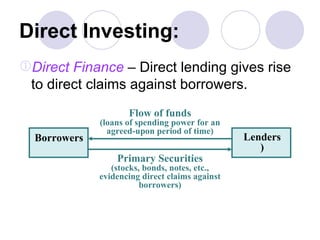
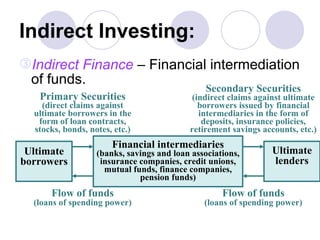
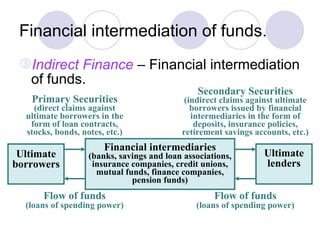
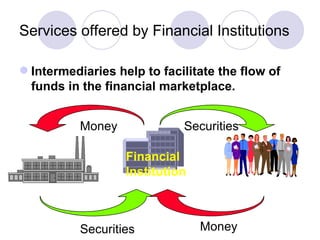
Financial markets allow for the exchange of funds between those who have savings (surplus units) and those who need funds for investment in real assets (deficit units). They do this through financial instruments that represent claims against issuers. There are two main types of financial markets - the money market for short-term instruments and the capital market for long-term debt and equity. Within each market, primary markets facilitate new issues while secondary markets allow for the exchange of existing securities. Financial intermediaries such as banks, insurance companies, and pension funds facilitate indirect finance by collecting funds through various financial claims and allocating them through purchases of direct claims.