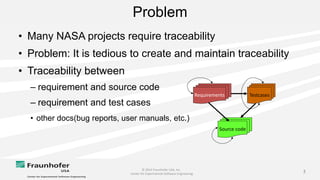
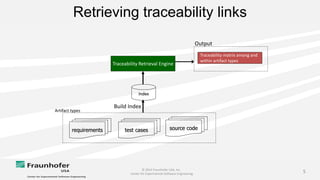
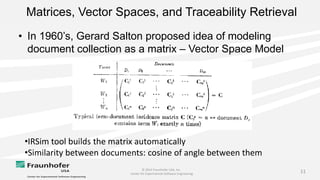
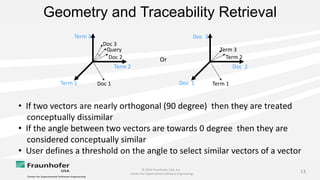
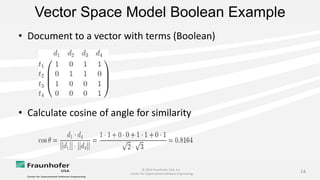
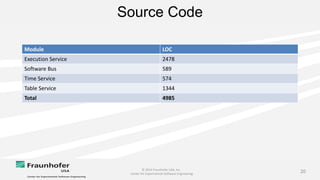
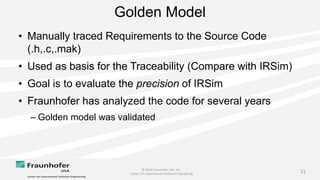
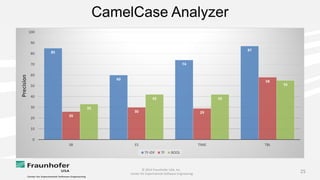
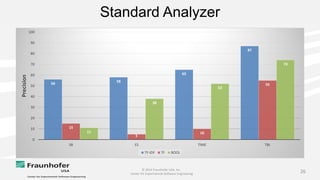
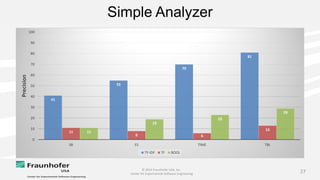
The document discusses the challenges of maintaining traceability in NASA projects and introduces the IR-SIM tool designed to automate this process by generating traceability links between requirements, source code, and test cases. A preliminary empirical study was conducted using NASA's Core Flight Software to evaluate the tool's effectiveness, with results indicating that a combination of CamelCase and TF-IDF parsing strategies yielded the best precision in tracing. The study emphasizes the need for further validation across different systems and addresses potential issues affecting traceability accuracy.