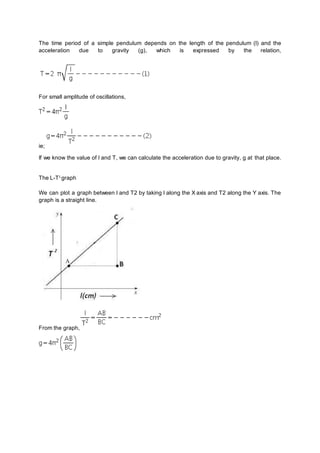
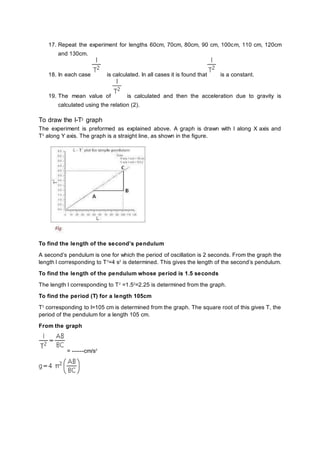
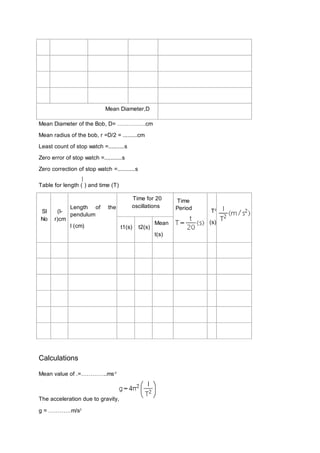
The document outlines the objectives and procedures for measuring the acceleration due to gravity using a simple pendulum. It details the theoretical background, necessary materials, and step-by-step instructions for conducting the experiment, including data collection and calculation of results. A graph of length versus time squared (l-t²) is also described to derive further insights about pendulum properties.