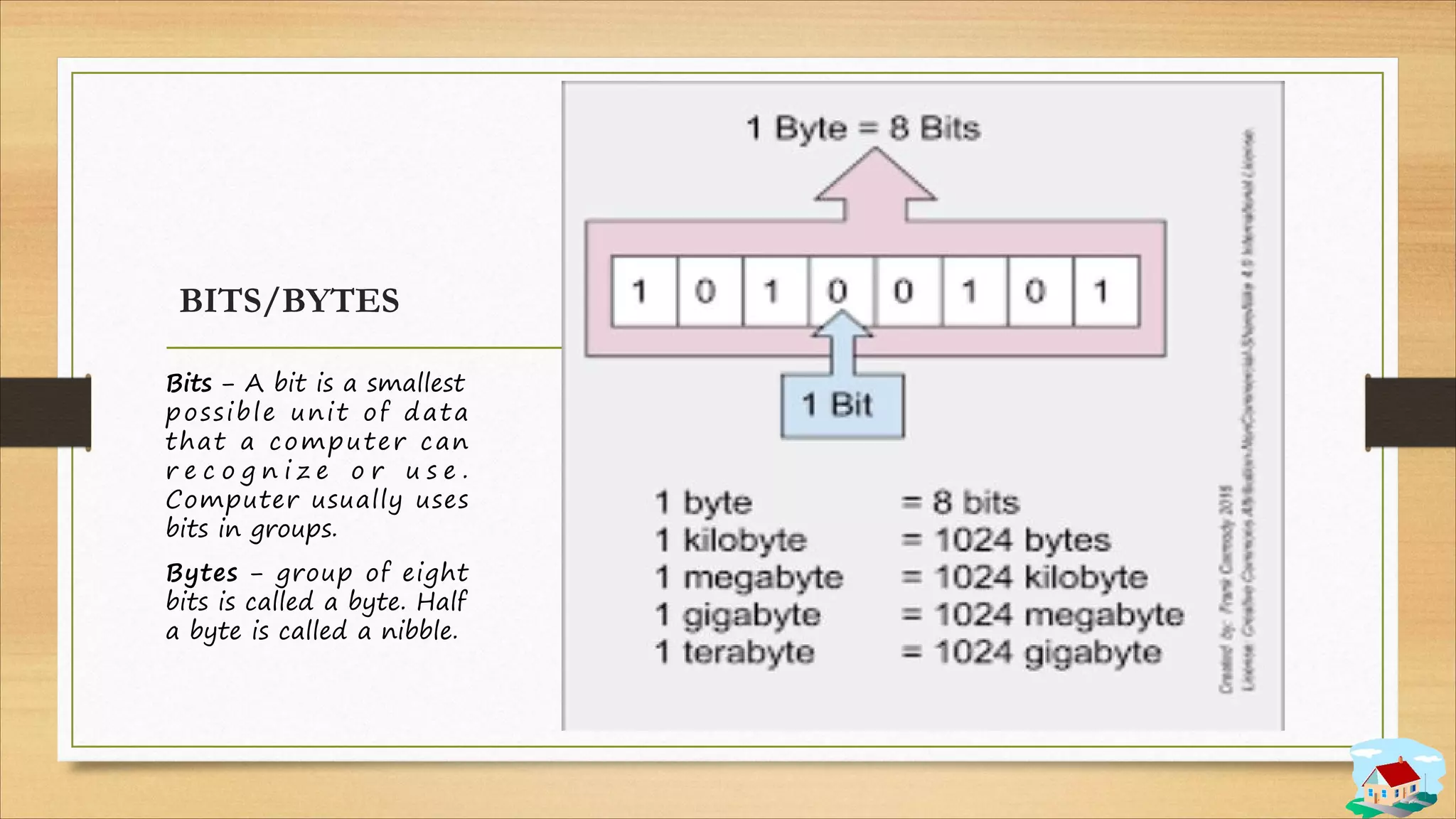
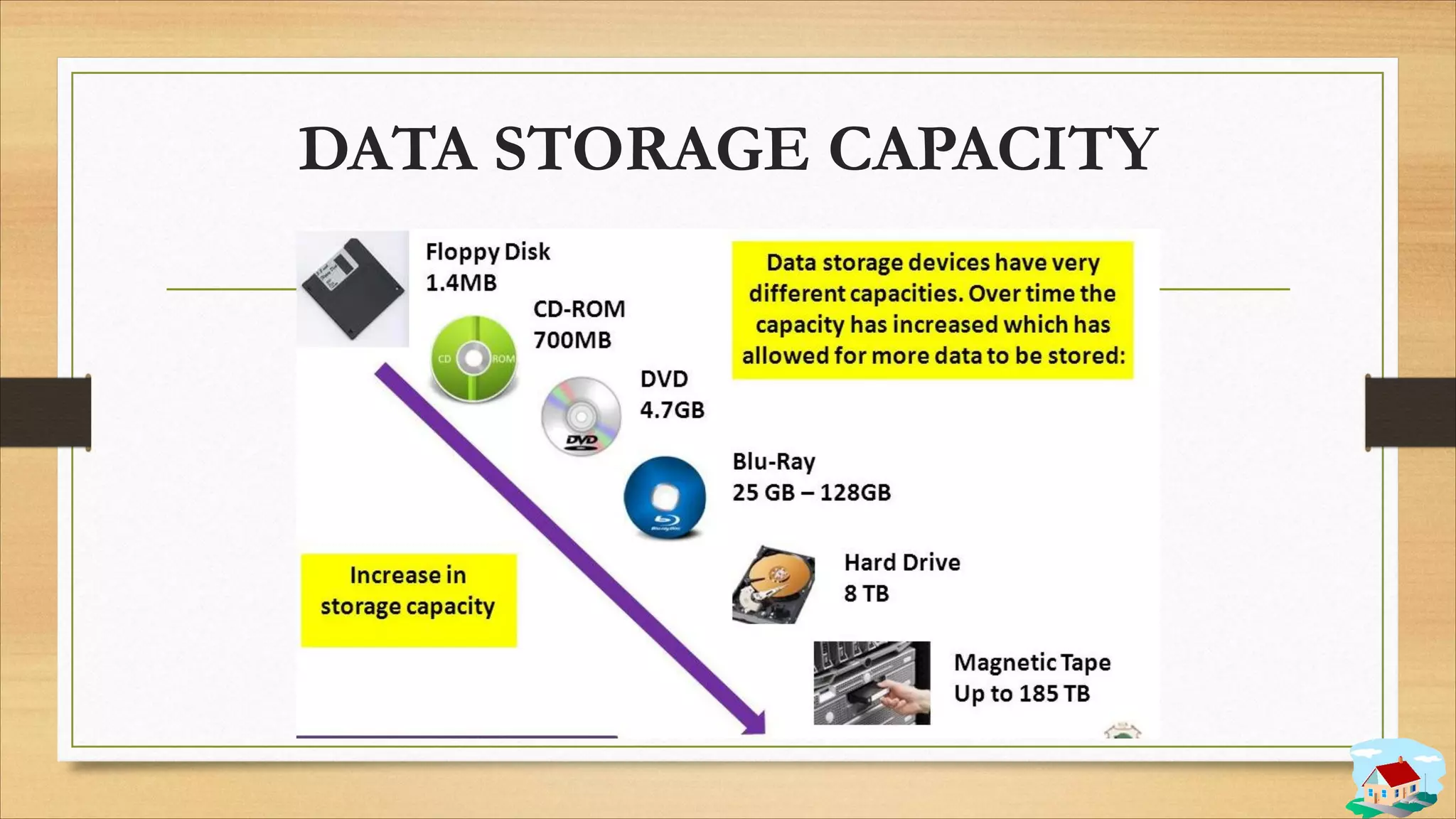
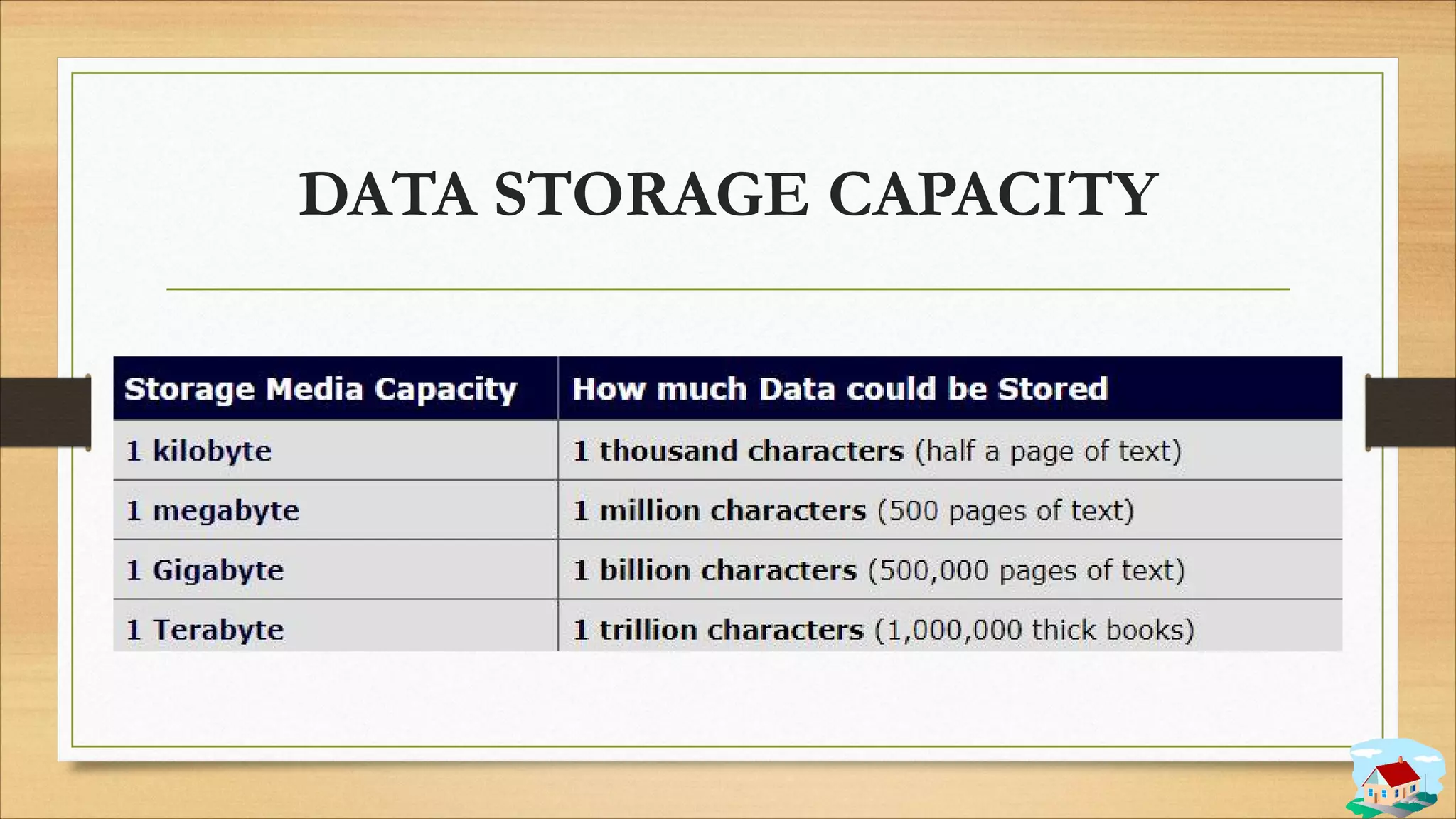
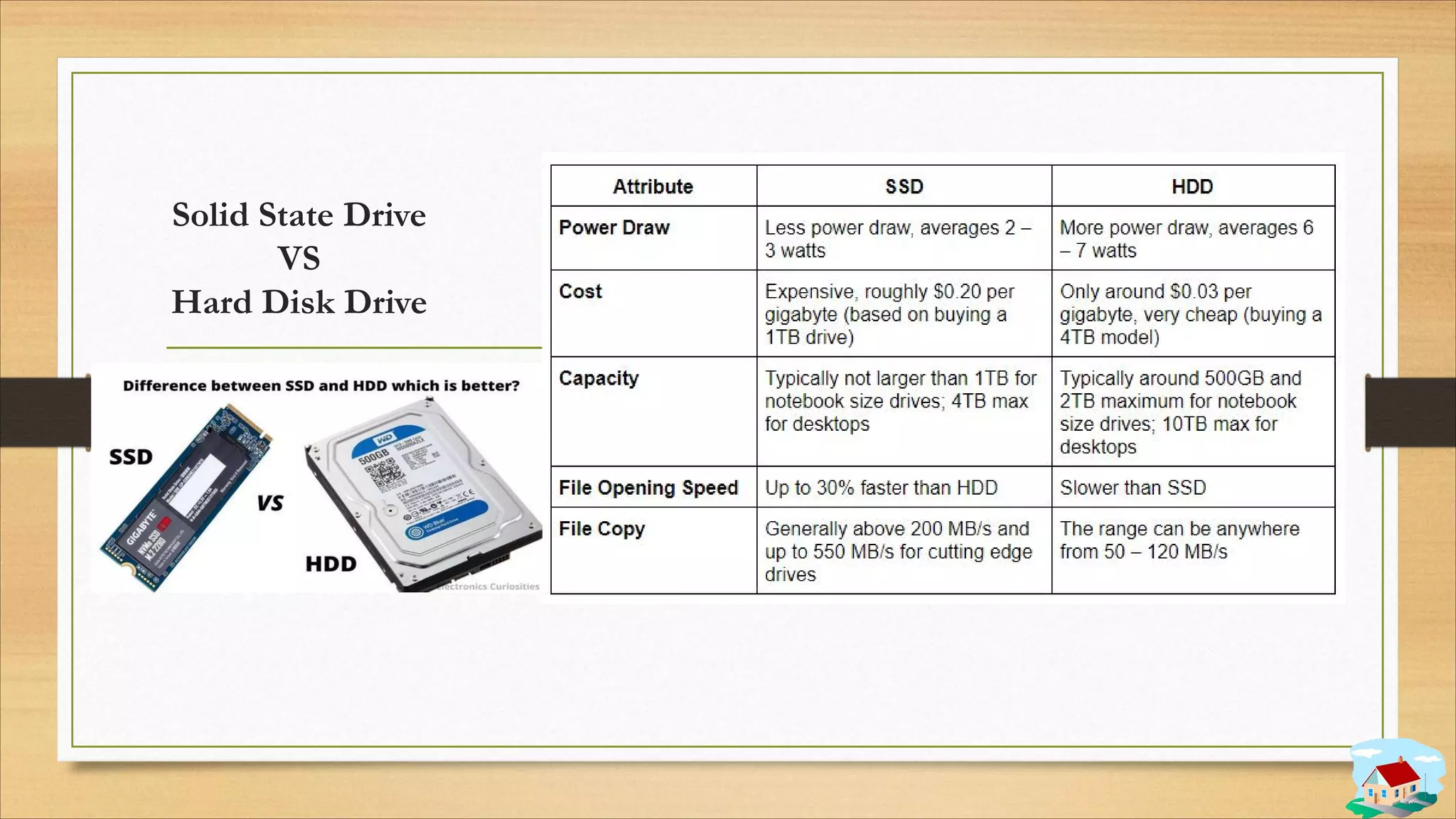
3. Data storage concepts like bits, bytes, and storage units.
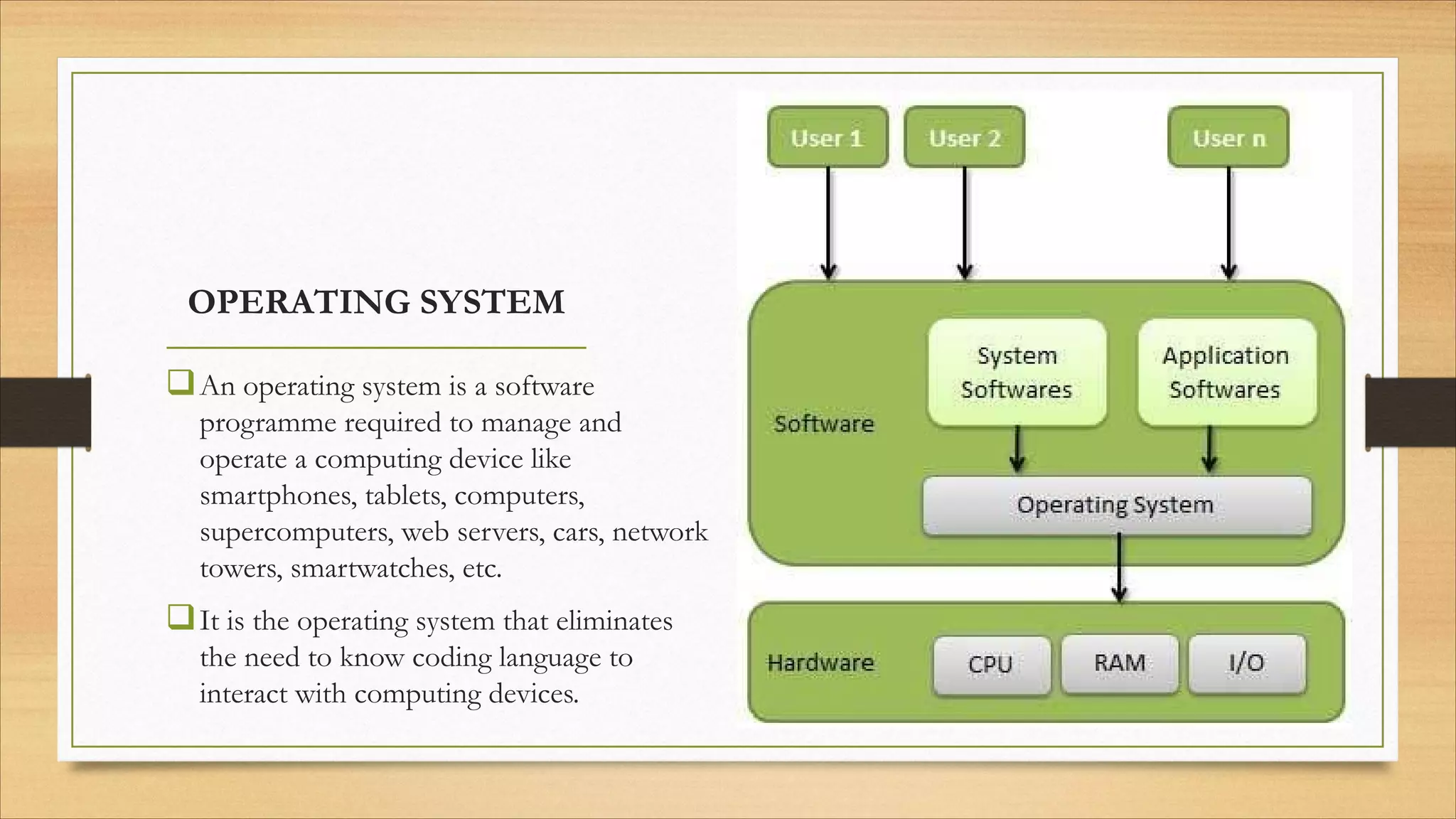
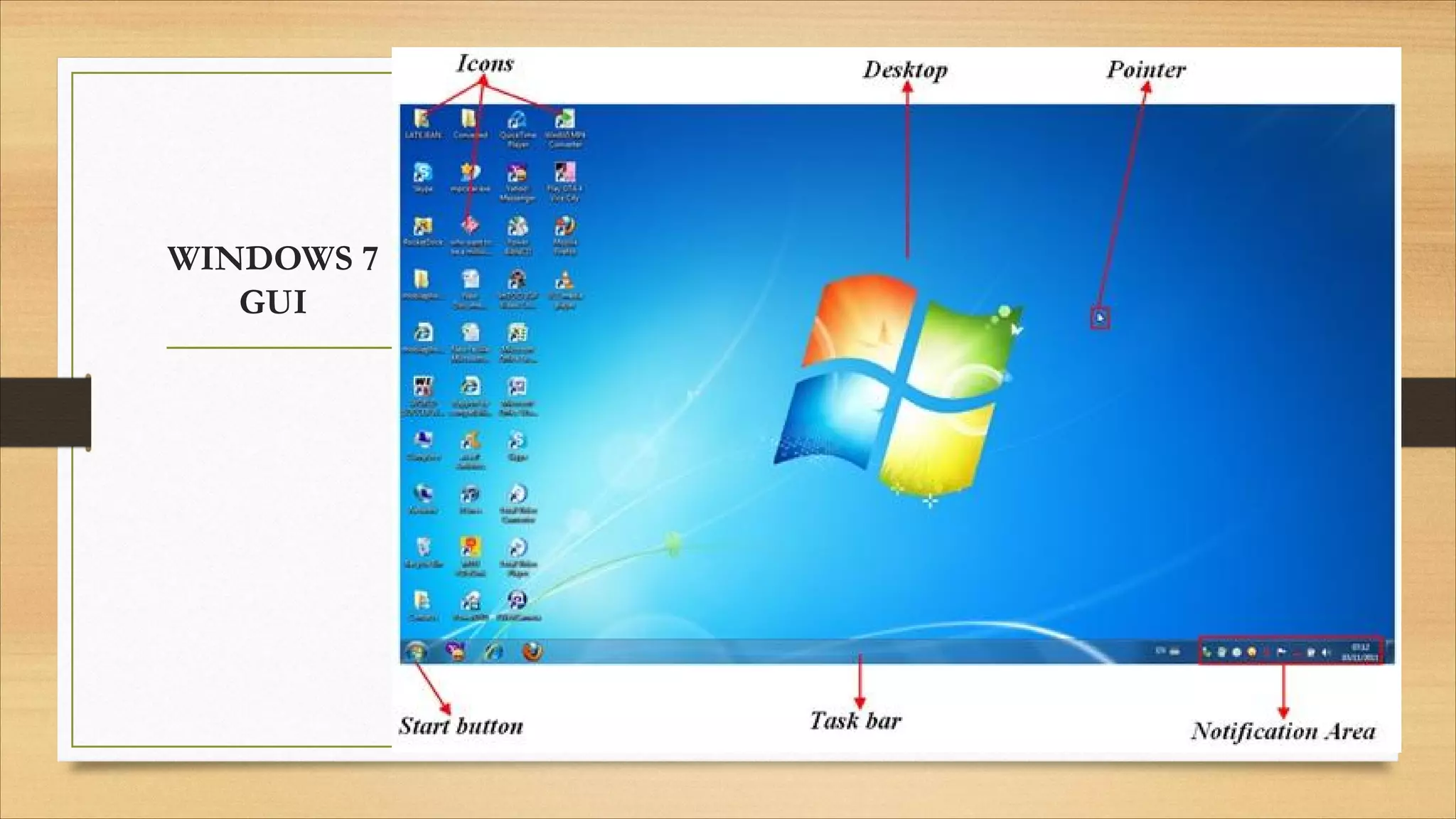
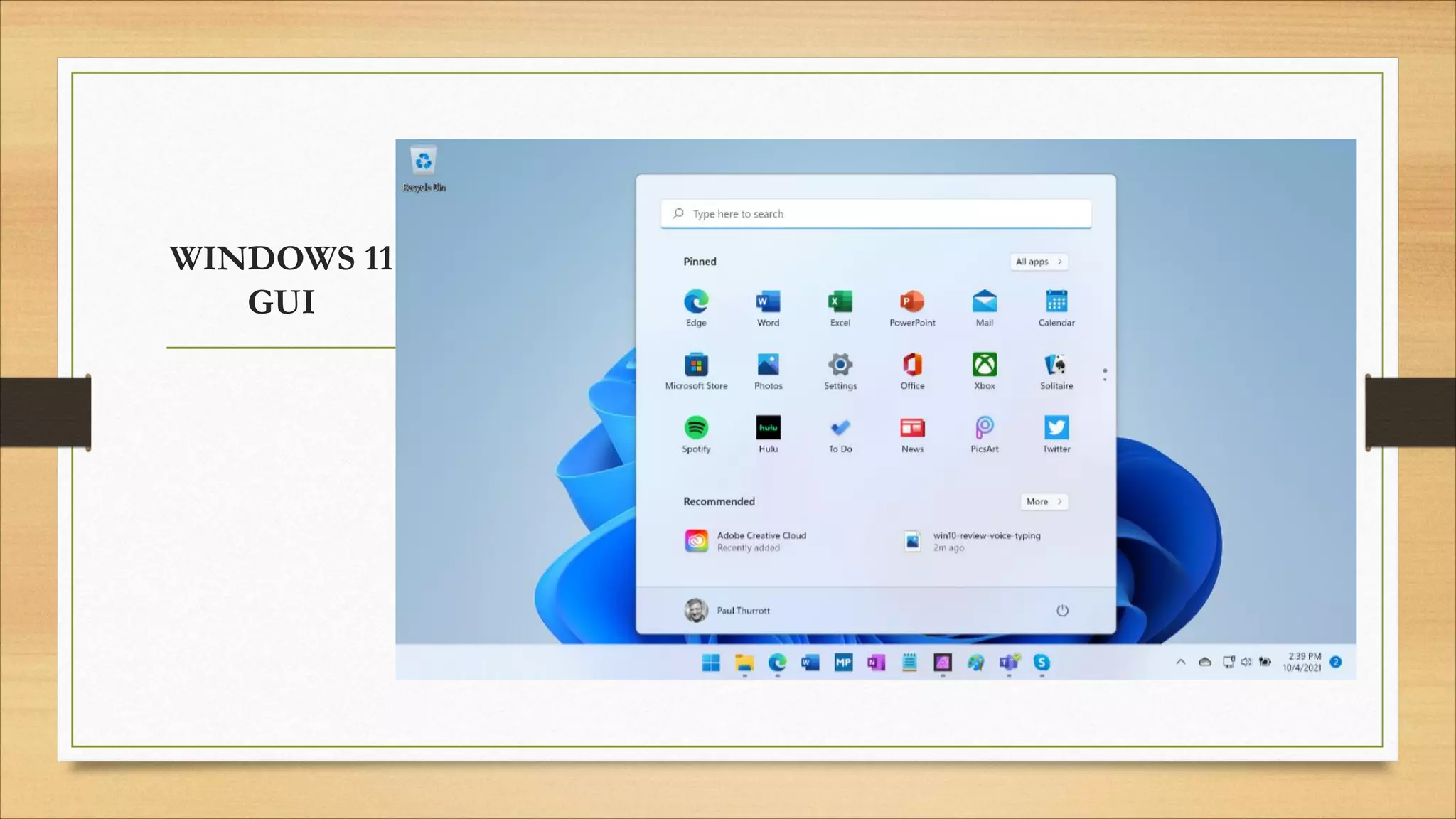
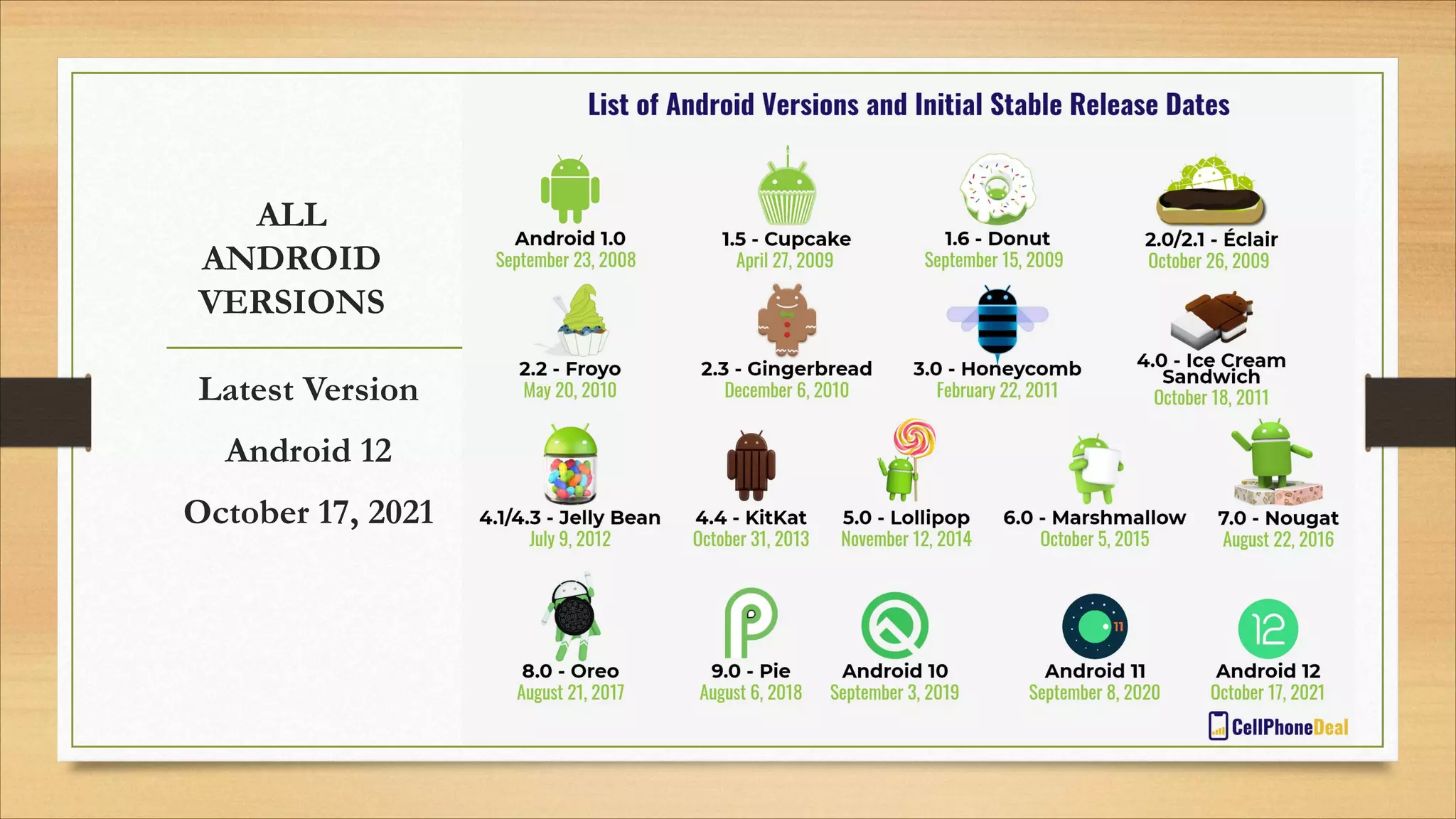
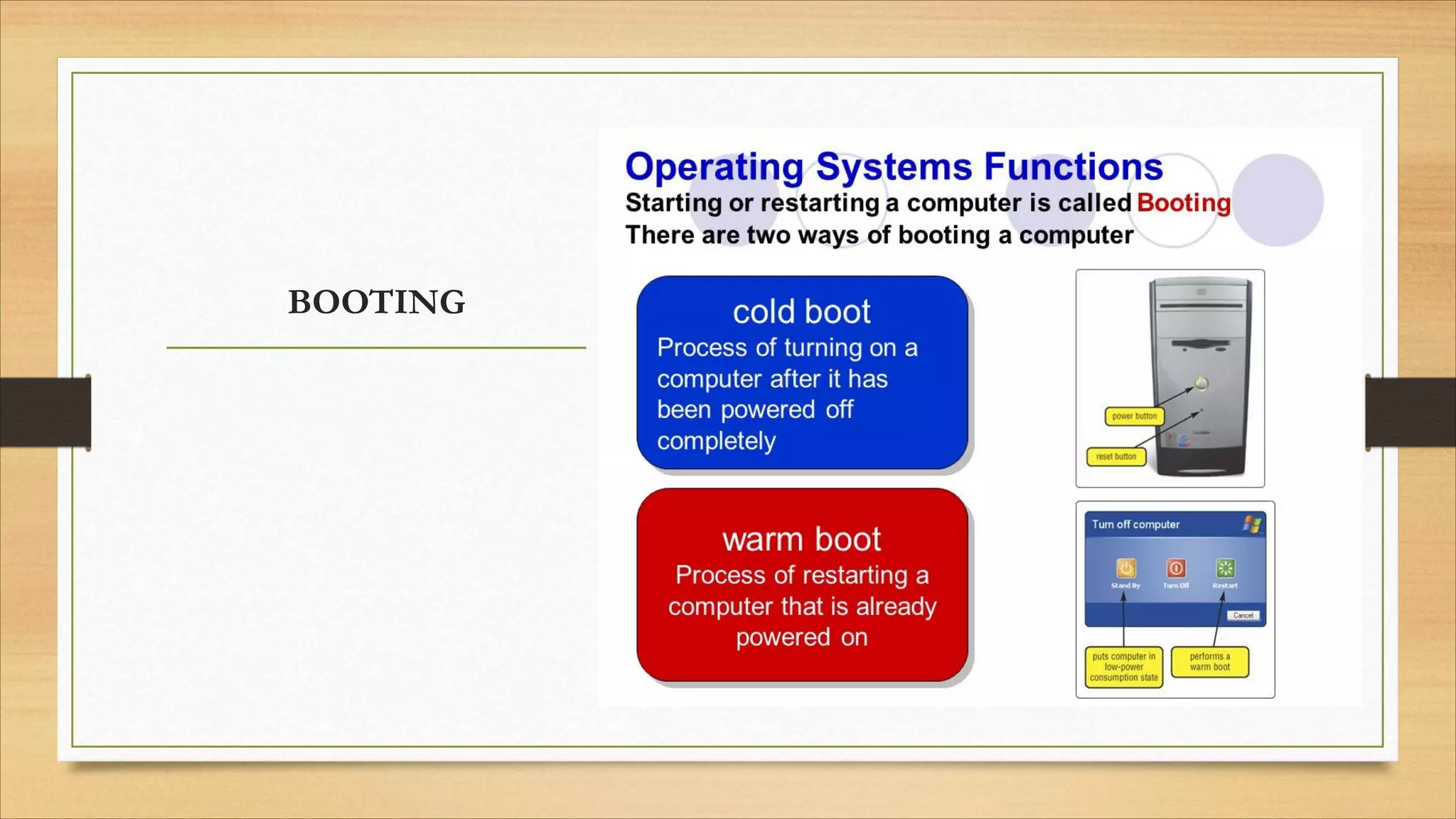
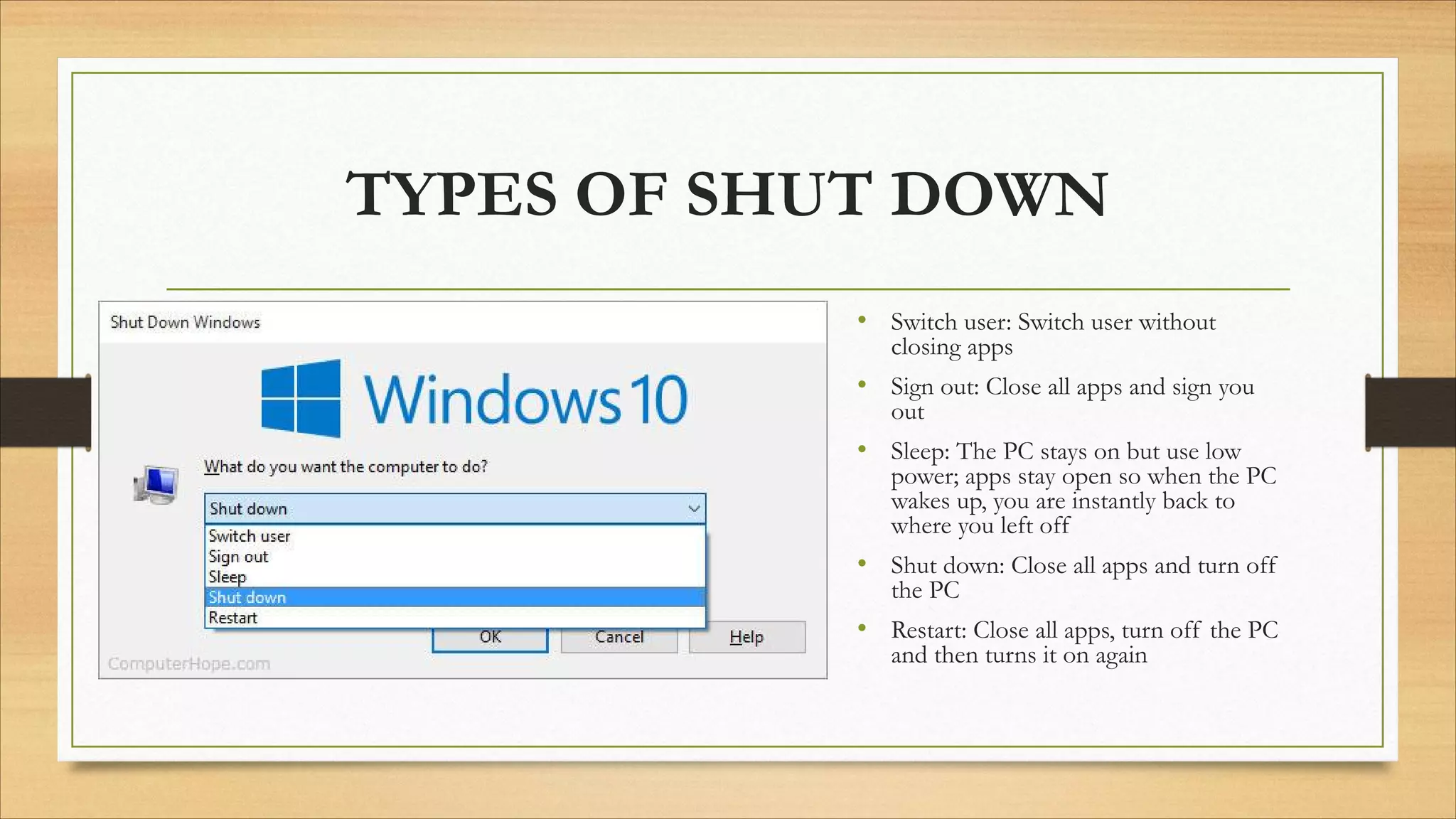
4. Operating systems, popular OSes, and basic OS functions like booting and shutting down.
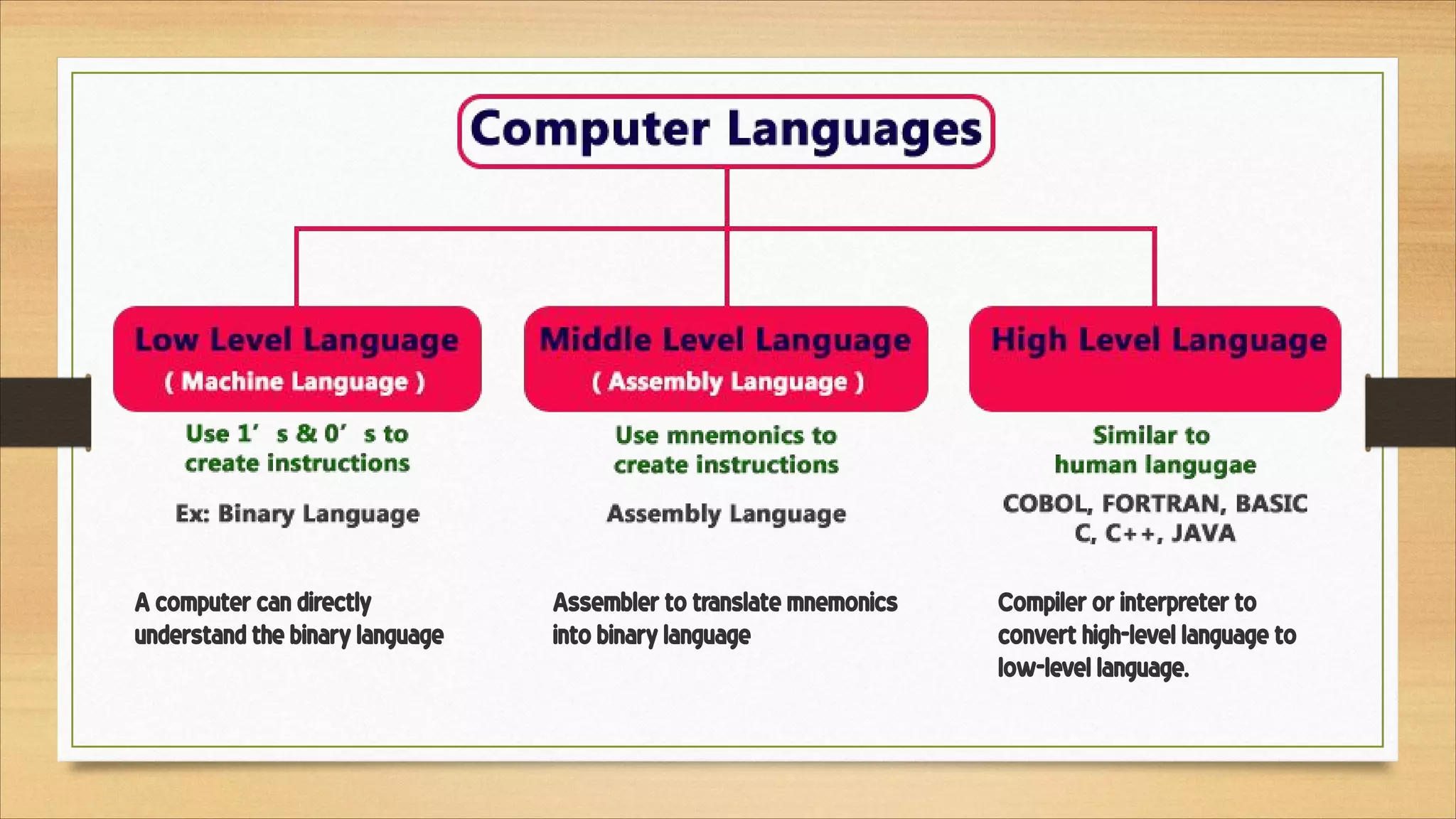
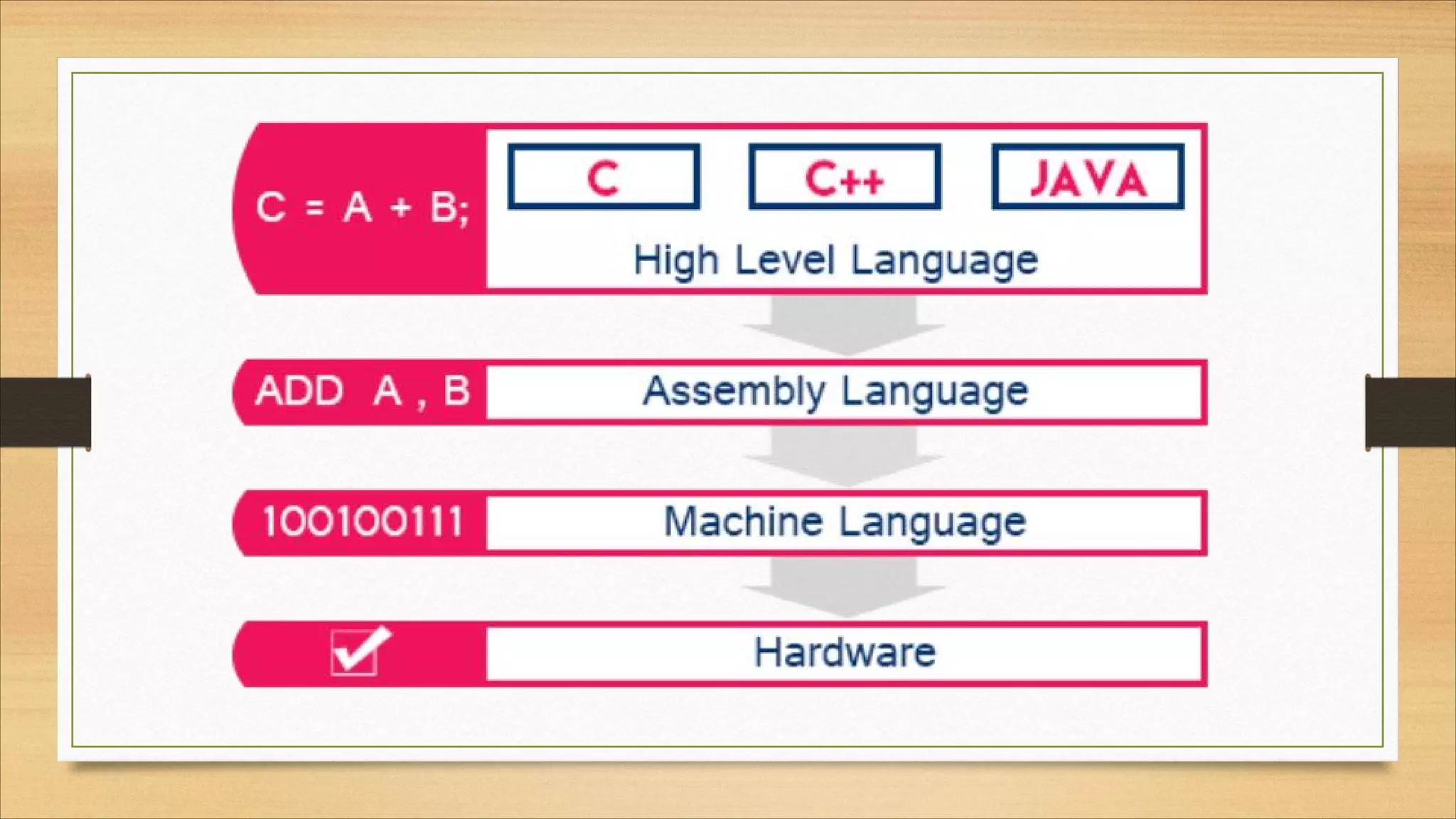
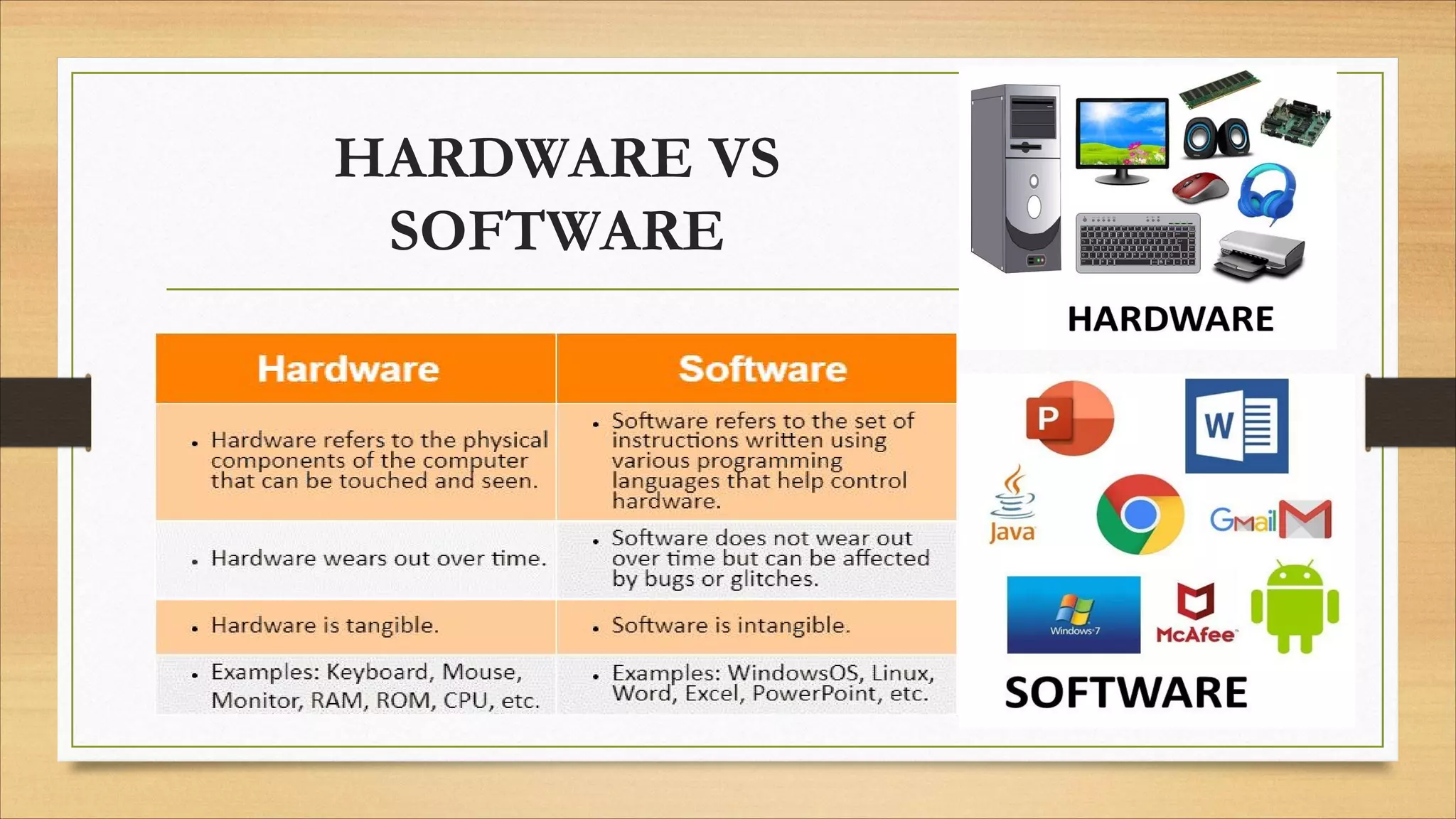
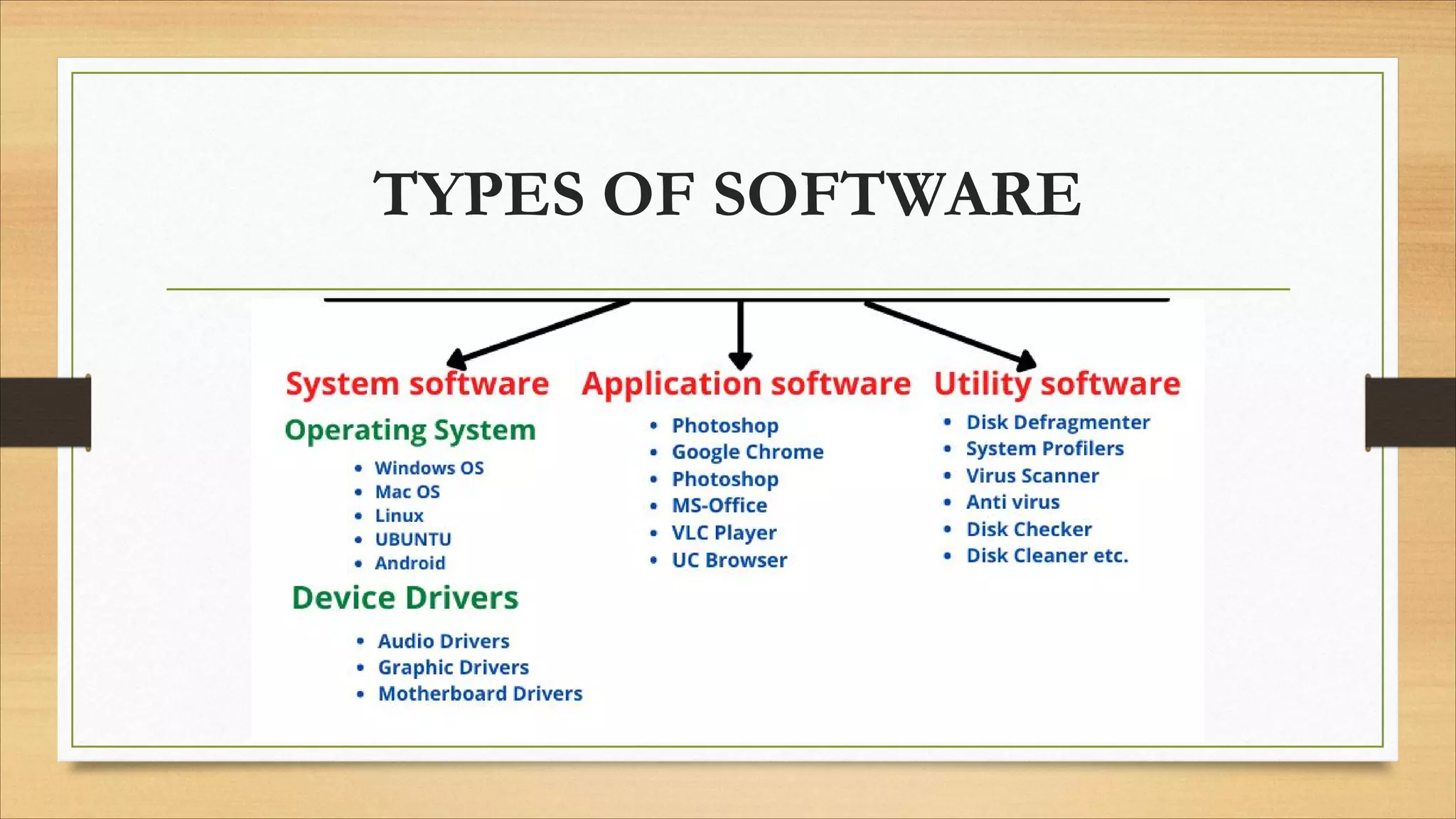
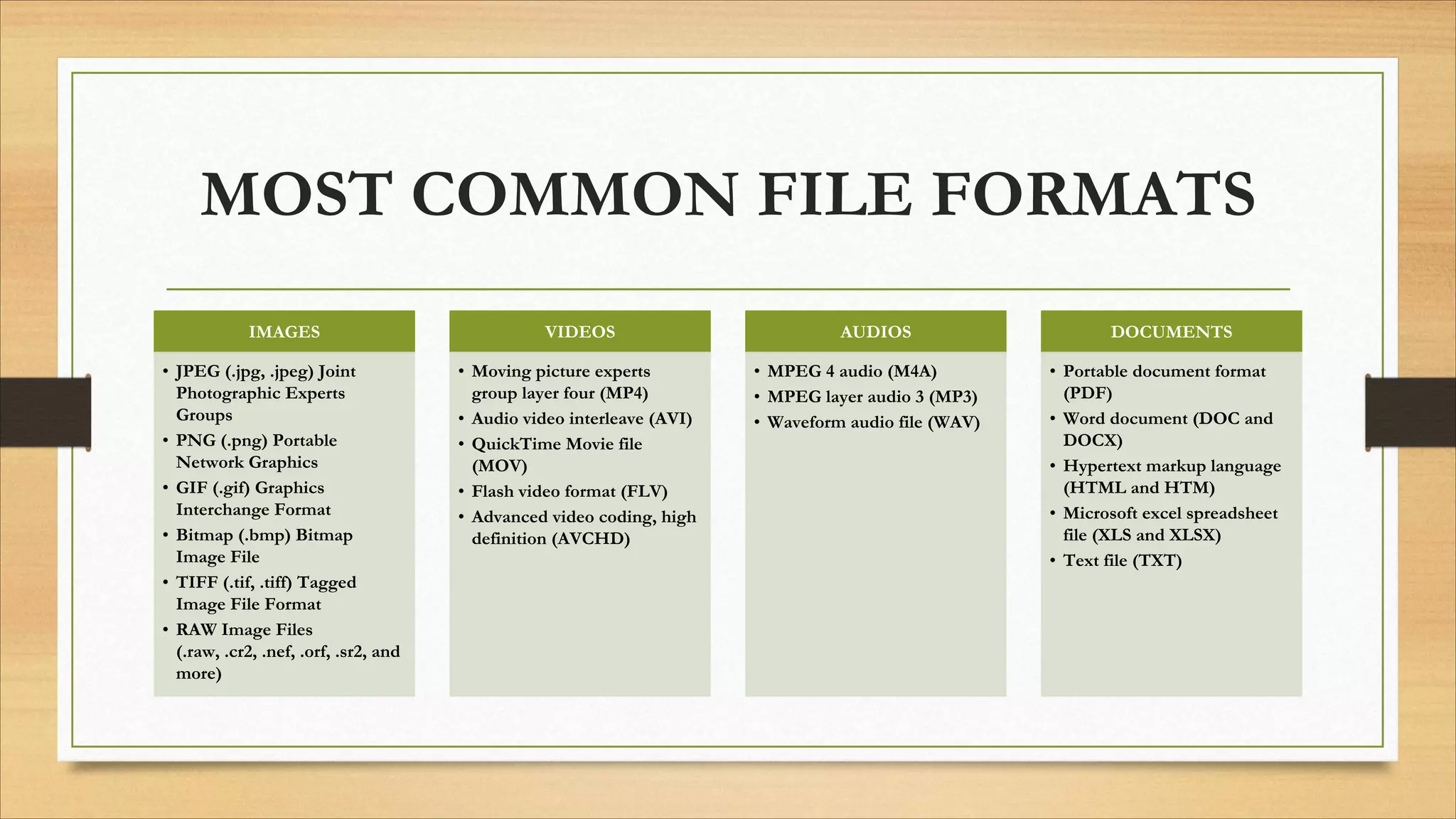
5. Common file formats, software types, and basic computer terminology.