Embed presentation
Downloaded 96 times
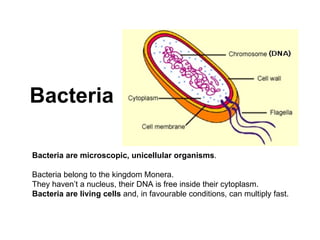
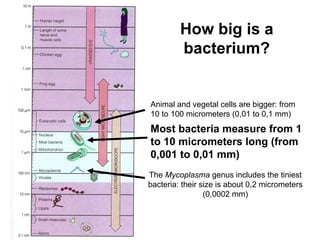
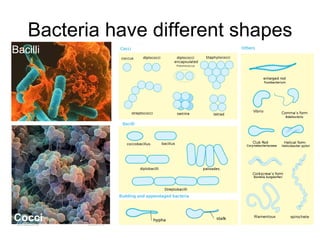

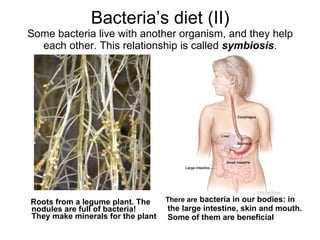
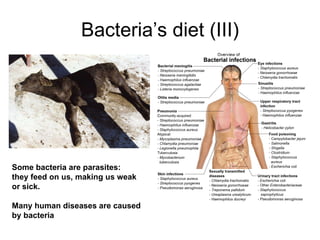

Bacteria are unicellular organisms belonging to the kingdom Monera, lacking a nucleus and capable of rapid multiplication under favorable conditions. They vary in size from 0.2 to 10 micrometers and can have different diets including saprophytic, symbiotic, or parasitic relationships. Cyanobacteria, an older life form, perform photosynthesis and contribute to aquatic ecosystems.






