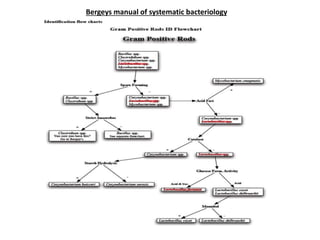
This study evaluated the antimicrobial activity of bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus isolated from curd samples against common pathogens. Lactobacillus strains were isolated from curd using MRS media and identified through morphological and biochemical tests. The isolates were screened for bacteriocin production using agar well diffusion assay against E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Clear inhibition zones were observed around the wells containing supernatant from Lactobacillus cultures, indicating they produced bacteriocin with antimicrobial activity against the test pathogens. This demonstrates the potential of using bacteriocin from Lactobacillus as natural preservatives.