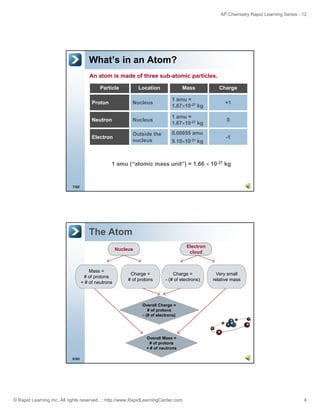
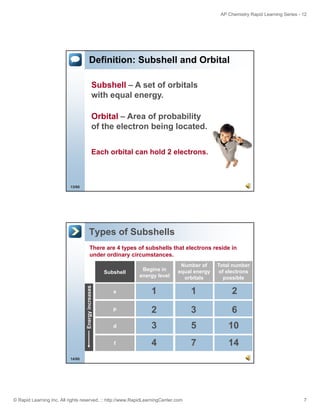
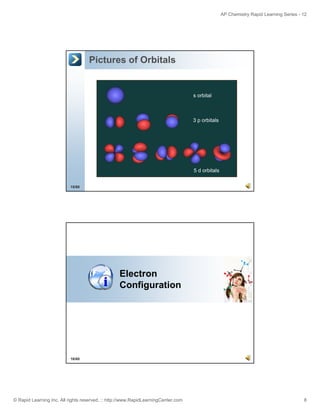
The document is an introduction to atomic structure and electron configurations from the Rapid Learning Center's AP Chemistry series. It begins by defining atoms and their subatomic particles. It then explains how electrons are arranged in energy levels, subshells, and orbitals. The three main rules for determining electron configurations are also introduced: Aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and Pauli exclusion principle. Examples are provided of writing electron configurations using boxes and arrows notation as well as spectroscopic notation. Relationships between electron configurations and the periodic table are also discussed. Finally, the document briefly covers how ions form full valence shells in their electron configurations.












![AP Chemistry Rapid Learning Series - 12
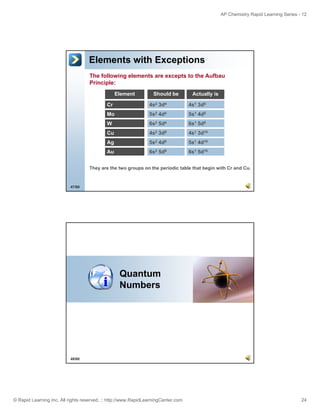
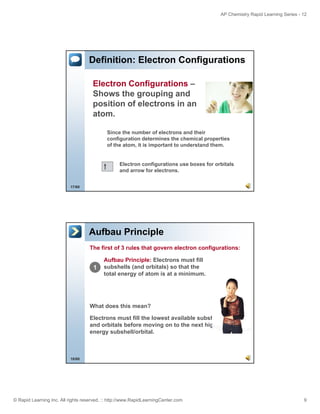
Definition: Noble Gas Notation
Noble Gas – Group 8 of the Periodic
Table. They contain full valence shells.
Noble Gas Notation – Noble gas is
used to represent the core (inner)
electrons and only the valence shell
is shown.
Br
Spectroscopic
2
2
6
2
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5
[Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 5
Noble gas
The “[Ar]” represents the core electrons and only the valence electrons are shown.
39/60
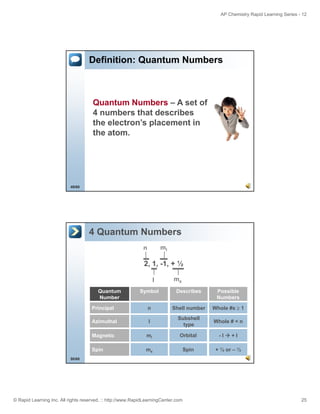
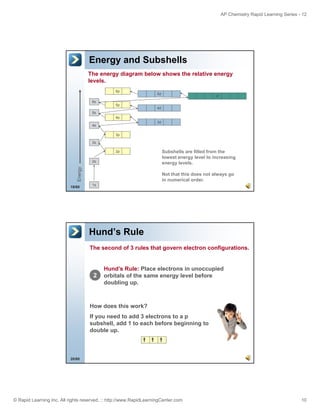
Which Noble Gas Do You Choose?
How do you know which noble gas to use to
symbolize the core electrons?
Think: Price is Right.
How d you win on the Price is Right?
H
do
i
th P i i Ri ht?
By getting as close as possible without going over.
Choose the noble gas that’s closest without going over!
Noble Gas
He
2
Ne
10
Ar
18
Kr
40/56
# of electrons
36
Xe
54
© Rapid Learning Inc. All rights reserved. :: http://www.RapidLearningCenter.com
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicstructures-131223210234-phpapp02/85/Atomic-structures-20-320.jpg)
![AP Chemistry Rapid Learning Series - 12
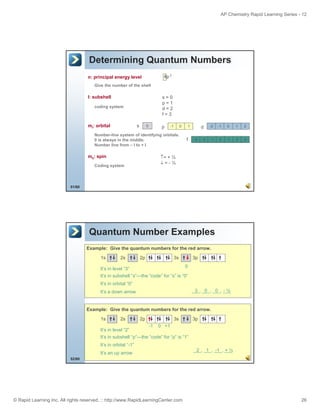
Where Does the Noble Gas Leave Off?
How do you know where to start off after using a
noble gas?
Use the periodic table!
1s
He
2p
2s
Ne
3p
Ar
4s
3d
4p
Kr
5s
4d
5p
Xe
6p
Rn
3s
6s
4f
5d
7s
5f
6d
The noble gas fills the subshell that it’s at the end of.
Begin filling with the “s” subshell in the next row to show
valence electrons.
41/60
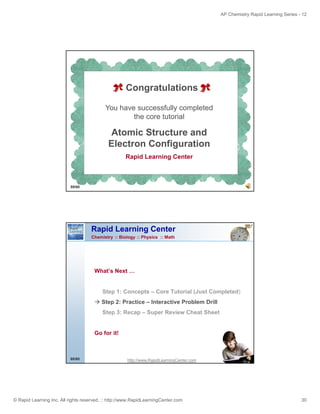
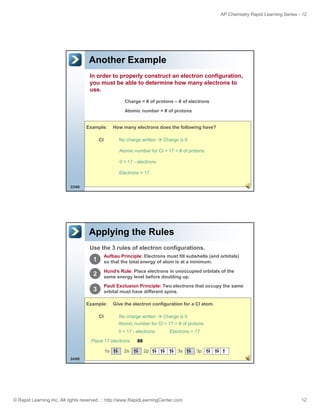
Noble Gas Notation Example
1
Determine the number of electrons to place.
2
Determine which noble gas to use.
3
Start where the noble gas left off and write spectroscopic
notation for the valence electrons.
Example:
As
Give the noble gas notation for As.
No charge written
Charge is 0
Atomic number for As = 33 = # of protons
0 = 33 - electrons
Electrons = 33
Place 33 electrons
Closest noble gas: Ar (18)
[Ar] 4s 2 3d 10 4p 3
Ar is full up through 3p
18 + 2 + 10 + 3 = 33
42/60
© Rapid Learning Inc. All rights reserved. :: http://www.RapidLearningCenter.com
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicstructures-131223210234-phpapp02/85/Atomic-structures-21-320.jpg)