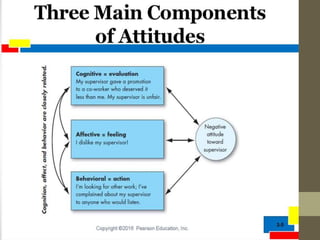
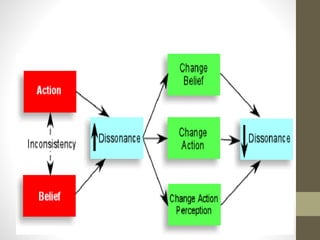
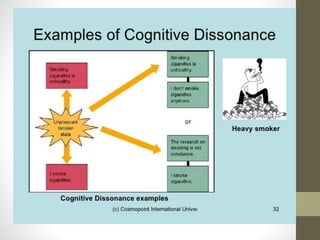
This document defines attitudes and describes the ABC model of attitudes. It discusses how attitudes are formed through direct contact, instruction, interaction with others, and observational learning. Attitude change can occur through persuasion or cognitive dissonance. Persuasion involves the source, message, and target audience, while cognitive dissonance is an inconsistency between cognitions and behaviors that causes tension motivating change.