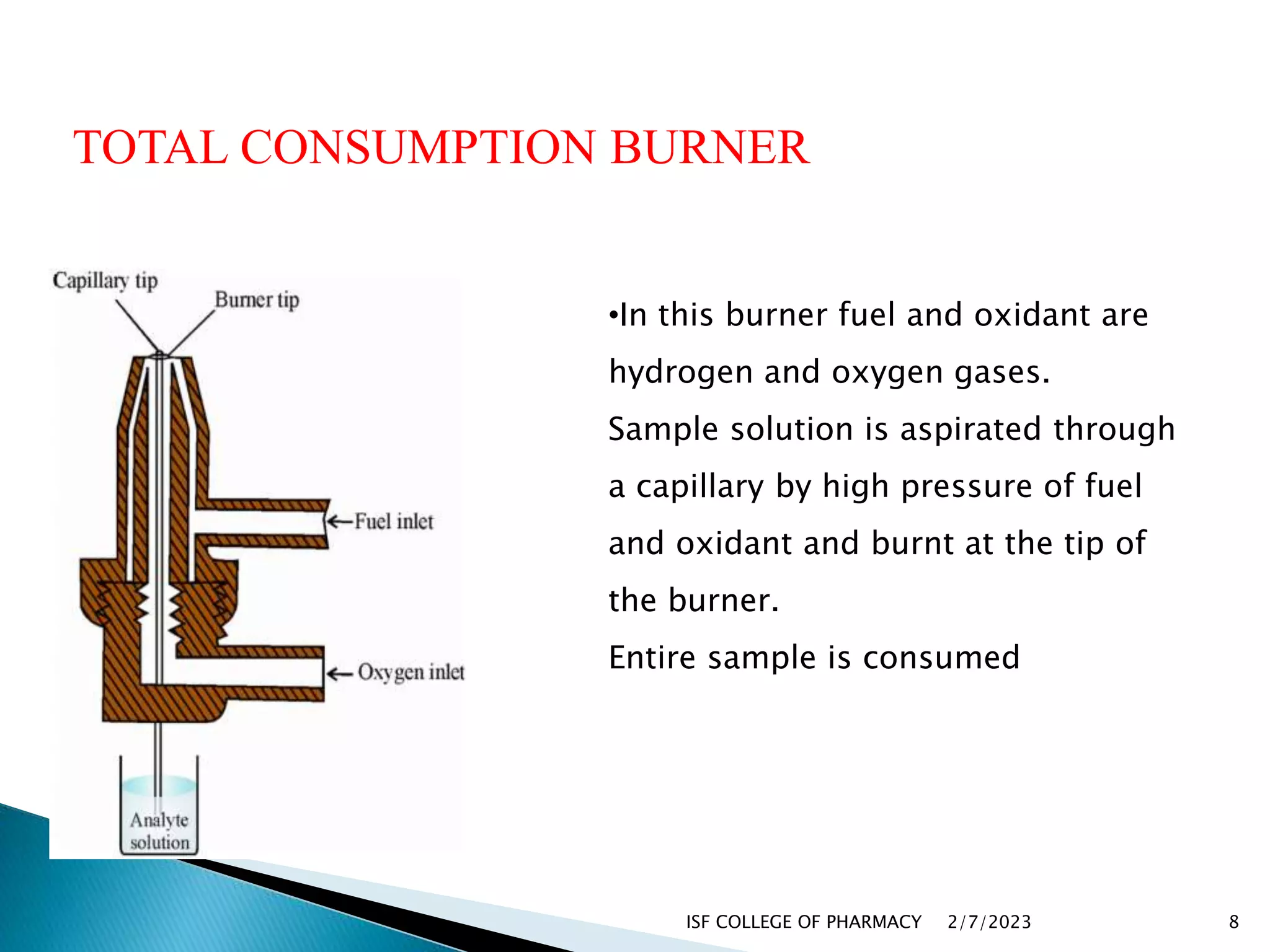
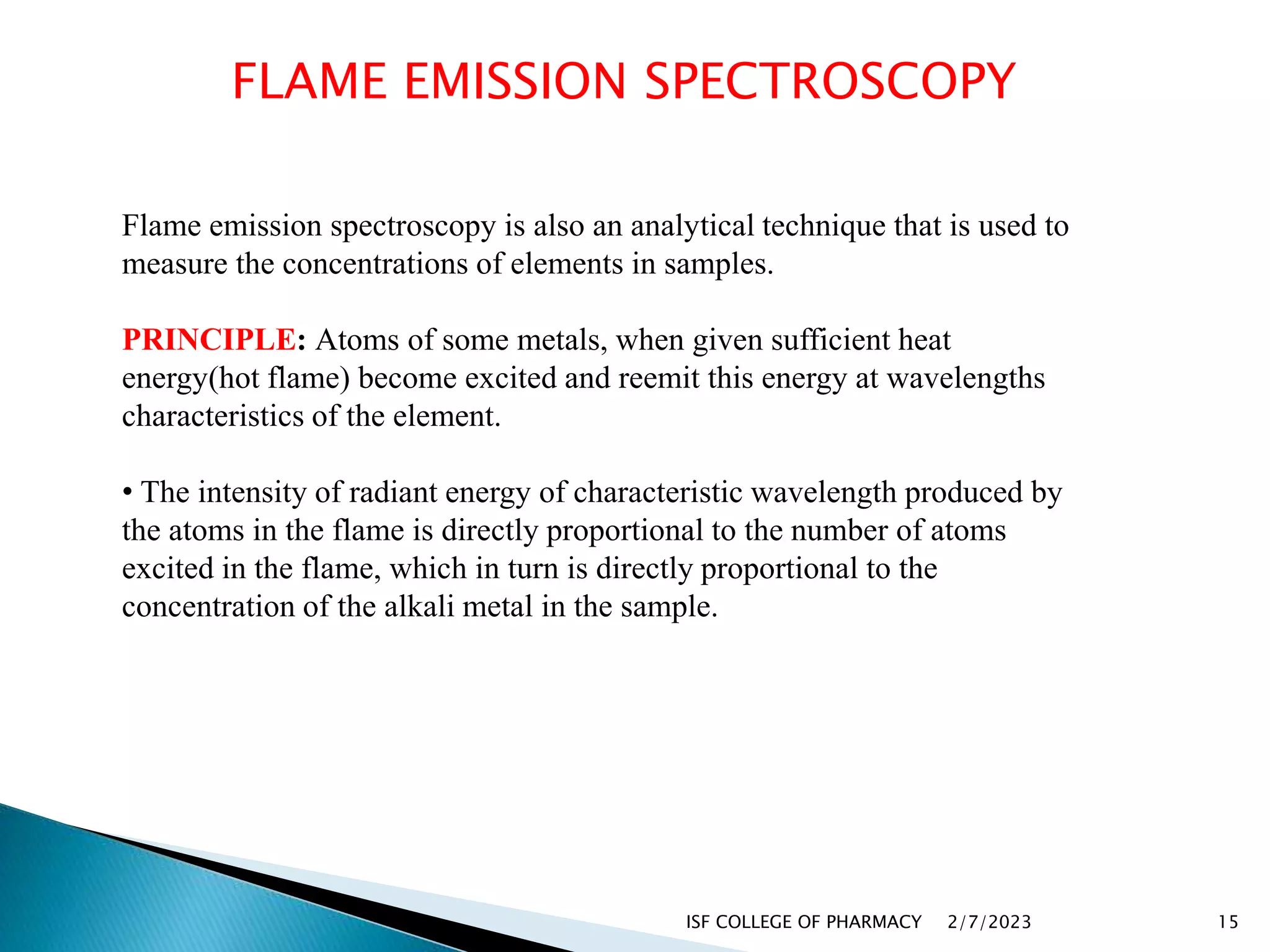
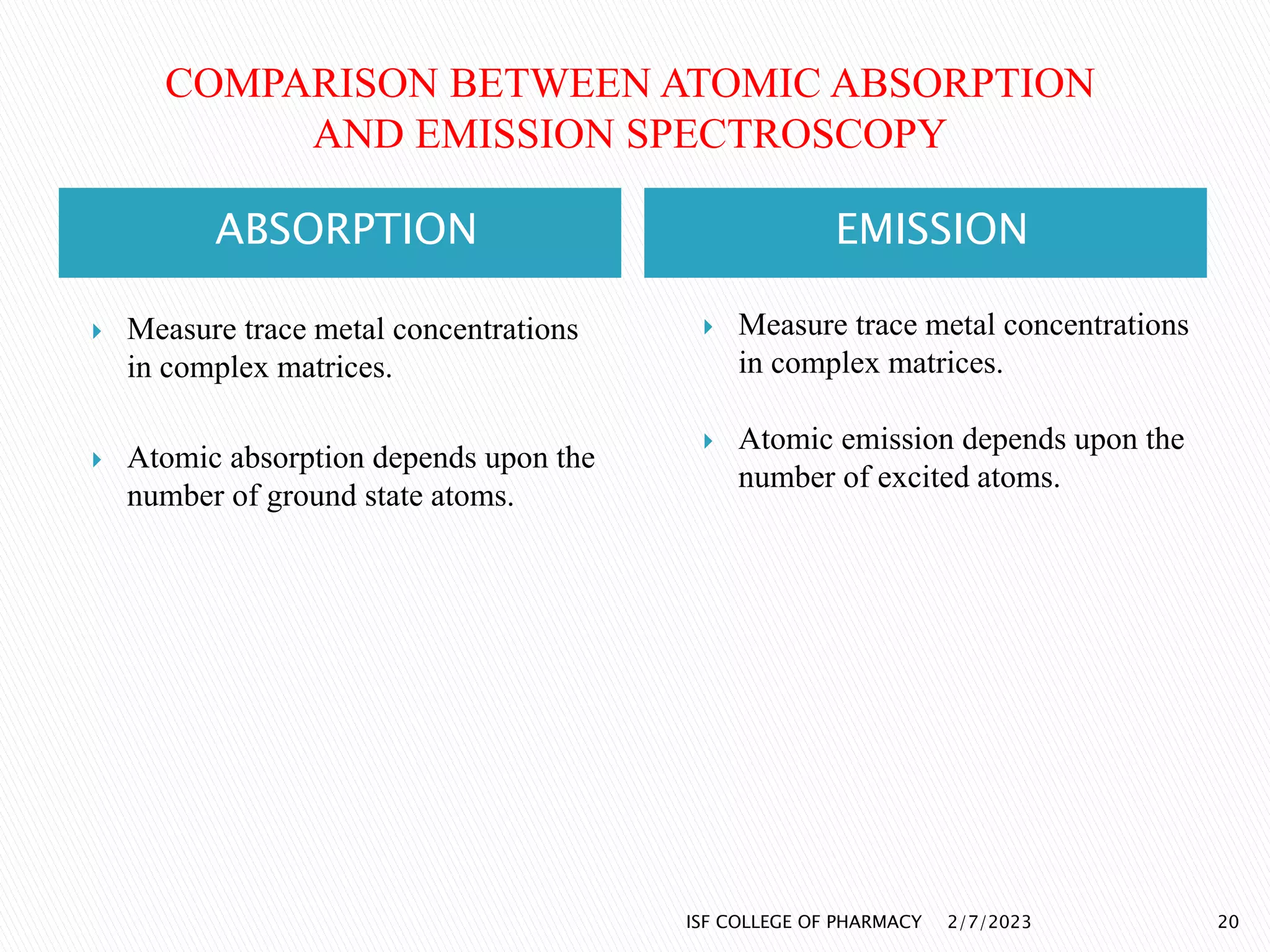
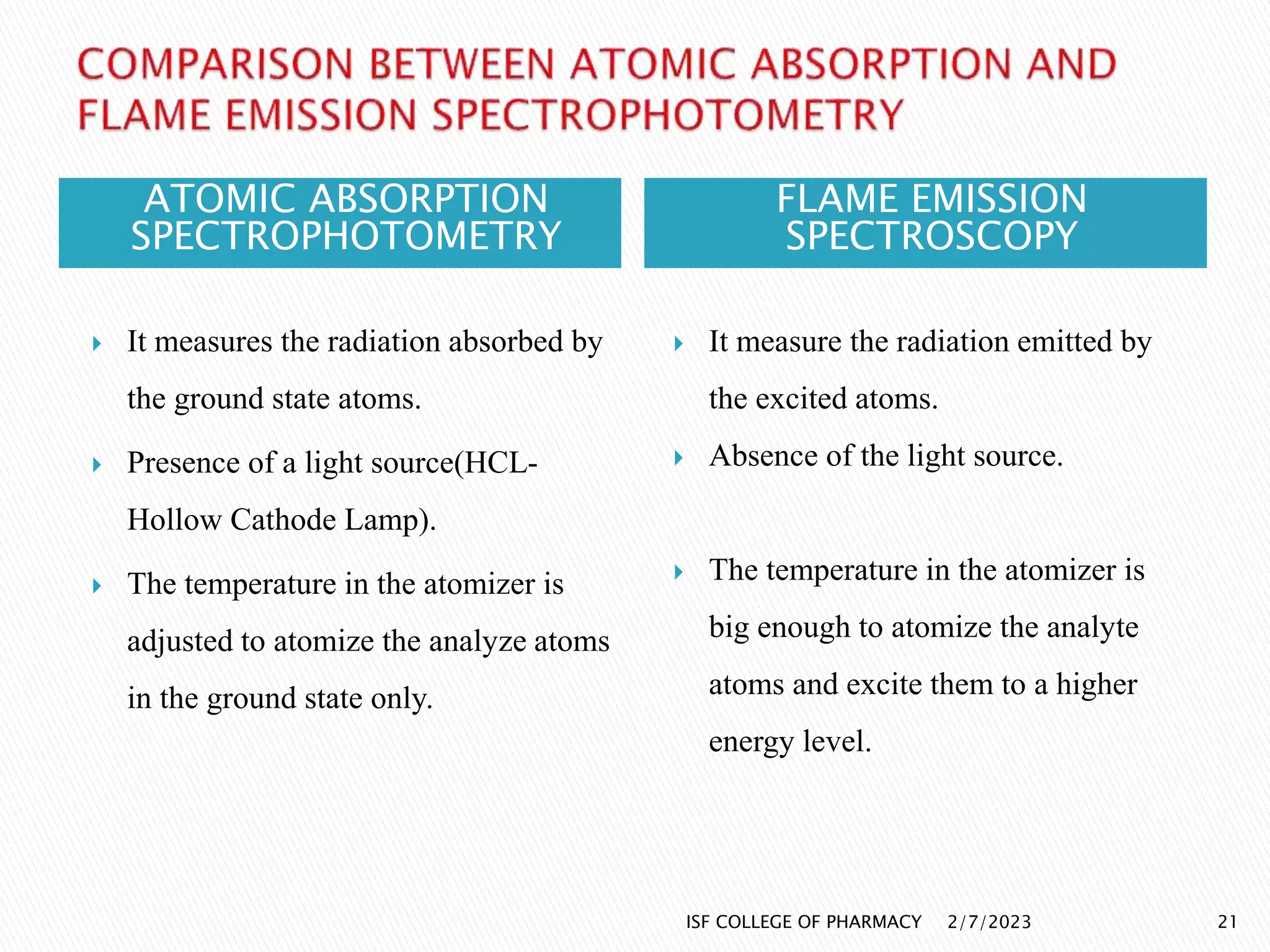
The document discusses atomic absorption spectrophotometry and flame emission spectroscopy, both analytical techniques for measuring element concentrations. Atomic absorption primarily detects metals and metalloids by measuring light absorption from ground state atoms, while flame emission spectroscopy analyzes excited atoms emitting characteristic wavelengths. Applications for both techniques include environmental monitoring, clinical analysis, and mining, alongside advantages and disadvantages associated with their use.