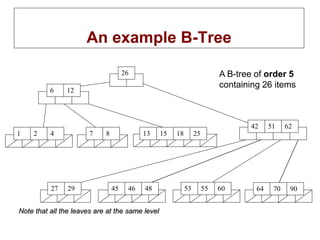
The document defines and provides an example of a B-tree, which is a tree data structure used to store sorted data. It then walks through constructing a B-tree of order 5 by inserting keys in order. The keys are inserted into leaf nodes, and if a leaf becomes too full, it is split and the middle key is promoted. This may cause parent nodes to split as well, all the way up to the root. The root will also split if needed, increasing the height of the tree. The document concludes by listing keys to insert into an empty B-tree as an exercise.