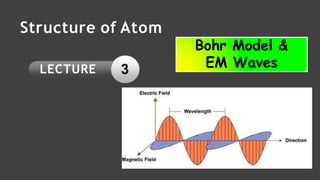
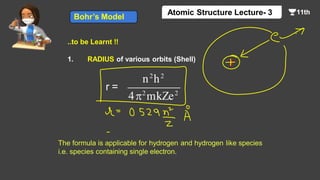
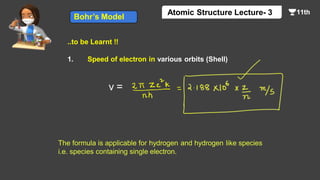
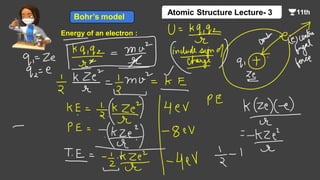
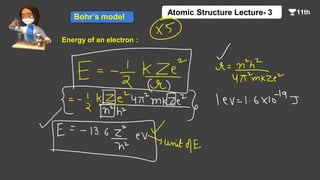
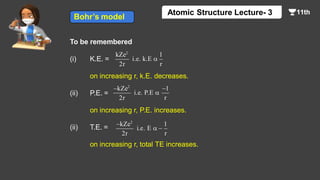
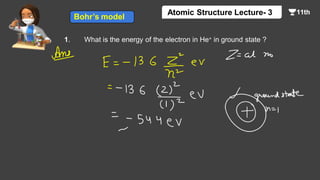
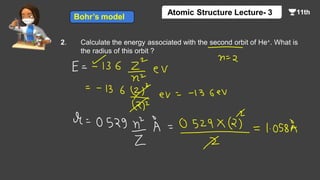
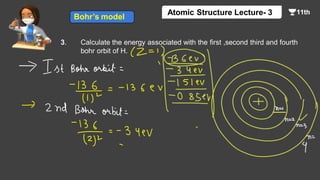
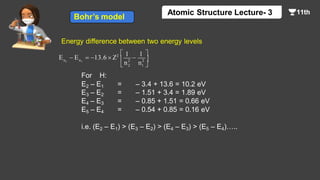
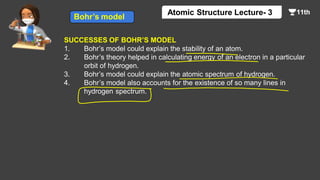
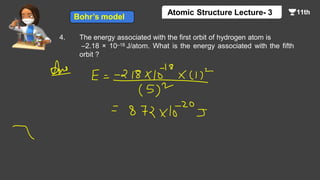
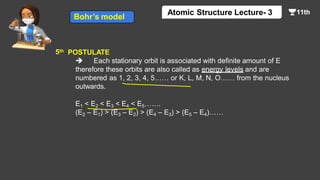
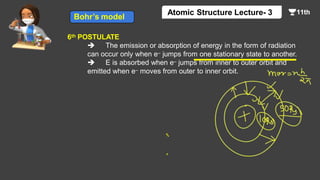
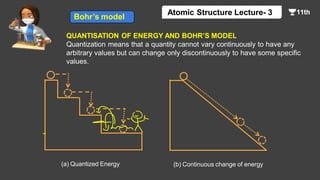
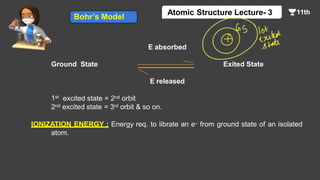
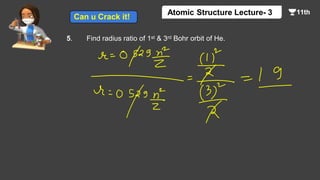
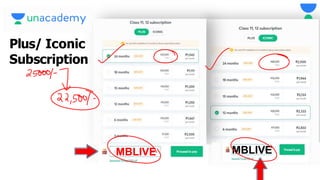
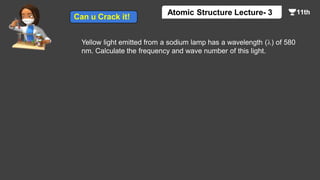
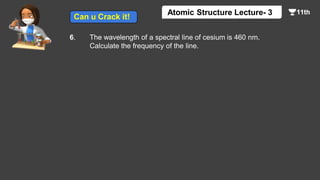
This document contains a lecture on the Bohr model of the atom and electromagnetic waves. It discusses Bohr's model, including formulas for the radius and speed of electrons in different orbits. It provides examples calculating the energy of electrons in different orbits of hydrogen and helium. It also covers the quantization of energy, absorption and emission of radiation, ionization energy, and the successes of Bohr's model in explaining atomic spectra and stability. The document ends with practice problems calculating wavelength, frequency, and wave number for different electromagnetic radiations.