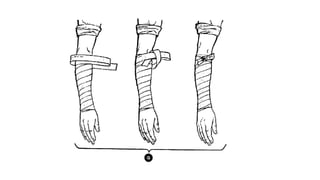
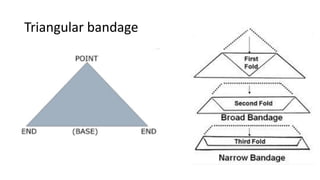
This document discusses various types of bandaging, splinting, and binders used to immobilize and support injured body parts. It describes different bandaging materials like gauze, muslin, and flannel and different types of bandages including triangular bandages, roller bandages, and tubular bandages. It outlines principles of bandaging like using proper size and material, positioning the patient comfortably, and avoiding pain or discomfort. Techniques for applying different types of roller bandages and fastening methods like knots and pins are also summarized. The document also discusses splinting principles like immobilizing the bone above and below fractures to prevent further damage.