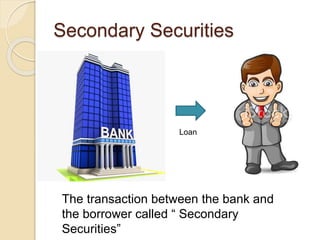
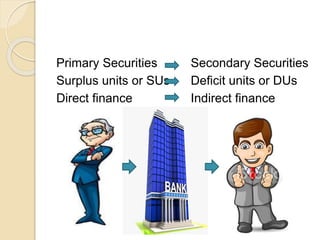
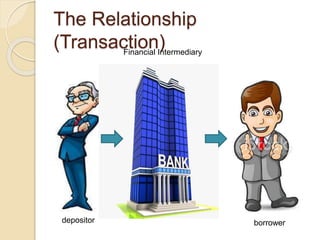
Banks act as financial intermediaries by bringing together depositors and borrowers. Depositors provide funds to banks through primary securities like deposits, and banks provide these funds to borrowers through secondary securities like loans. This allows for indirect finance between depositors and borrowers. As intermediaries, banks perform functions like risk transformation and matching deposit sizes with loan sizes. They also generate income by consolidating deposits and issuing loans. Common types of financial intermediaries include commercial banks, thrift banks, and depository institutions like savings banks.