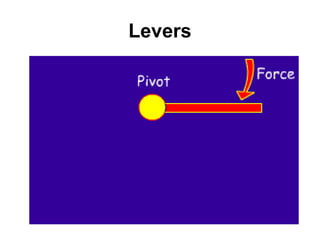
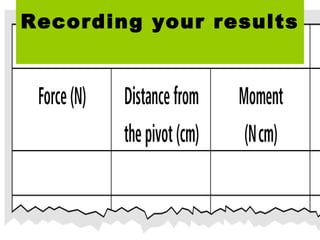
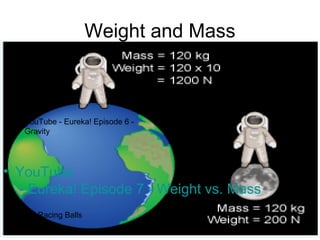
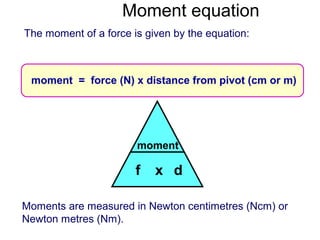
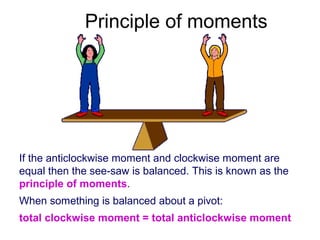
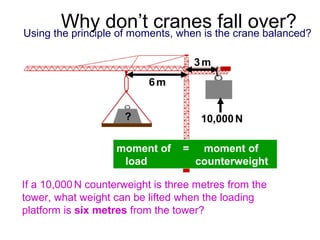
This document discusses levers and moments. It provides examples of levers in the body, such as bones and joints. It explains that the longer the lever, the bigger the force needed to move an object. It also discusses moments and how they are calculated by multiplying force by distance from the pivot. Examples are provided about balancing moments on a seesaw. The document also discusses how counterweights on cranes allow them to lift heavy loads by balancing the moments of the load and counterweight.