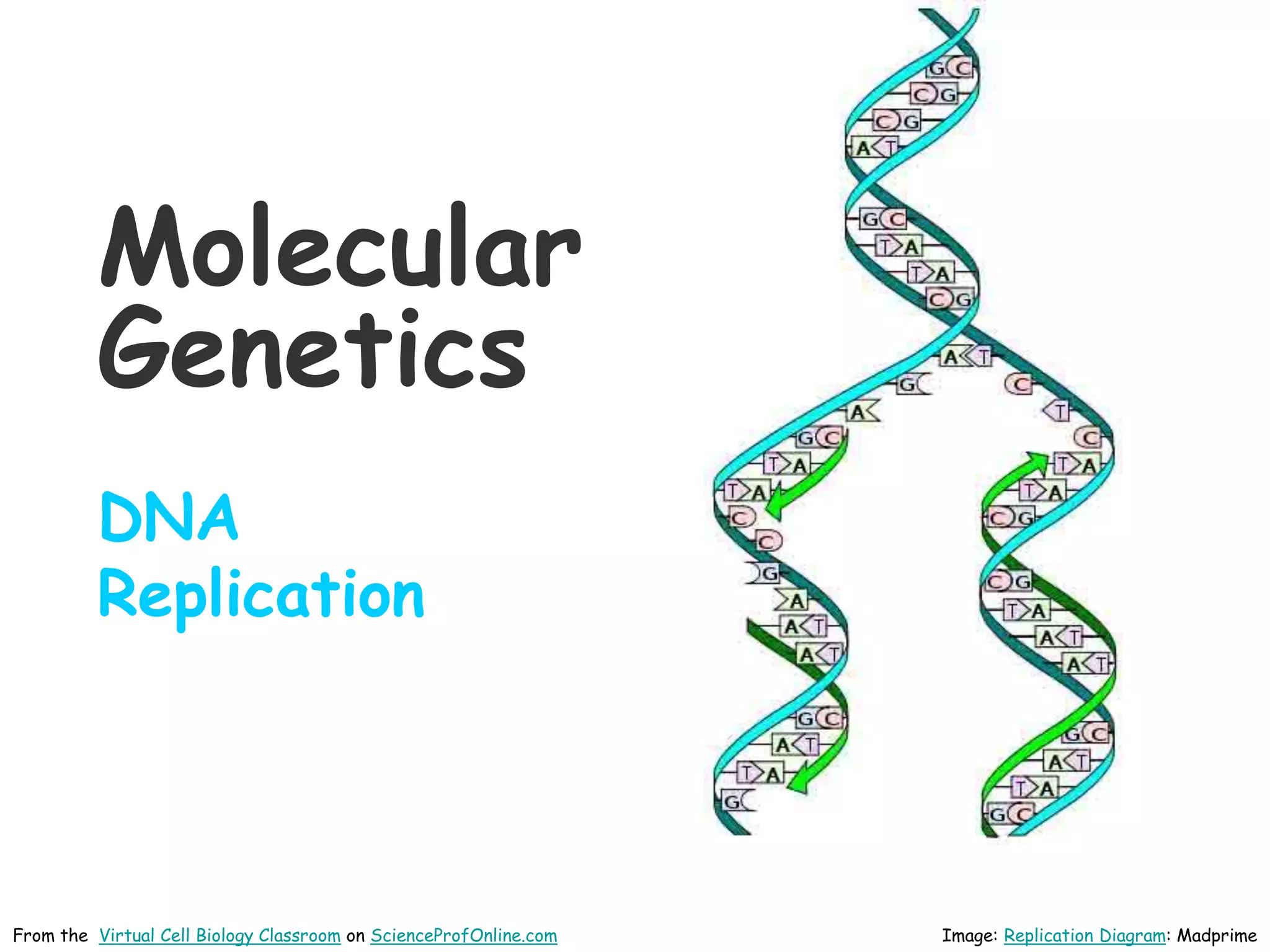
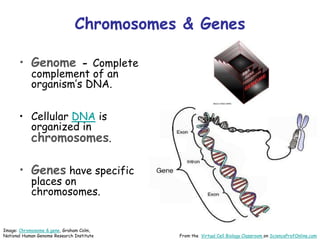
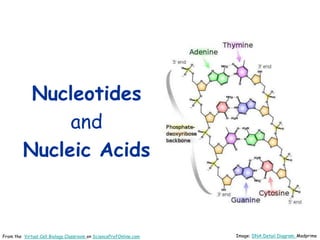
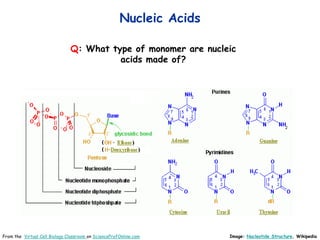
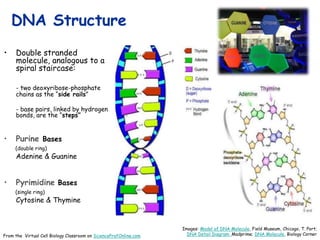
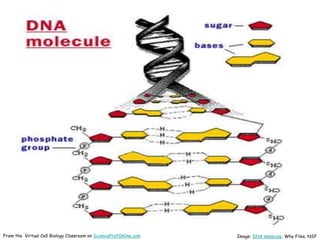
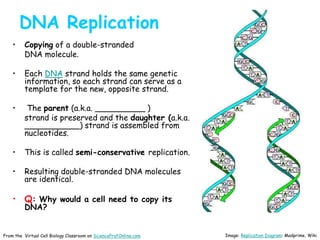
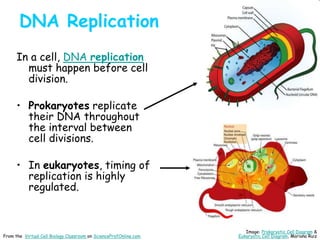
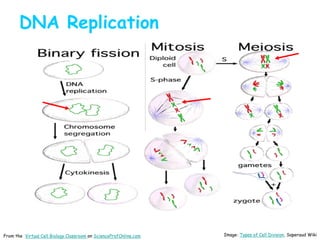
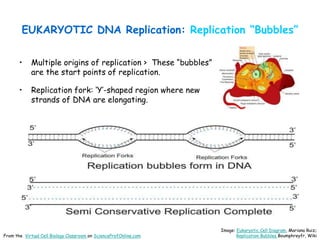
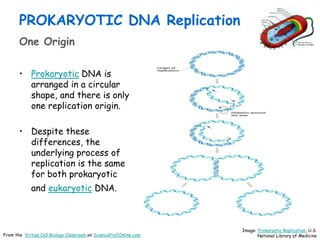
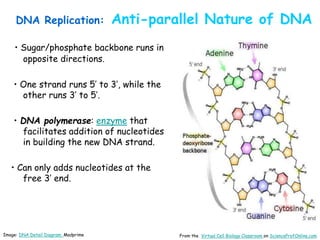
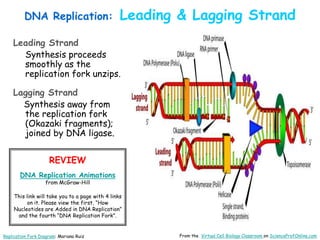
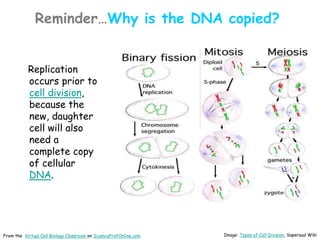
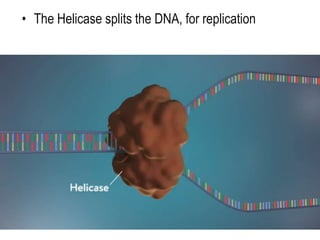
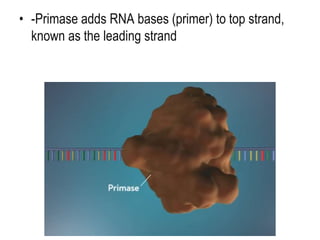
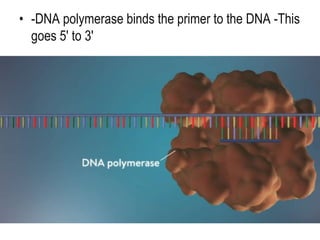
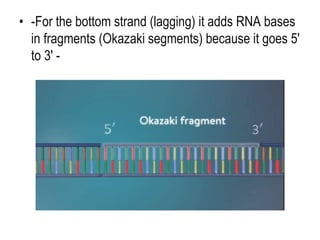
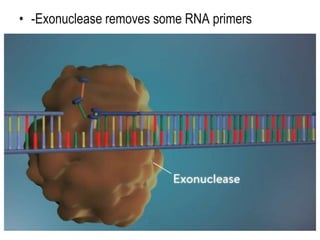
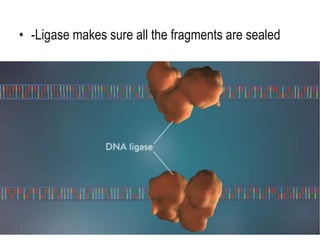
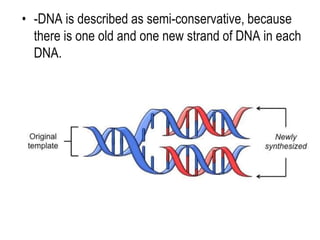
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. It involves unwinding the DNA double helix at the replication fork and using each original strand as a template to synthesize new partner strands. On the leading strand, DNA polymerase moves continuously to add nucleotides, while on the lagging strand it adds fragments called Okazaki fragments that are later joined together. This semi-conservative process ensures that each new cell has an exact copy of the original DNA.