The document describes an experiment to determine the acceleration due to gravity (g) and the radius of gyration (k) of a bar pendulum. A bar pendulum consists of a uniform bar that can be suspended at different holes along its length. The period of oscillation is measured for different holes and plotted against the distance from the center of gravity to create curves. From these curves, g and k can be calculated. Alternatively, the two-hole method uses the periods at two holes to directly calculate g and k using equations. The results from these two methods are then compared to each other and a direct calculation of k.



![A bar pendulum consists of a uniform rectangular
bar having a number of equidistant holes along its
length as shown in fig [a] . A small rod with a knife
edge can be passed through any of these holes and
the bar can be suspended with this rod as axis.The
pendulum can be made to oscillate in a vertical
plane about this axis.
DESCRIPTION :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barpendlumexperimentppt-220705095820-2e4270f6/75/Bar-Pendulum-experiment-ppt-pptx-4-2048.jpg)
![PRINCIPLE:
The bar pendulum is a kind of compound pendulum. If ‘K’ is the radius of gyation about a horizontal axis through the C .G.
of the bar and h is the distance of the axis of suspension from the C.G. the period of oscillation.
•
• When the period [T] about the different holes is plotted against distance h we get curves of the form shown in figure
[b]. For a given value of T ,there are 4 points [ A,B,C,and D] about which the periods are the same . The length of the
corresponding equivalent simple pendulum is
The period of the pendulum is the minimum when h=k. therefore distance
if T1 AND T2 are the periods about two wholes which are at distances h1 and h2 from the C.G.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barpendlumexperimentppt-220705095820-2e4270f6/75/Bar-Pendulum-experiment-ppt-pptx-5-2048.jpg)

![HHHH
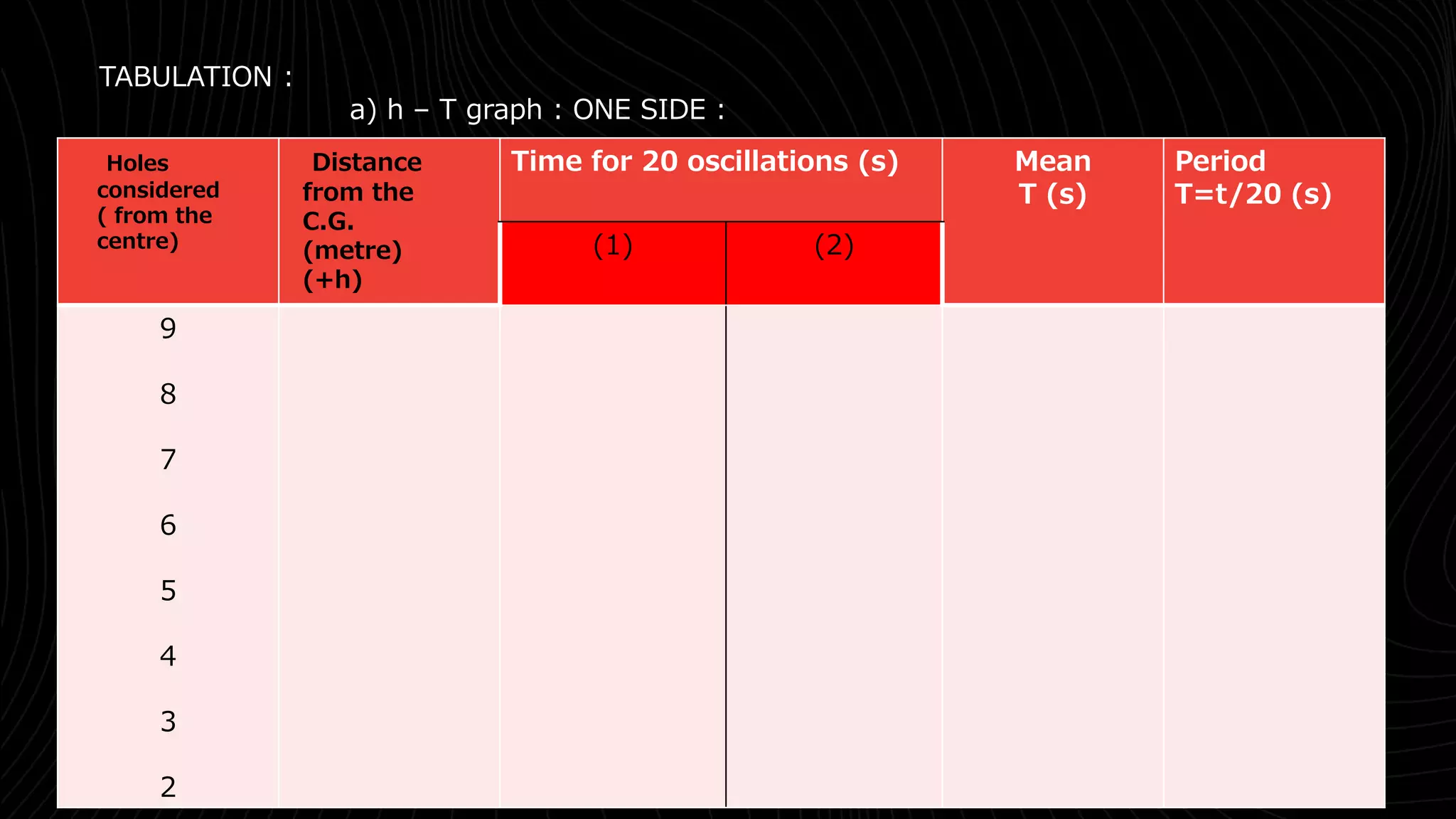
PROCEDURE:
The pendulum is suspended about a horizontal axis passing through the
9th hole from the center.
The distance h of the hole from the C.G. [ie.the central hole]
is measured .the pendulum is set into oscillation [small amplitude] and the
time for 20 oscilation is measured using a stop watch.from this period T ie the
time for one oscillation is found out.
This is reapeted for the different holes on either side of the center .the
acceleration due to gravity and radius of gyration can be determined by
two methods.
[a] h-T graph :
a graph is drawn taking T along Y axis and h along x axis . Two
symmetric curves as show in figure [b] are obtained .a straight line
ABCD is drawn parallel to X axis and L=AC+BD is calculated.if T is the period
corresponding to the line ABCD,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barpendlumexperimentppt-220705095820-2e4270f6/75/Bar-Pendulum-experiment-ppt-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![The calculation can be repeated by drawing other lines parallel to ABCD
The distance pq between the lowest points of the two curves is found out
The value of k by direct calculation
Where L is the length and B is the breadth of the bar
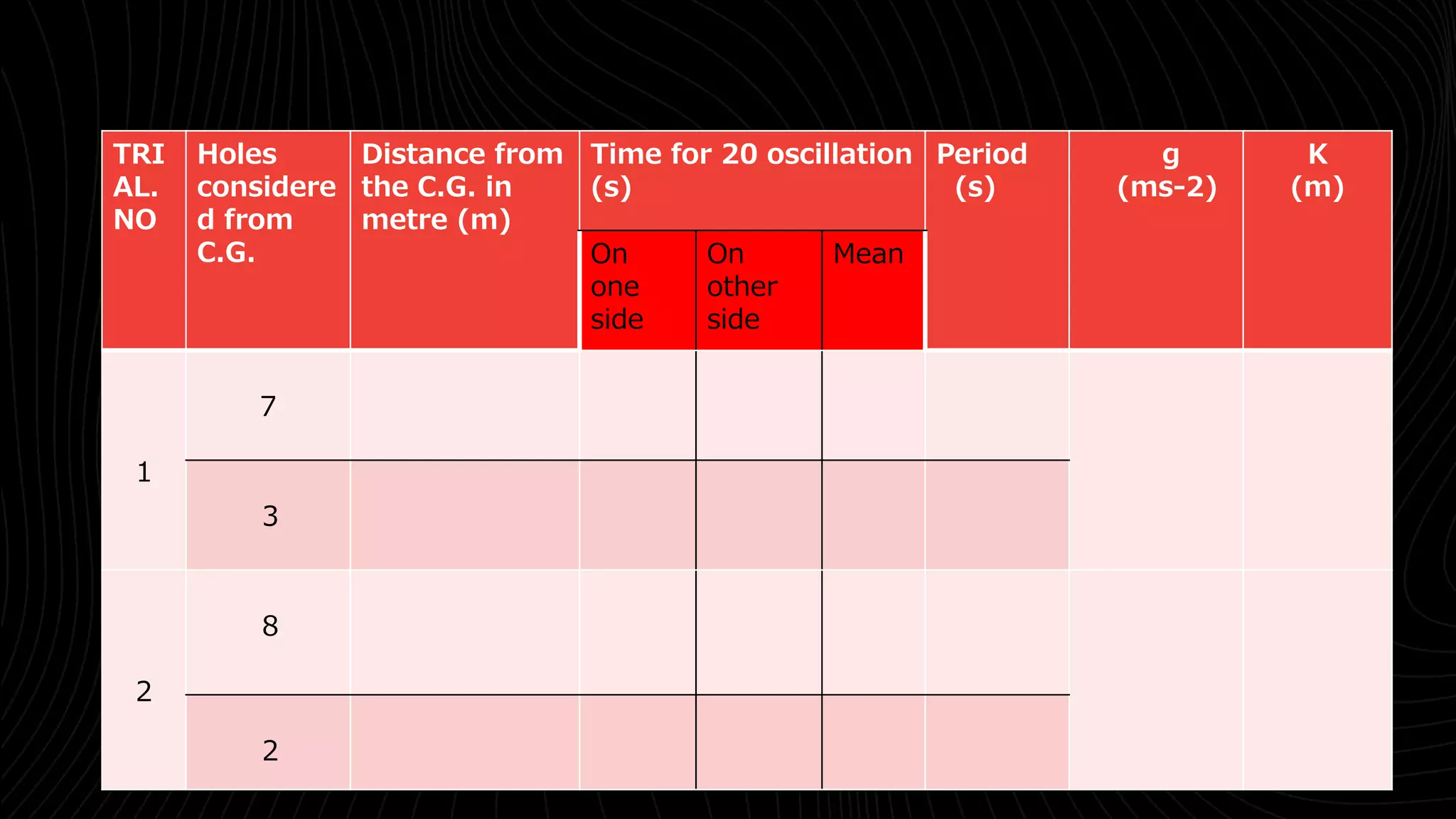
[b] Two-hole method:The periods T1 and T2 about any two holes [eg,,second and eighth or
third and seventh]are determined.The value of G and K are calculated using equations [3]
and [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barpendlumexperimentppt-220705095820-2e4270f6/75/Bar-Pendulum-experiment-ppt-pptx-8-2048.jpg)