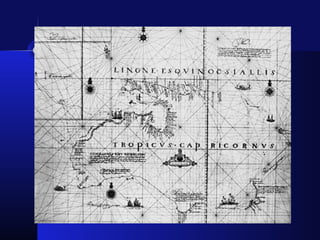
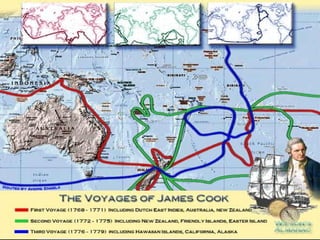
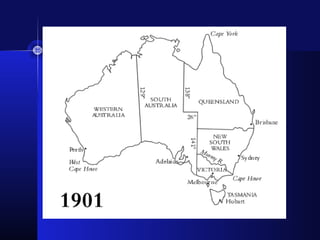
The Dutch were the first Europeans to explore Australia in 1606 but did not establish settlements. In 1770, Captain Cook claimed Australia for Britain and mapped parts of the eastern coast. In 1787, the British began transporting convicts to Australia to establish a penal colony in New South Wales. Throughout the 1800s, Britain continued sending convicts to Australian penal colonies while also allowing free settlers to establish farms and businesses. In 1901, the British colonies in Australia formed the self-governing Commonwealth of Australia.