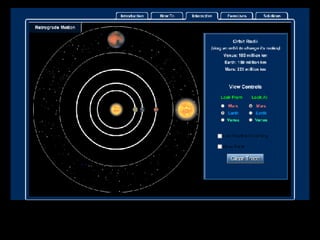
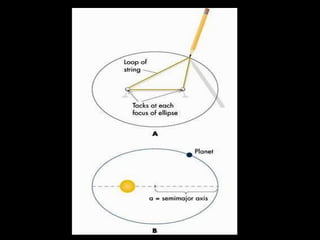
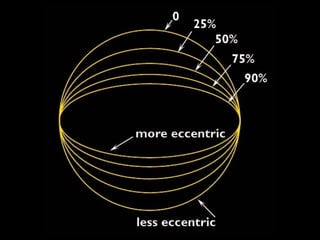
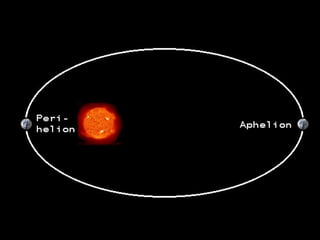
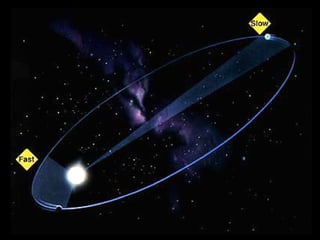
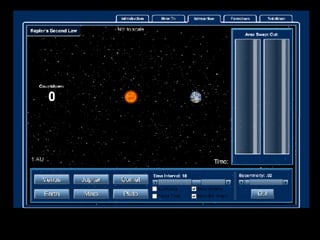
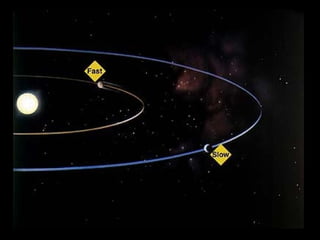
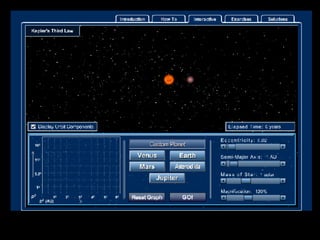
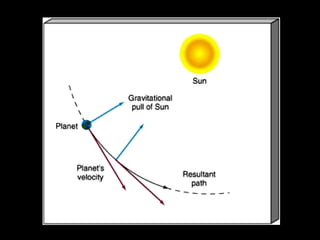
This document summarizes models of the solar system from ancient to modern times. It describes the geocentric model where Earth is the center, then introduces the heliocentric model where the Sun is at the center accepted today. Kepler analyzed Brahe's planetary observation data to formulate his three laws of planetary motion: 1) Elliptical orbits with Sun at one focus, 2) Equal area swept in equal time, 3) Period squared is proportional to semi-major axis cubed. Newton later generalized gravity with his law of universal gravitation.