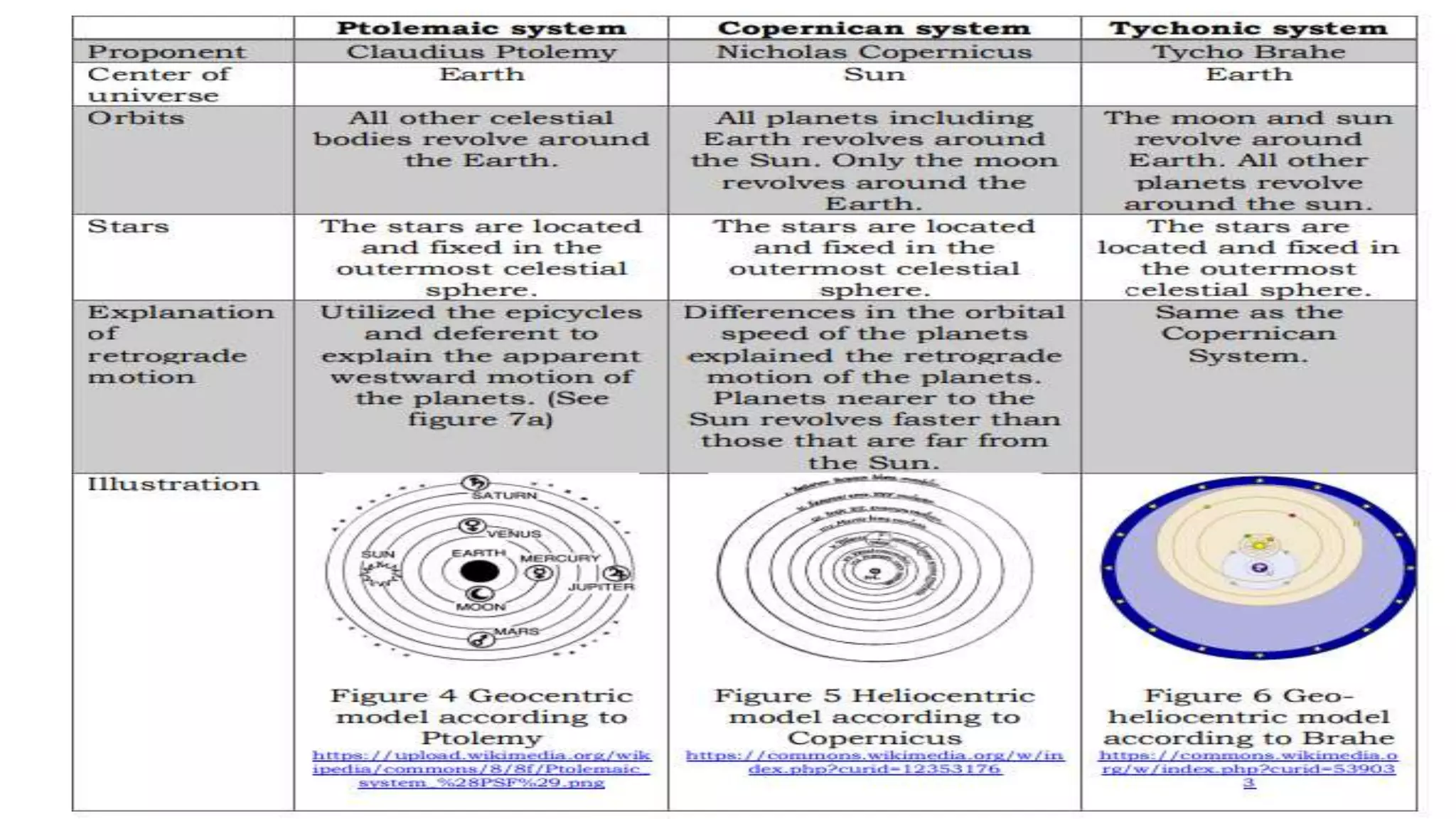
Here are two potential responses in 2-3 sentences each:
1. I would show my flat-earther friend that no matter which way I point the Frisbee, it will always cast a circular shadow on the ball, demonstrating that only a spherical object can do this. Eratosthenes proved the Earth was round using a similar shadow experiment over 2000 years ago.
2. Tycho Brahe spent over 20 years meticulously recording the positions of planets with unprecedented accuracy. This treasure trove of observational data was invaluable for Kepler to analyze and discover the elliptical orbits of planets, replacing the imperfect circular/epicyclic models. Without Brahe's precise records, Kepler would not have been able to derive his revolutionary laws of planetary



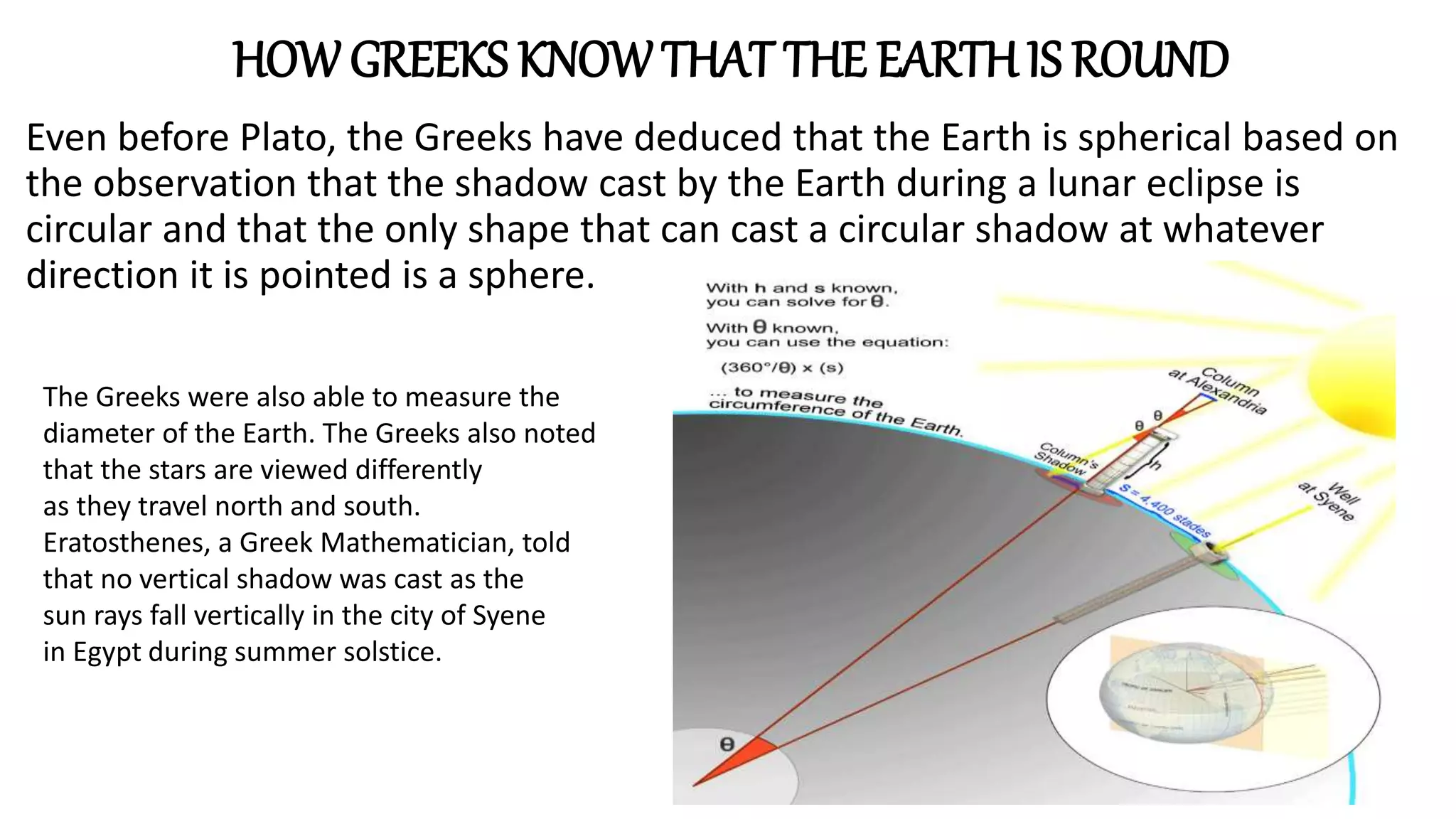
![•Eratosthenes noted that at the same time a shadow was
cast as the sun rays fell at an angle of 7.2° [one fiftieth
(1/50) of a circle in ancient Greek writings] in the city of
Alexandria. He assumed that the sun was so distant that
the rays fall parallel to each other on the Earth’s surface
and that the difference in the shadows cast in the two
cities was due to the curvature of Earth’s round surface.
The distance between Syene and Alexandria was found to
be 5000 stadia (approx. 800 km). Thus, Eratosthenes
thought the Earth’s circumference must be 50 x 5000 stadia
or 250,000 stadia (40,000 kilometers). Now, what is the
significance of the spherical shape of Earth? The sense of
symmetry by Greeks demands a spherical Earth located at
the center of the sphere of heavens.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/models-of-the-universe-230124044549-b3f3a7f2/75/Models-of-the-Universe-pptx-6-2048.jpg)