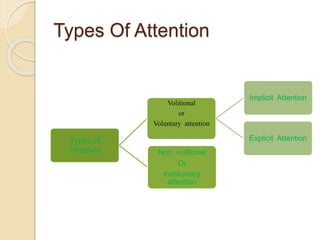
Attention is the focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus while ignoring others. It is a selective mental process where an individual chooses a stimulus according to their interests and attitudes from multiple environmental stimuli. Attention can be voluntary, requiring conscious effort, or involuntary, occurring without effort. Voluntary attention includes implicit attention from a single willful act and explicit attention requiring repeated willful acts. Involuntary attention is aroused without conscious effort. Factors influencing attention include external stimuli characteristics like size, intensity, movement, and internal factors like interests, habits, emotions, and past experiences.