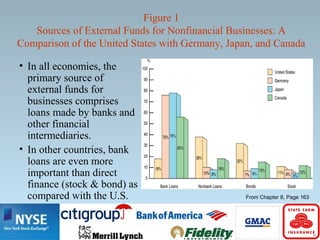
This document provides an overview of indirect finance (financial intermediation). It discusses how financial intermediaries transfer funds from lenders to borrowers through issuing their own IOUs to lenders and acquiring IOUs from borrowers. It then describes the key functions of financial intermediaries, including risk sharing, liquidity, and information services. Finally, it outlines the major types of financial intermediaries - depository institutions like banks, contractual savings institutions like insurance companies, and investment intermediaries.