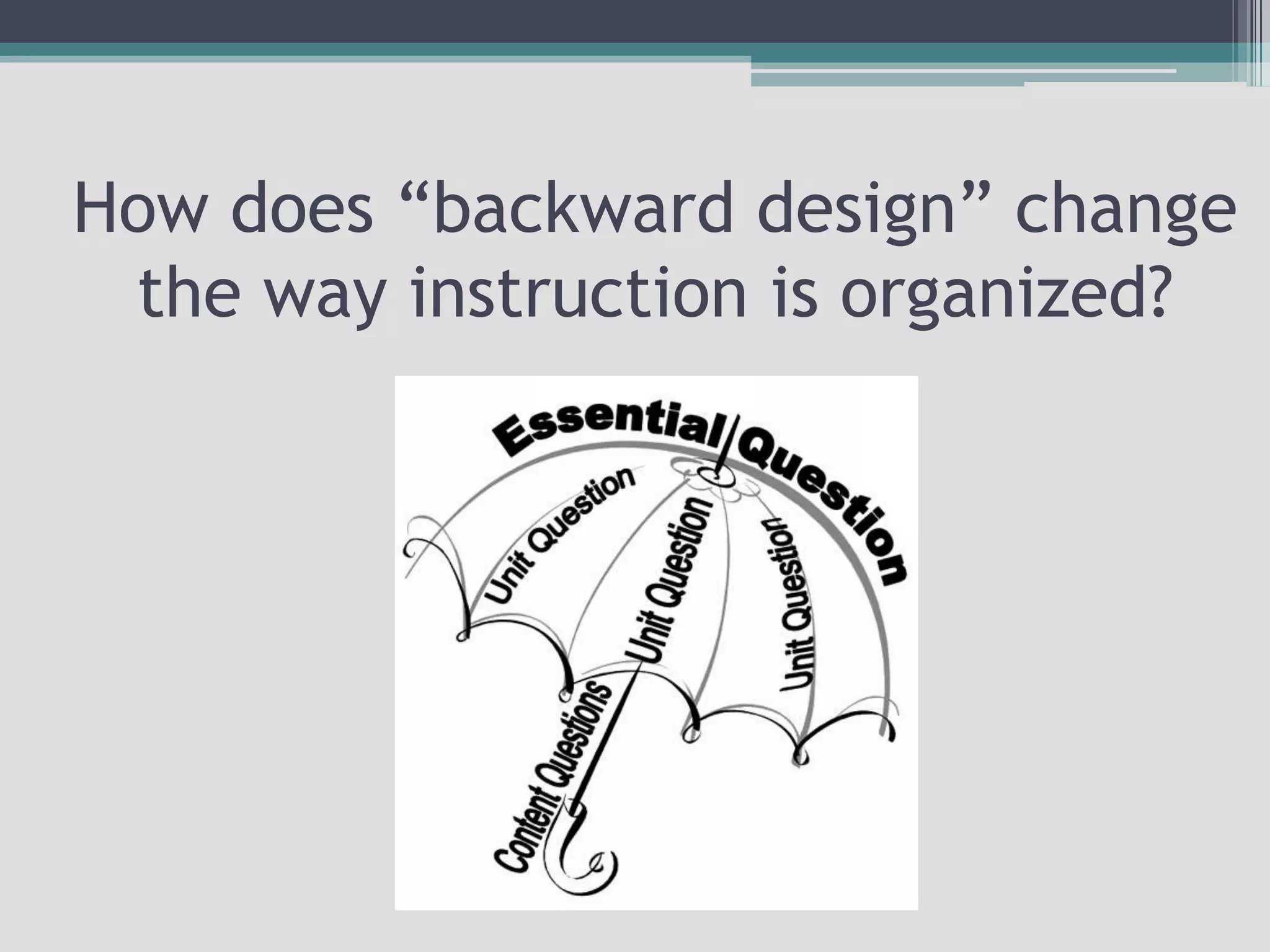
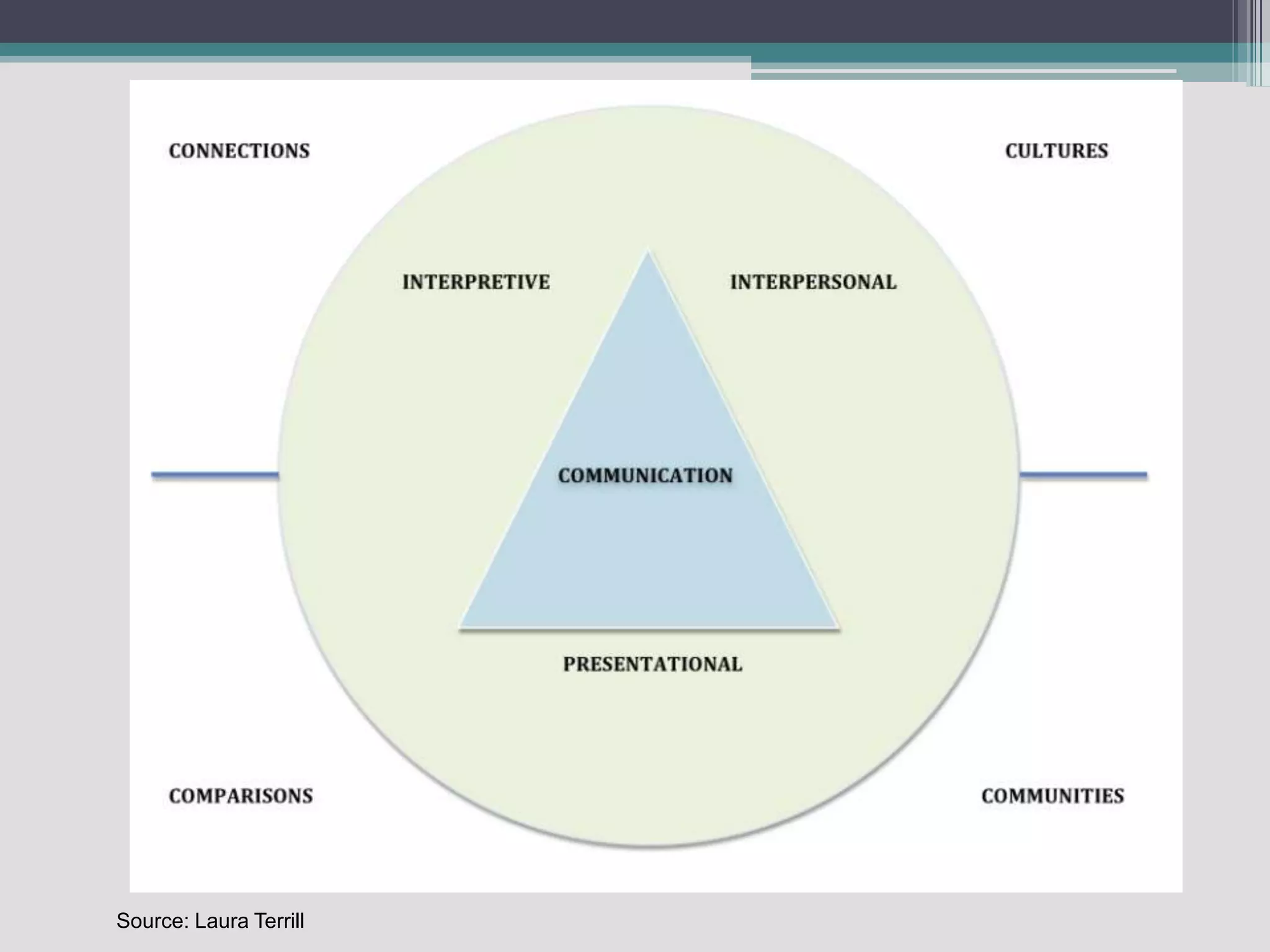
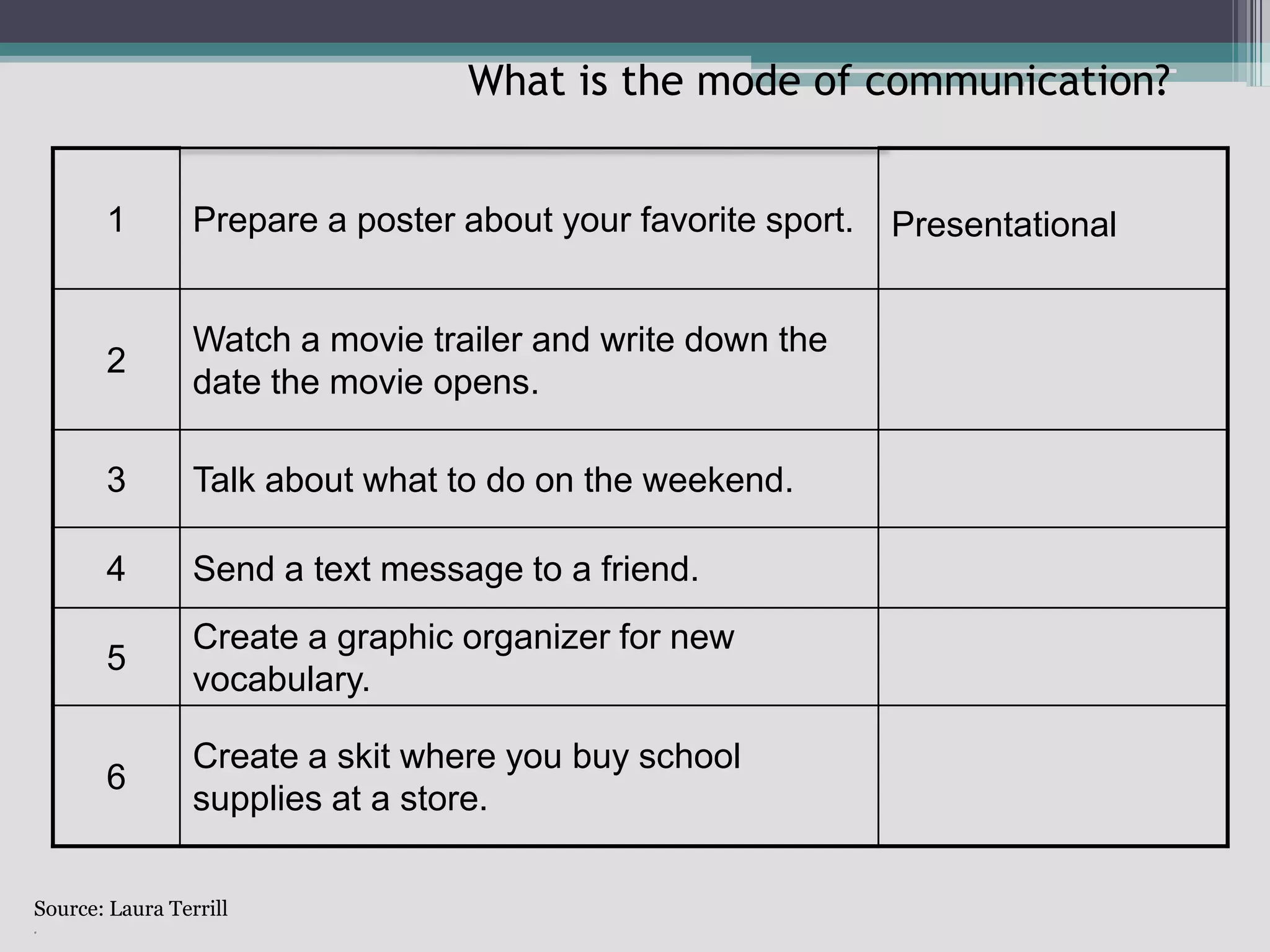
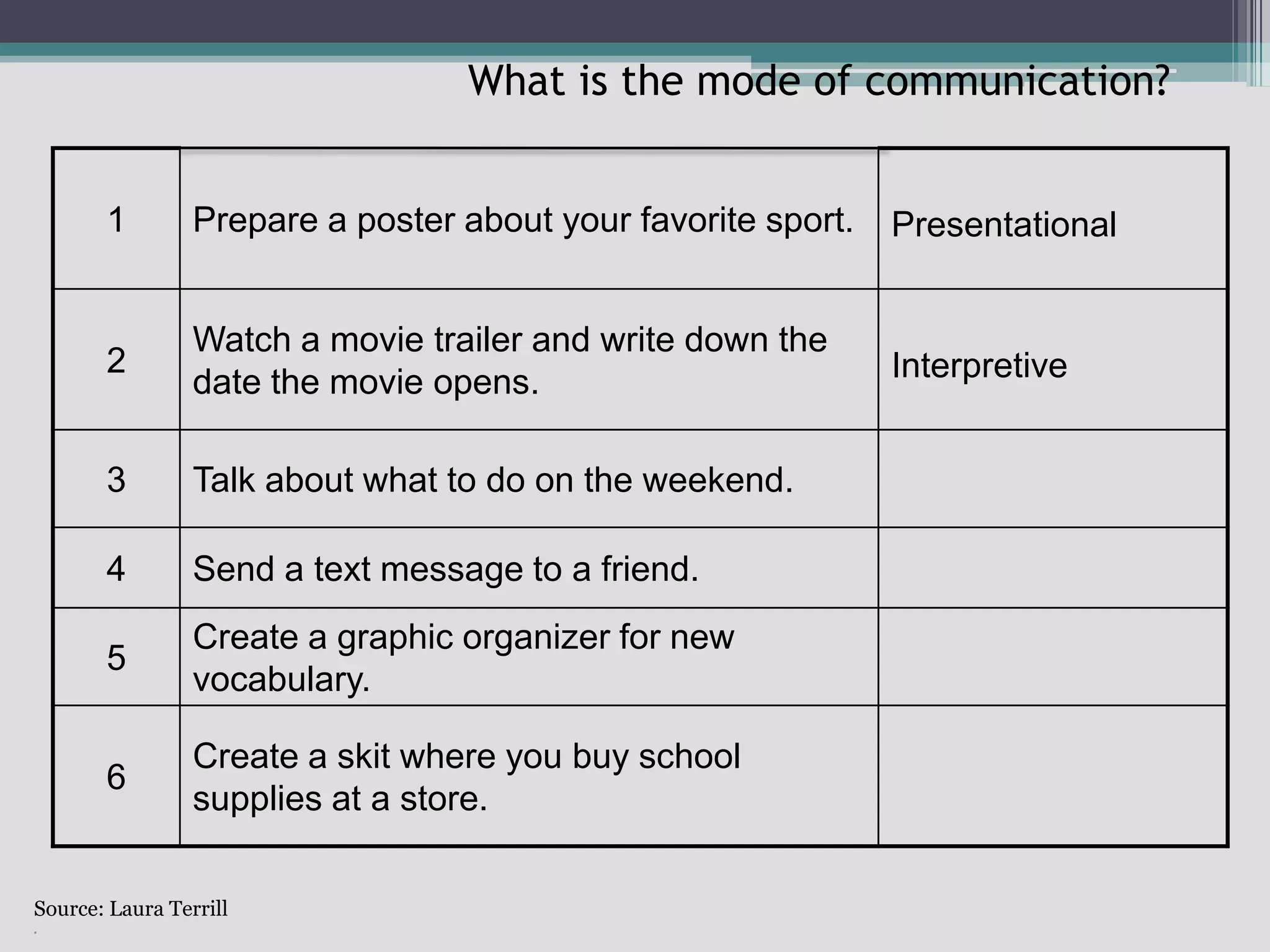
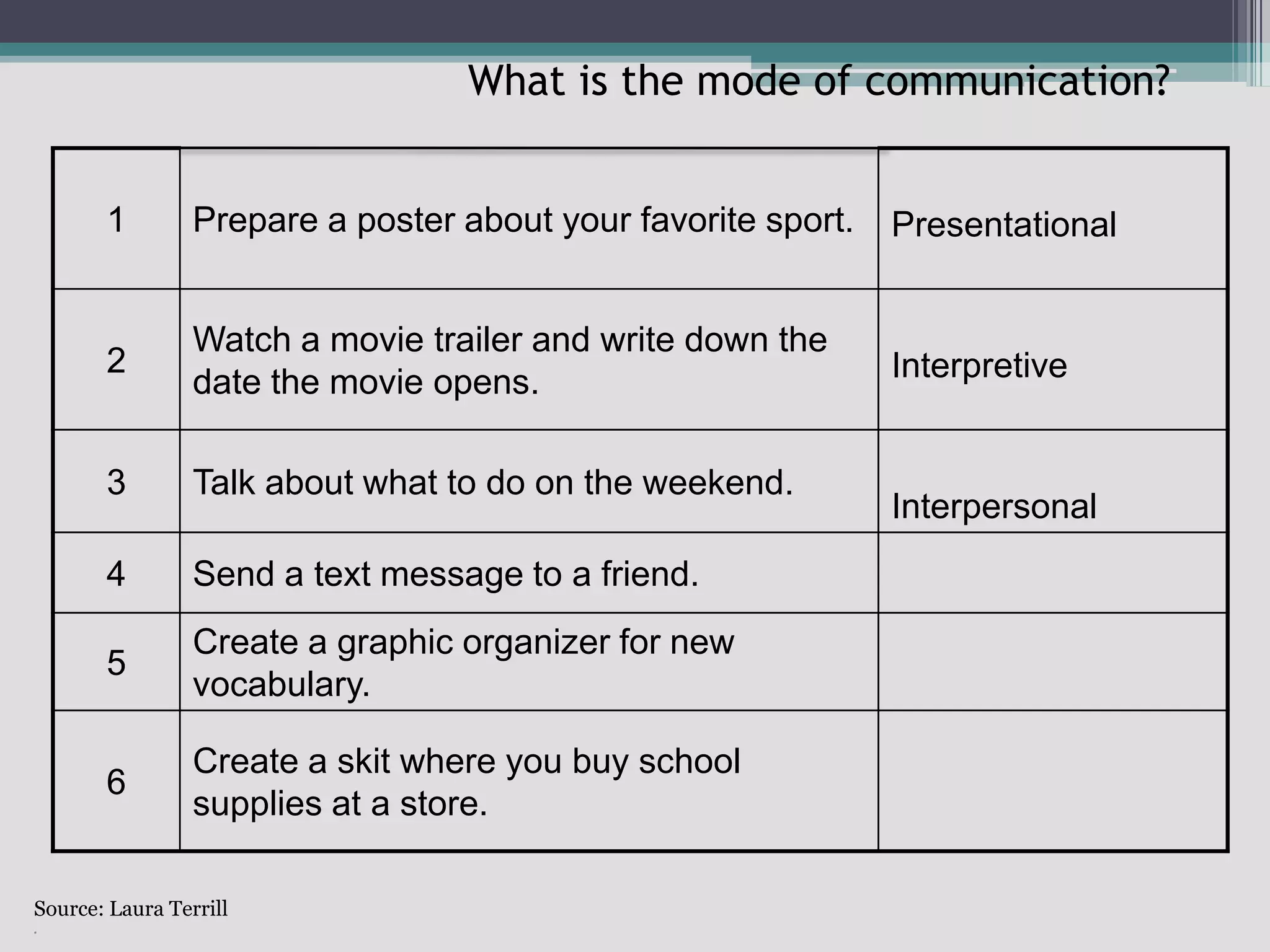
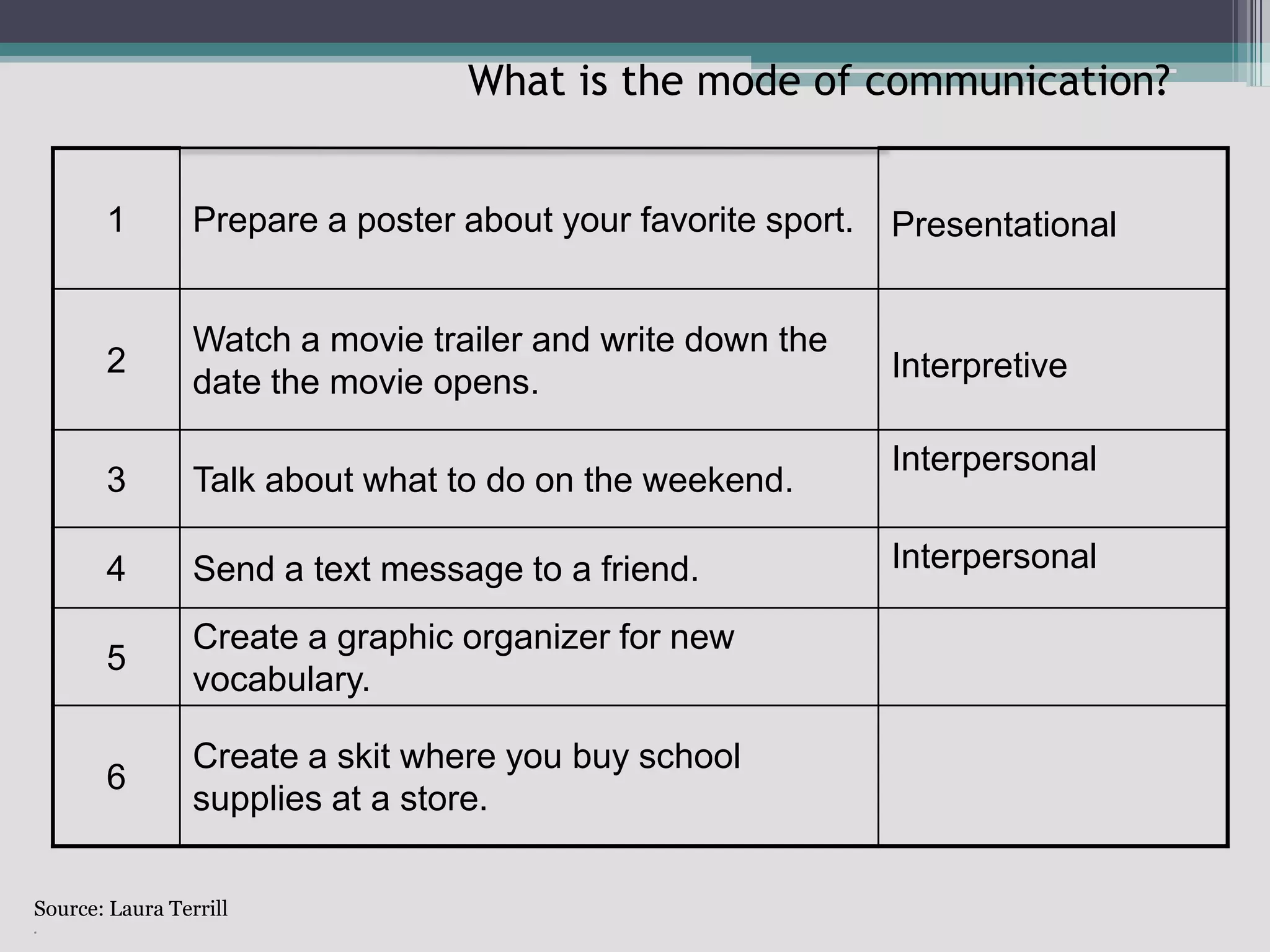
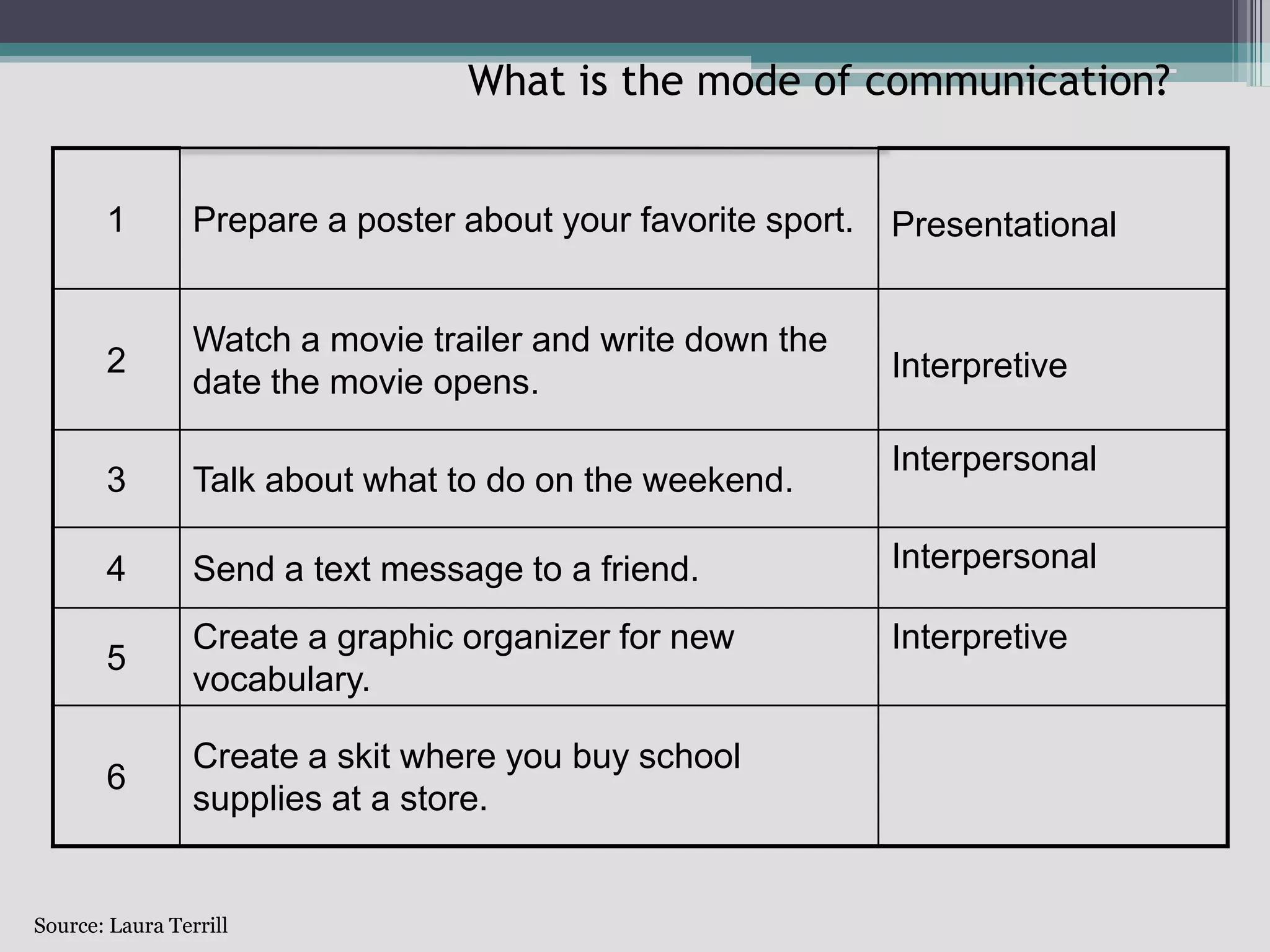
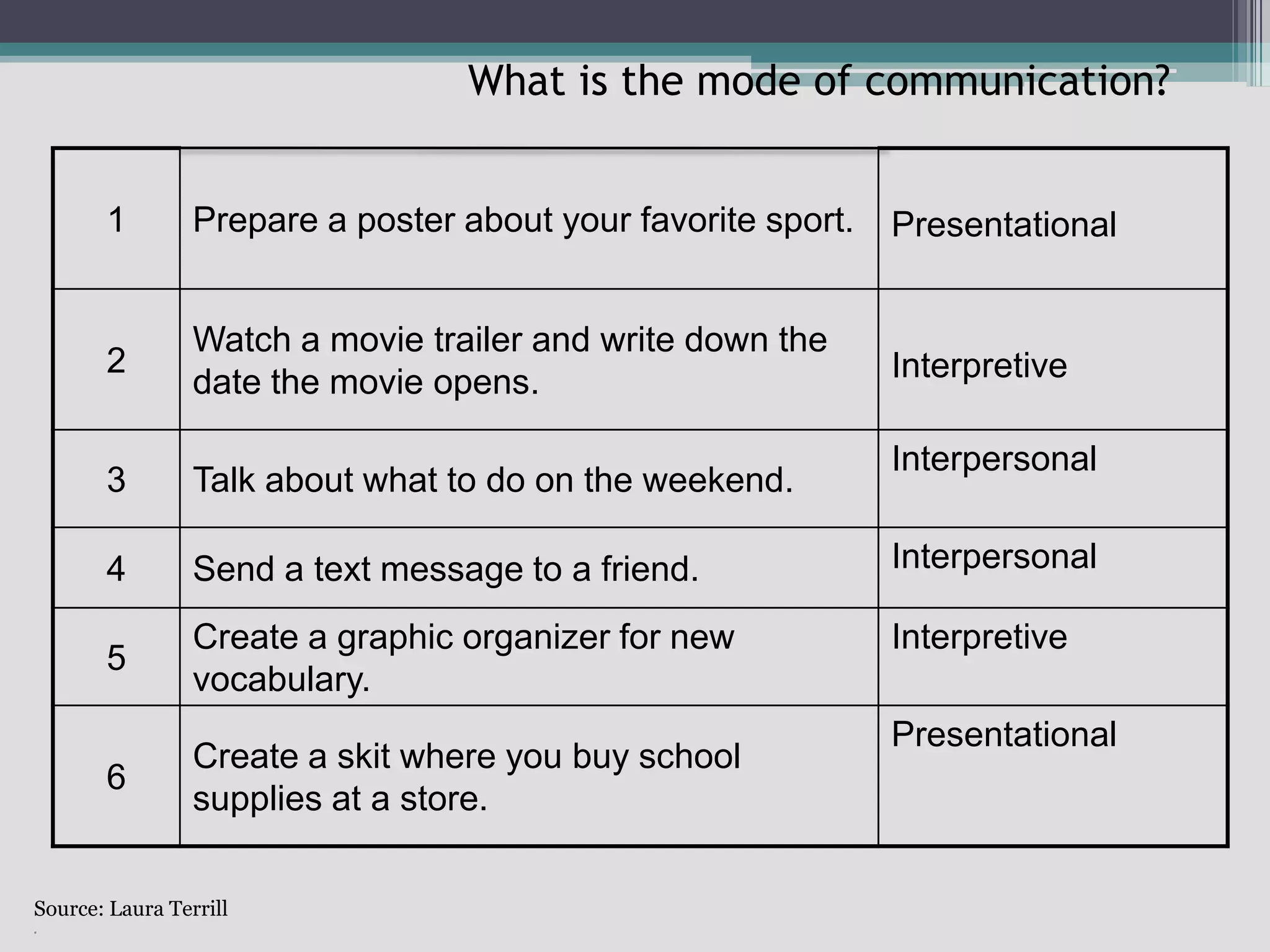
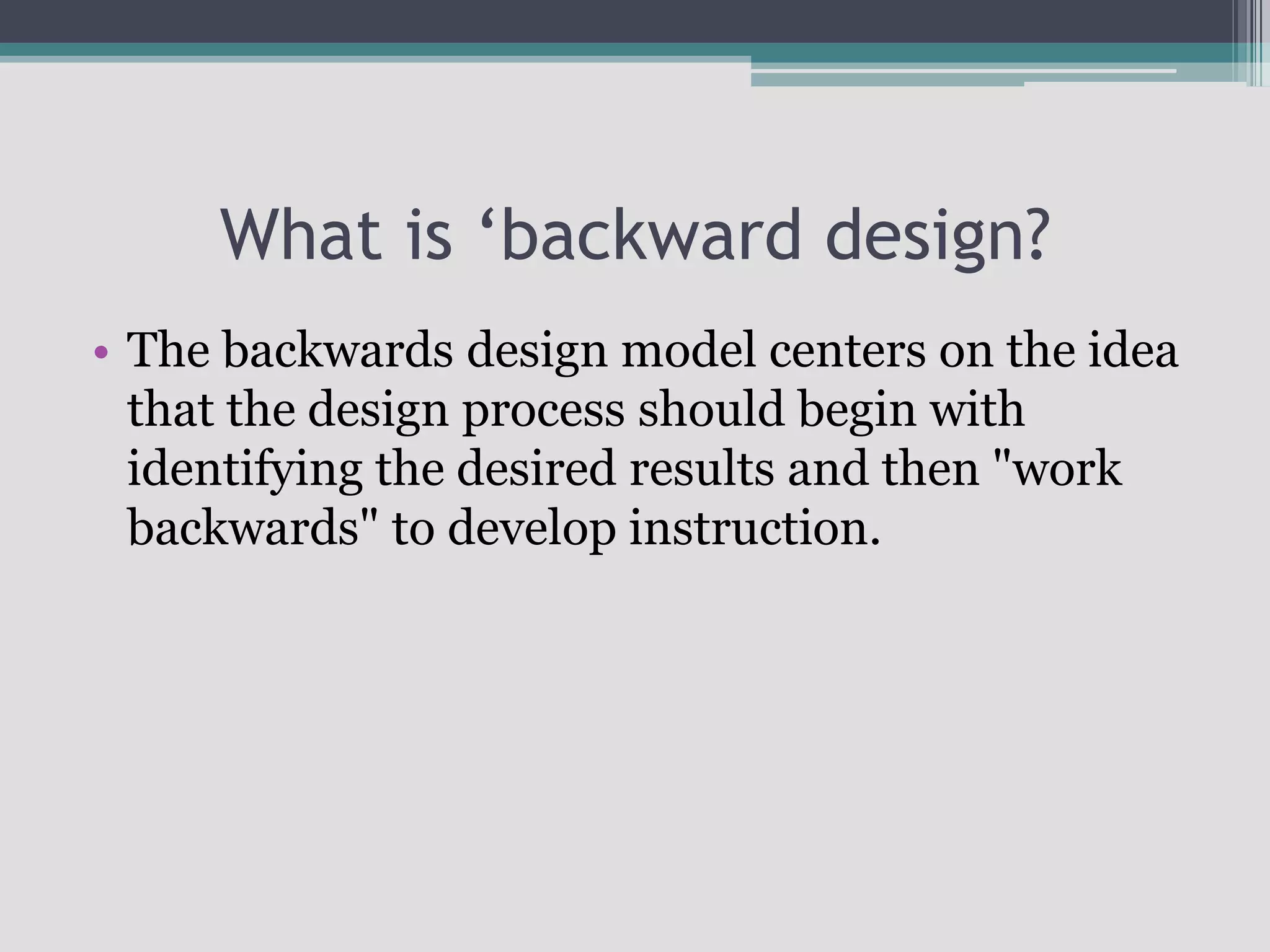
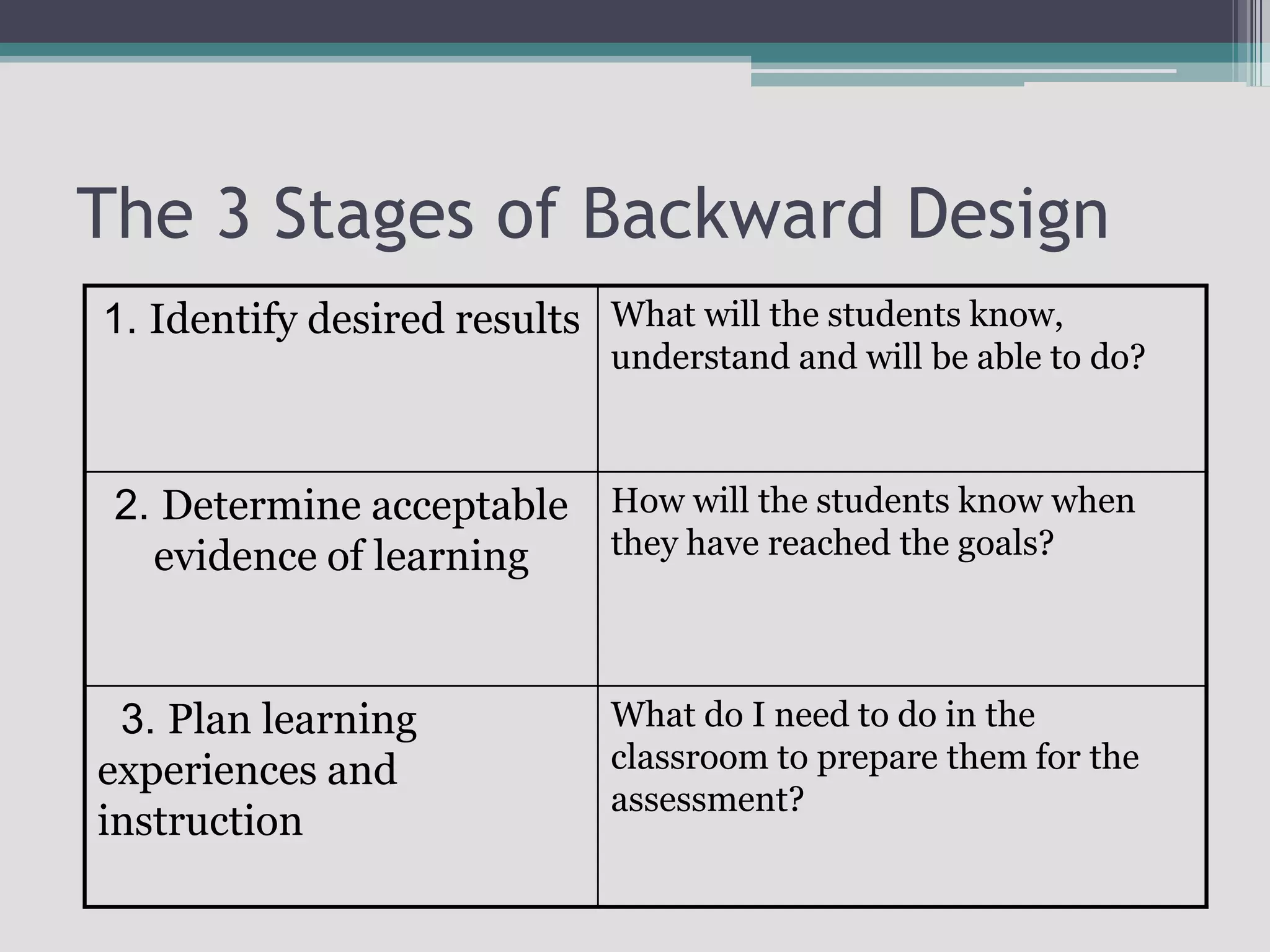
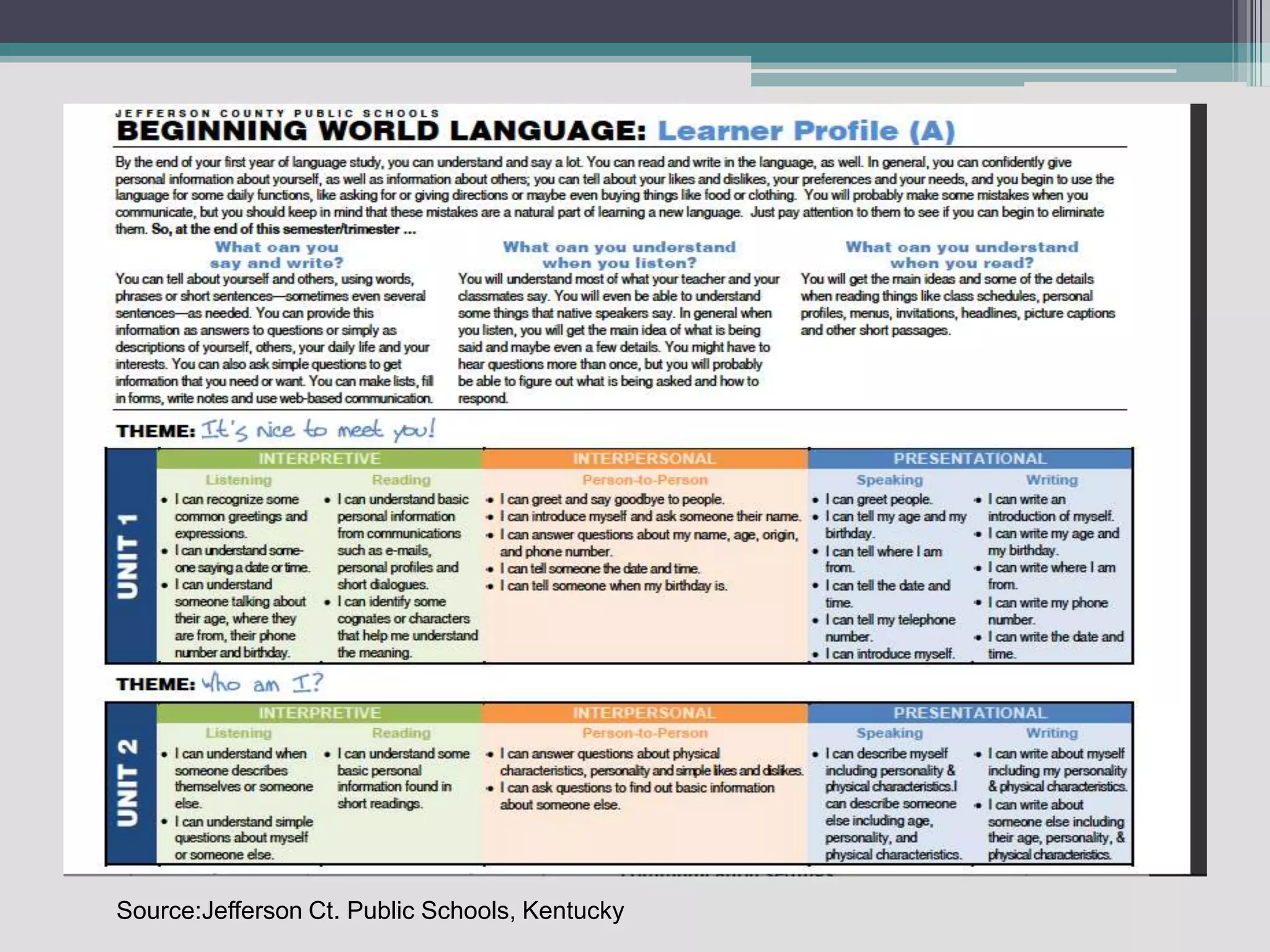
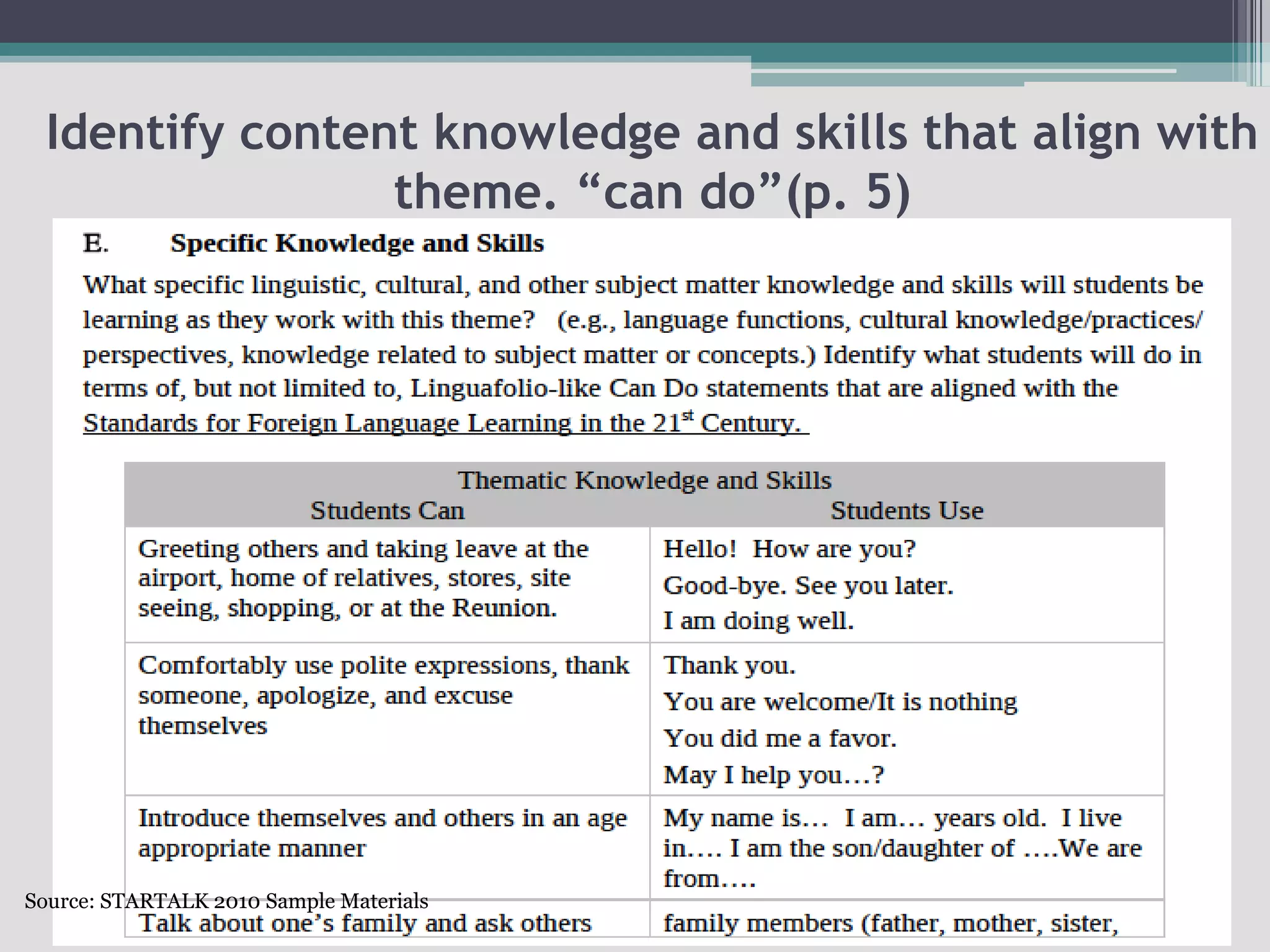
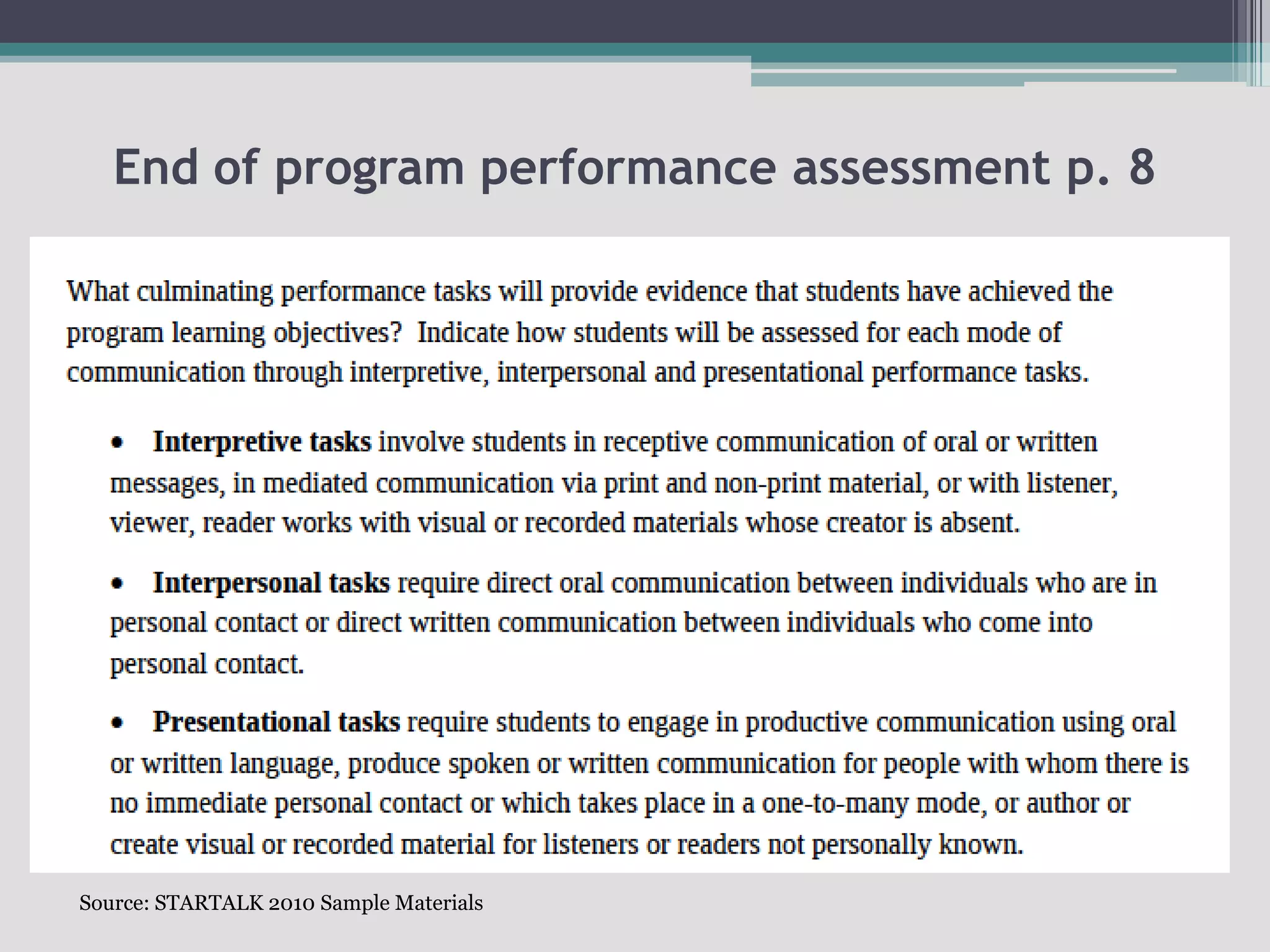
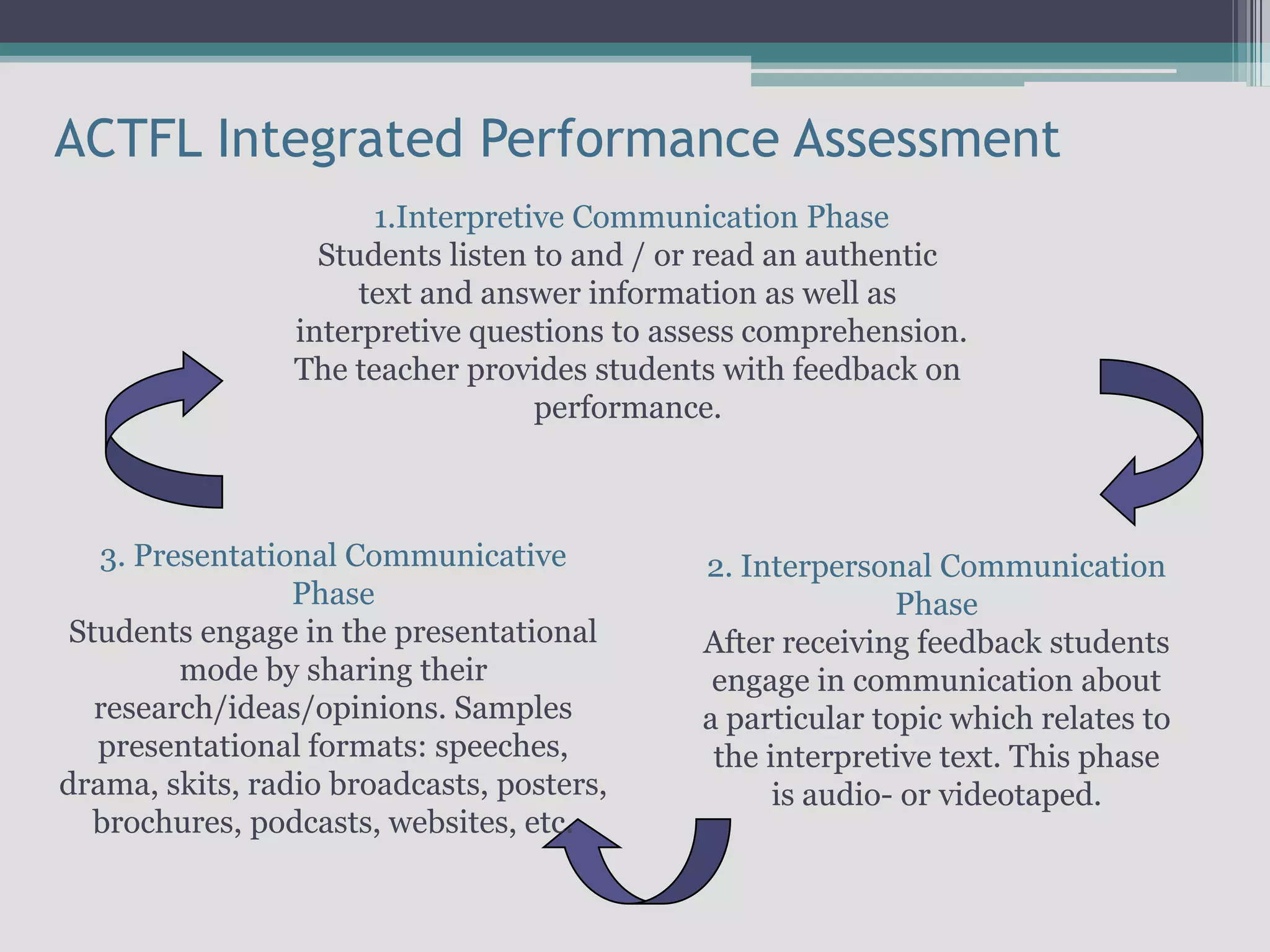
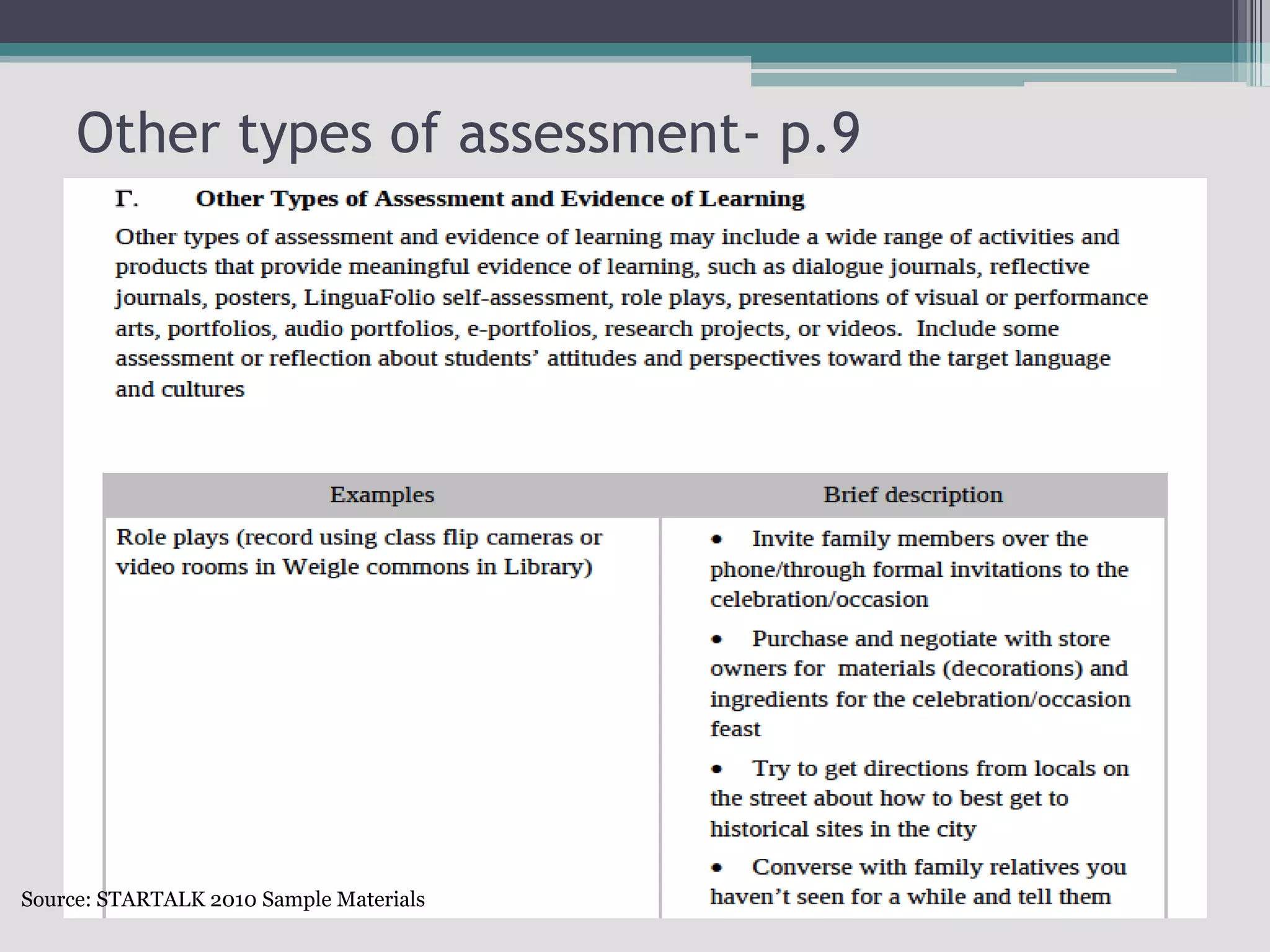
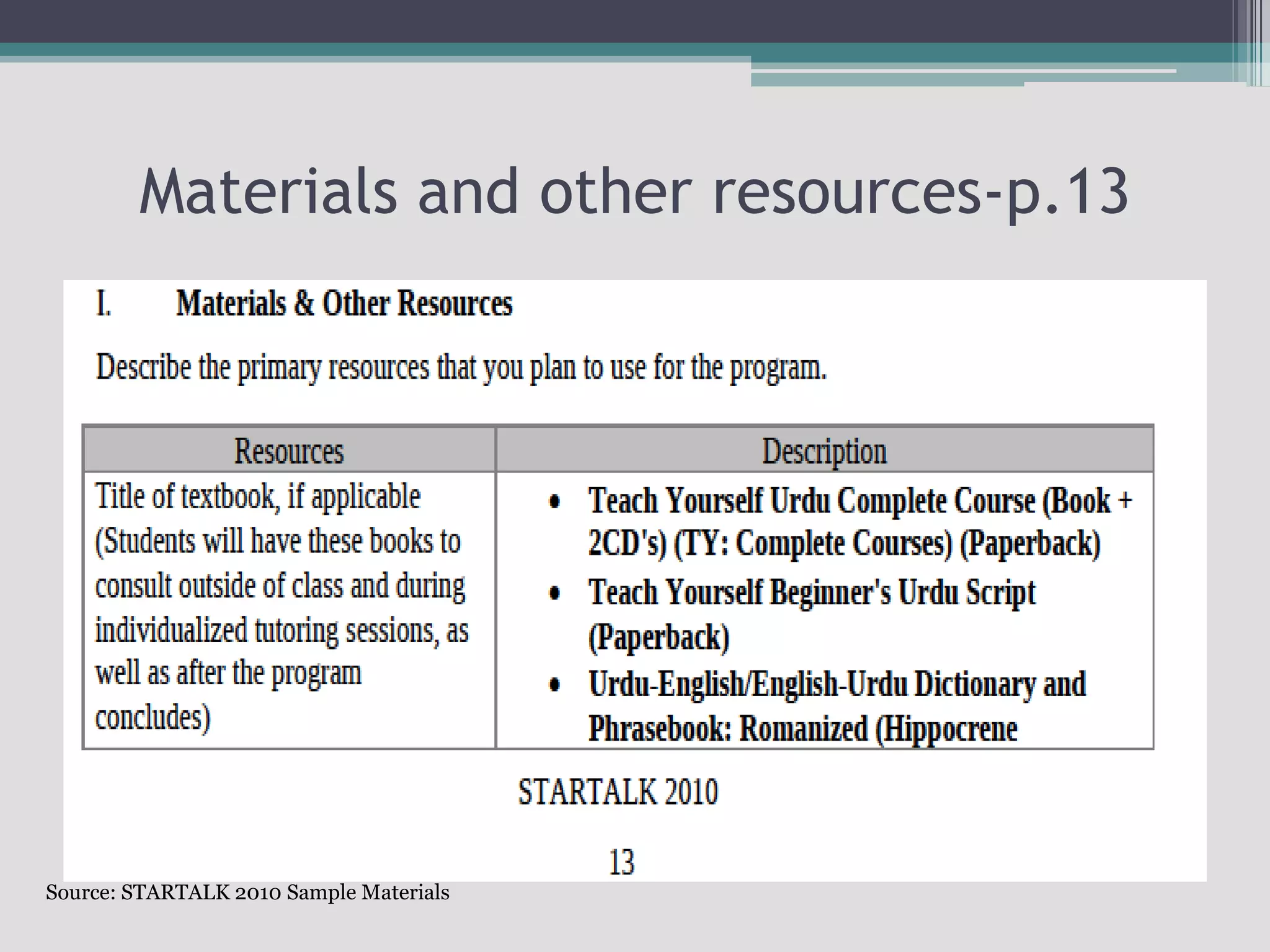
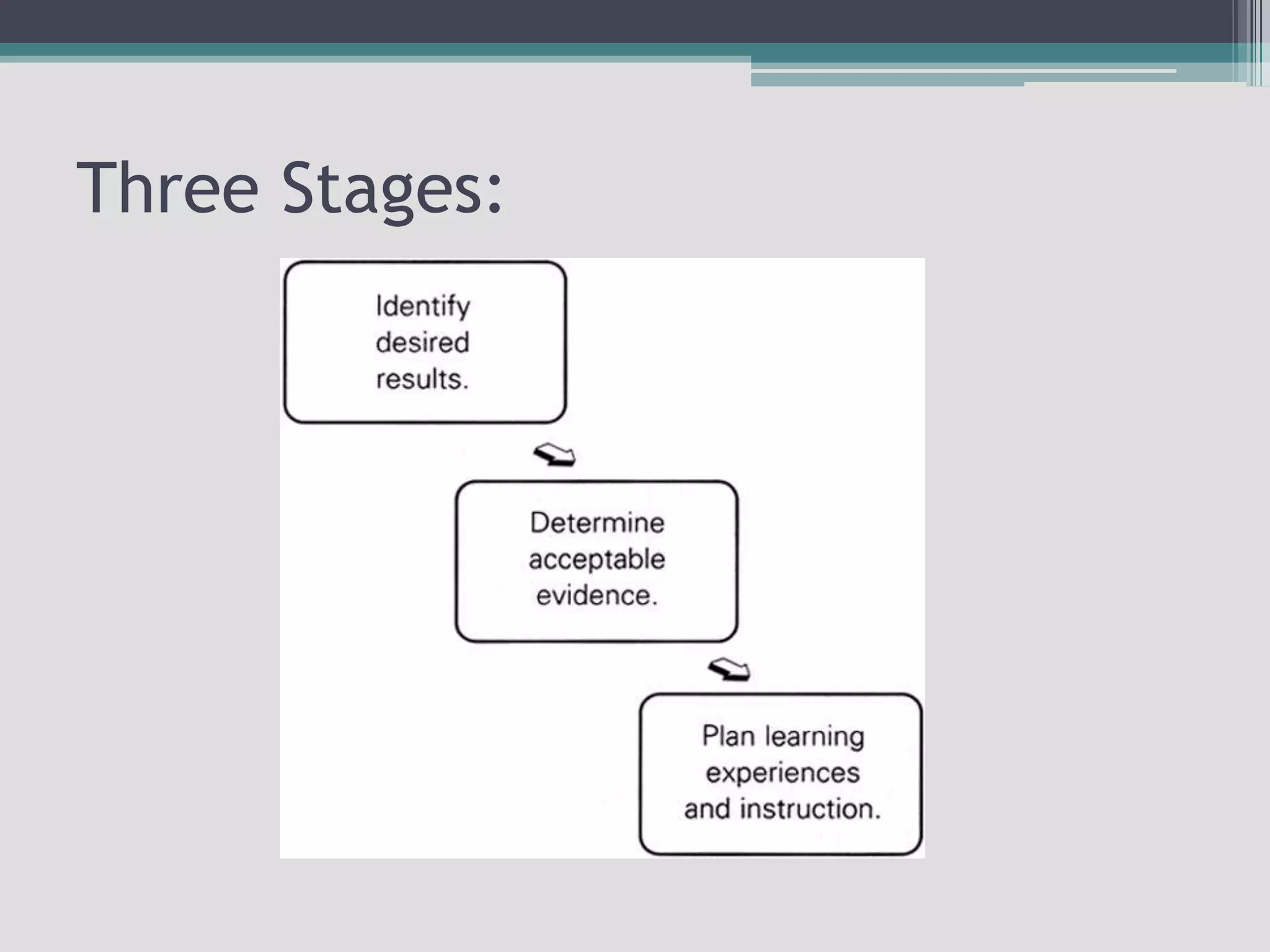
The document discusses the principles of backward design for creating student-centered thematic units. Backward design is a framework that involves starting with the desired learning outcomes and goals, then designing assessments to measure those outcomes, and finally developing instructional activities to help students achieve the outcomes. The document provides information on the three stages of backward design: 1) identifying desired results like standards and objectives, 2) determining acceptable evidence of student learning through assessment, and 3) developing learning plans and instruction. It also discusses how to design thematic units around key concepts and aligned assessments using this approach.