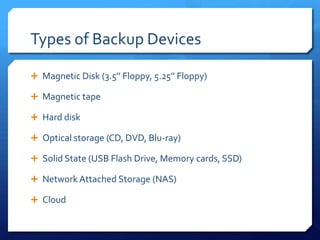
This document discusses different types of backup storage devices. It defines backup as copying computer data so it can be restored after data loss. There are three main types of backups: full, containing complete system images; incremental, saving changes since the last full or incremental backup; and differential, saving changes since the last full backup. Common backup storage devices include magnetic disks, tapes, hard disks, optical discs, solid state drives, network attached storage, and cloud storage. These devices differ in terms of capacity, cost, transfer speeds, security, and portability.