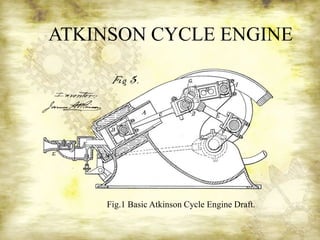
This presentation summarizes the Atkinson cycle engine. It discusses how James Atkinson invented the cycle in 1882 to provide efficiency over power density. The presentation describes the ideal thermodynamic cycle process and working principle of the Atkinson cycle. It identifies types of engines that use the Atkinson cycle, such as differential, gas, and Utilite engines. The presentation also outlines pros and cons of the Atkinson cycle engine as well as its applications in automobiles and future scope.