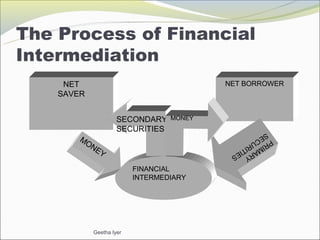
Financial intermediation is the process where financial intermediaries accept funds from savers and lend those funds to borrowers. This allows for maturity and liquidity transformation between net savers and net borrowers. Financial intermediaries are important as they are major providers of funds to borrowers compared to financial markets. Regulations aim to address moral hazard and curb excessive risk taking by intermediaries given the risks involved in financial services.