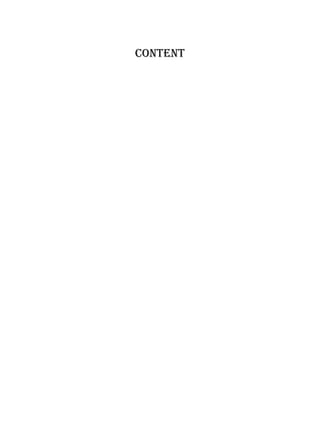
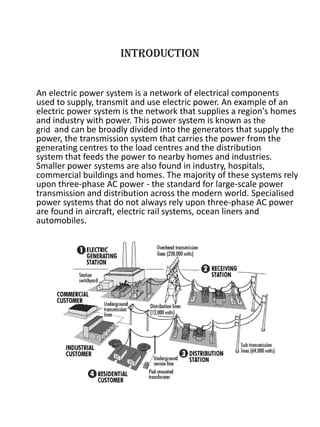
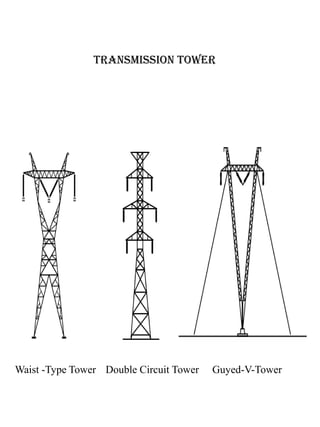
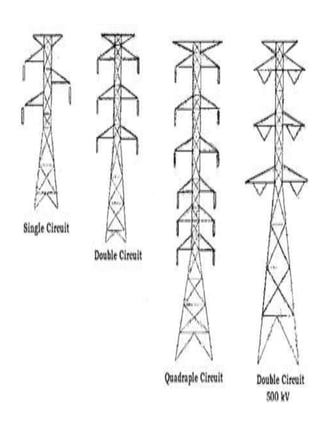
The document discusses the key components of an electric power system: electricity generation, which involves generating power from sources like combustion, nuclear fission, or renewable resources; transmission over high-voltage lines to transport power from generation centers to load centers; and distribution through lower voltage lines to deliver power to homes and businesses. It also briefly describes different types of transmission towers and substations that facilitate moving power through the system.