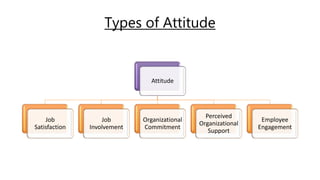
The document discusses the concept of attitude in psychology, defining it as a collection of emotions, beliefs, and behaviors toward various subjects. It categorizes attitudes into negative and positive types and explores different expressions of job-related attitudes, including job satisfaction, job involvement, organizational commitment, perceived organizational support, and employee engagement. The discussion highlights how these attitudes affect individual behavior and organizational dynamics.