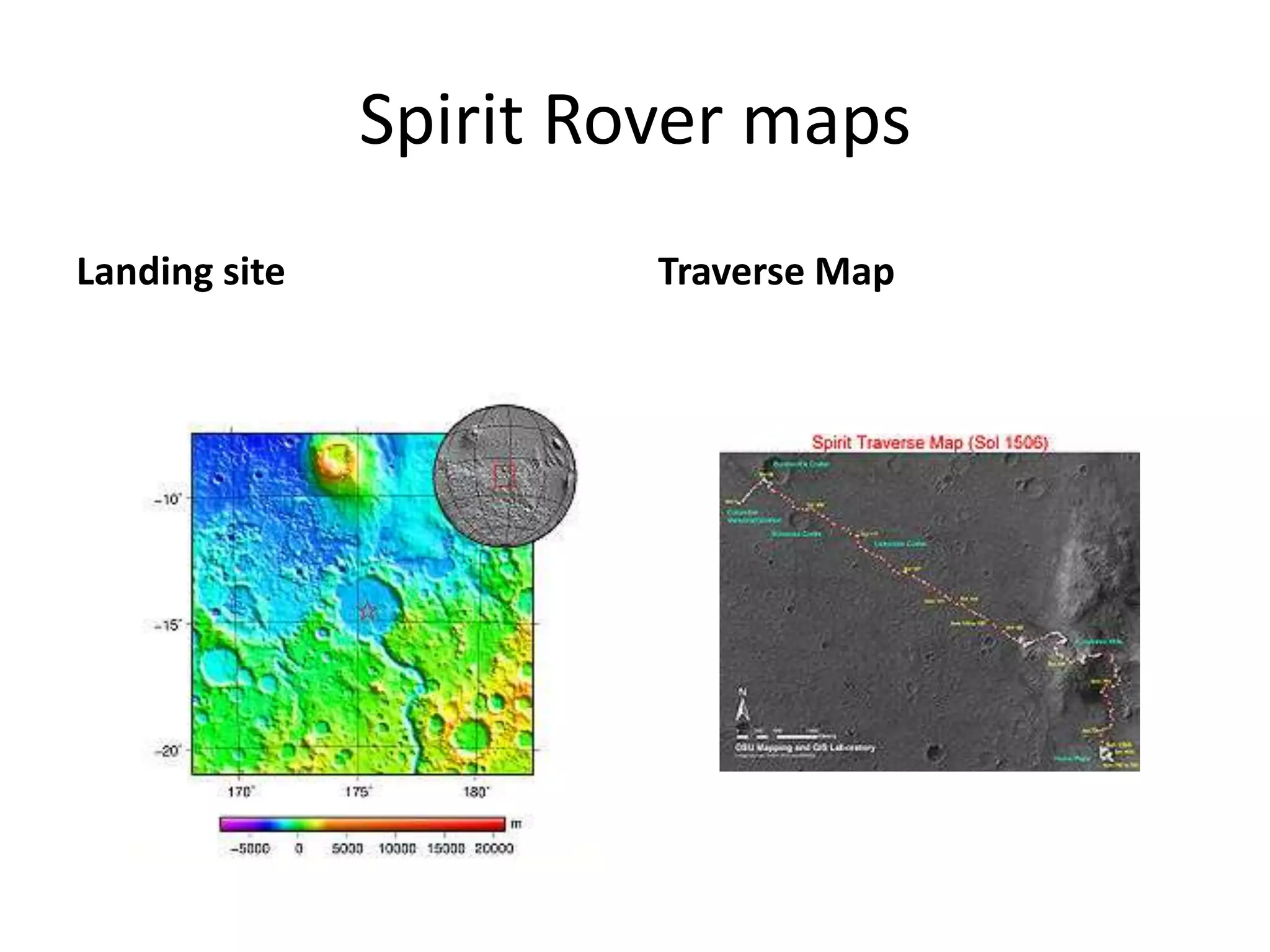
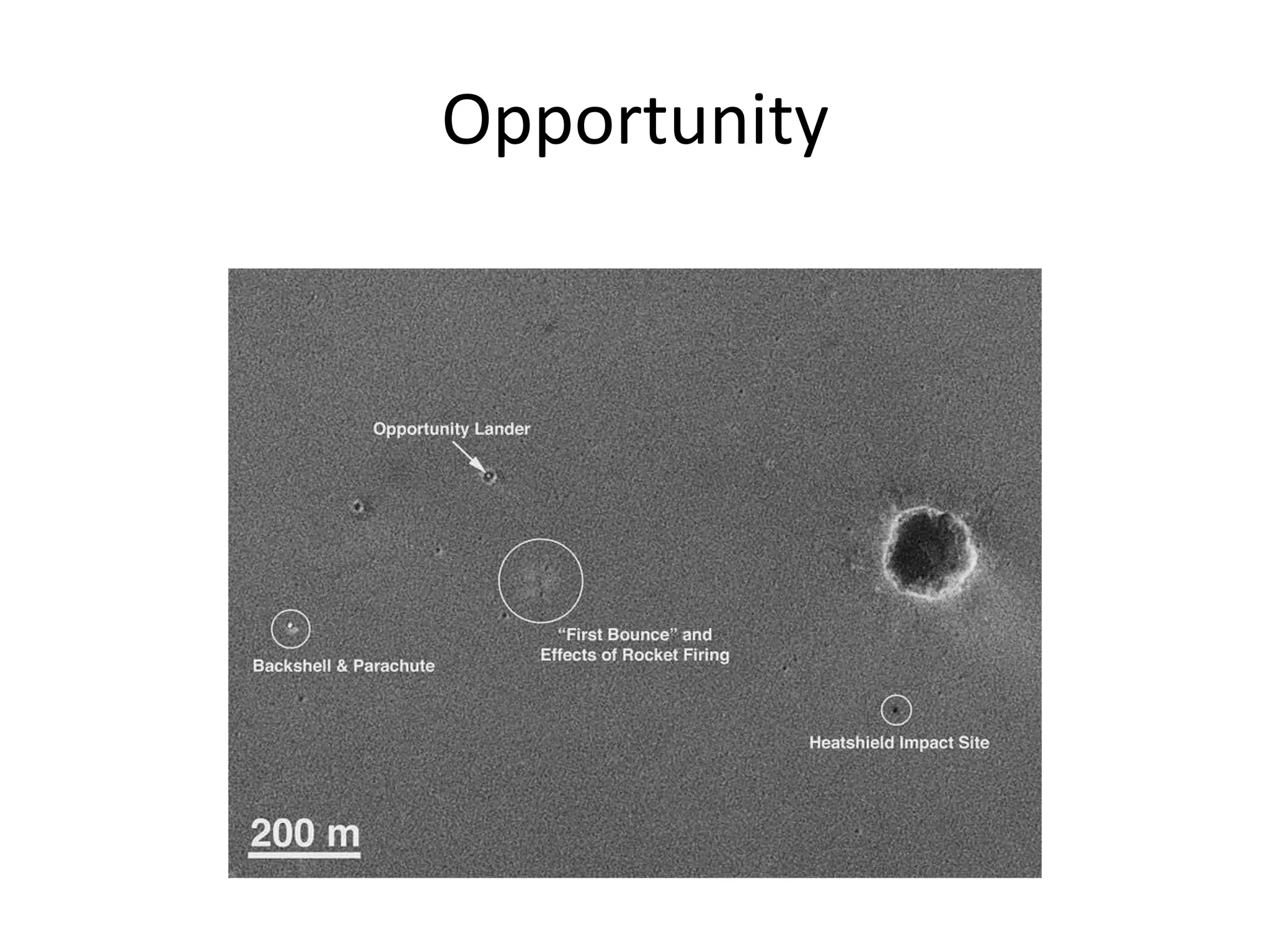
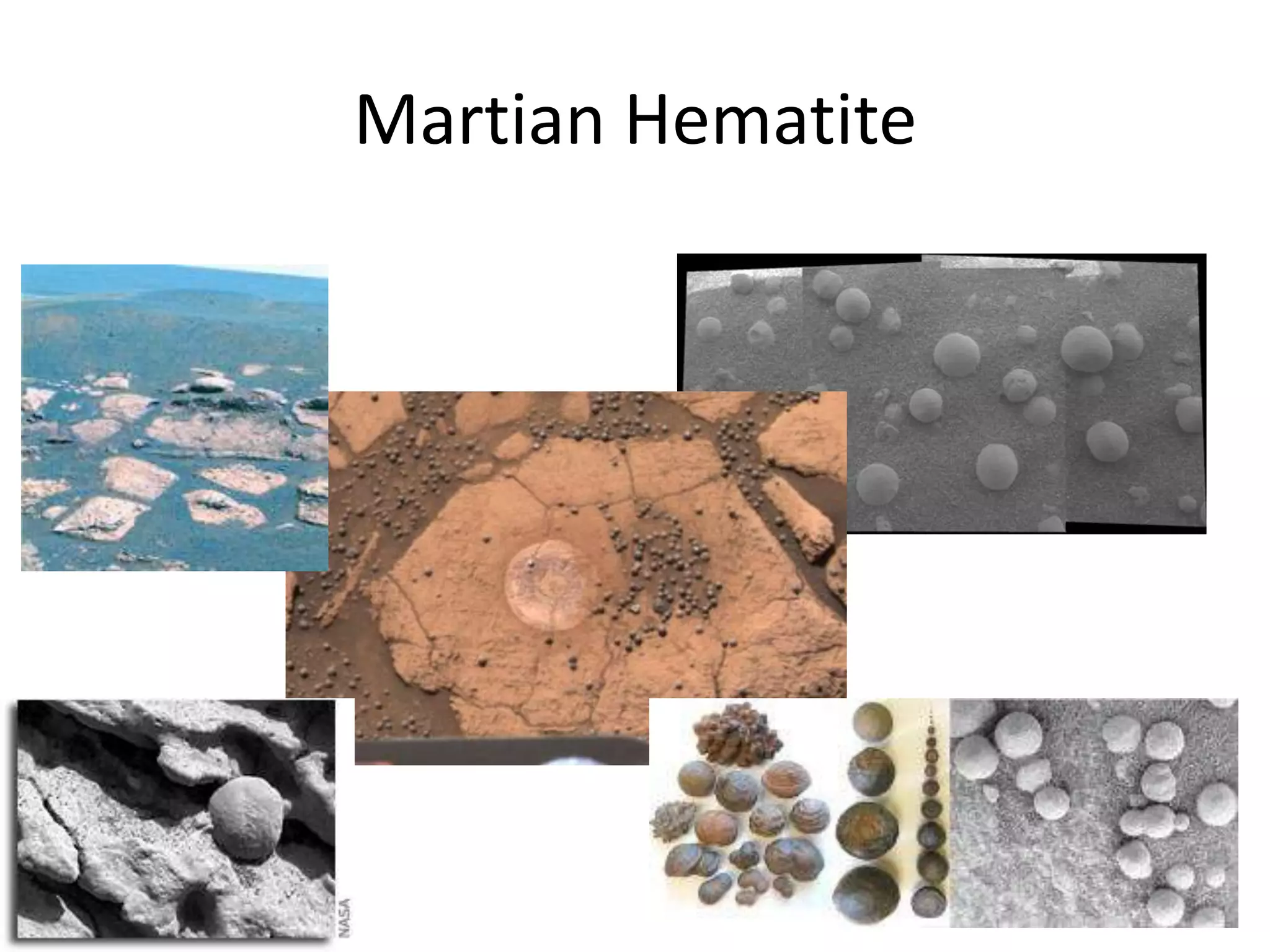
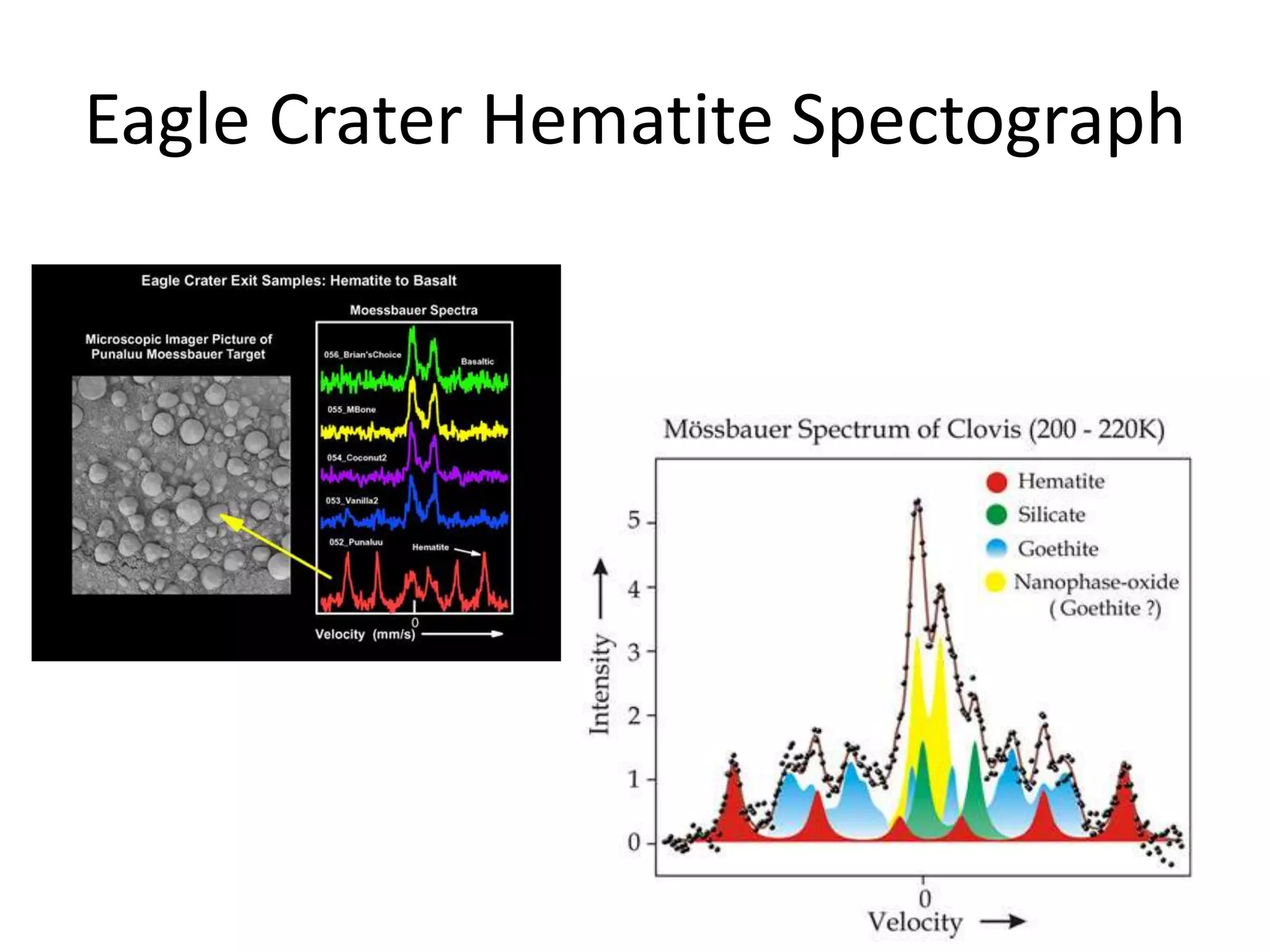
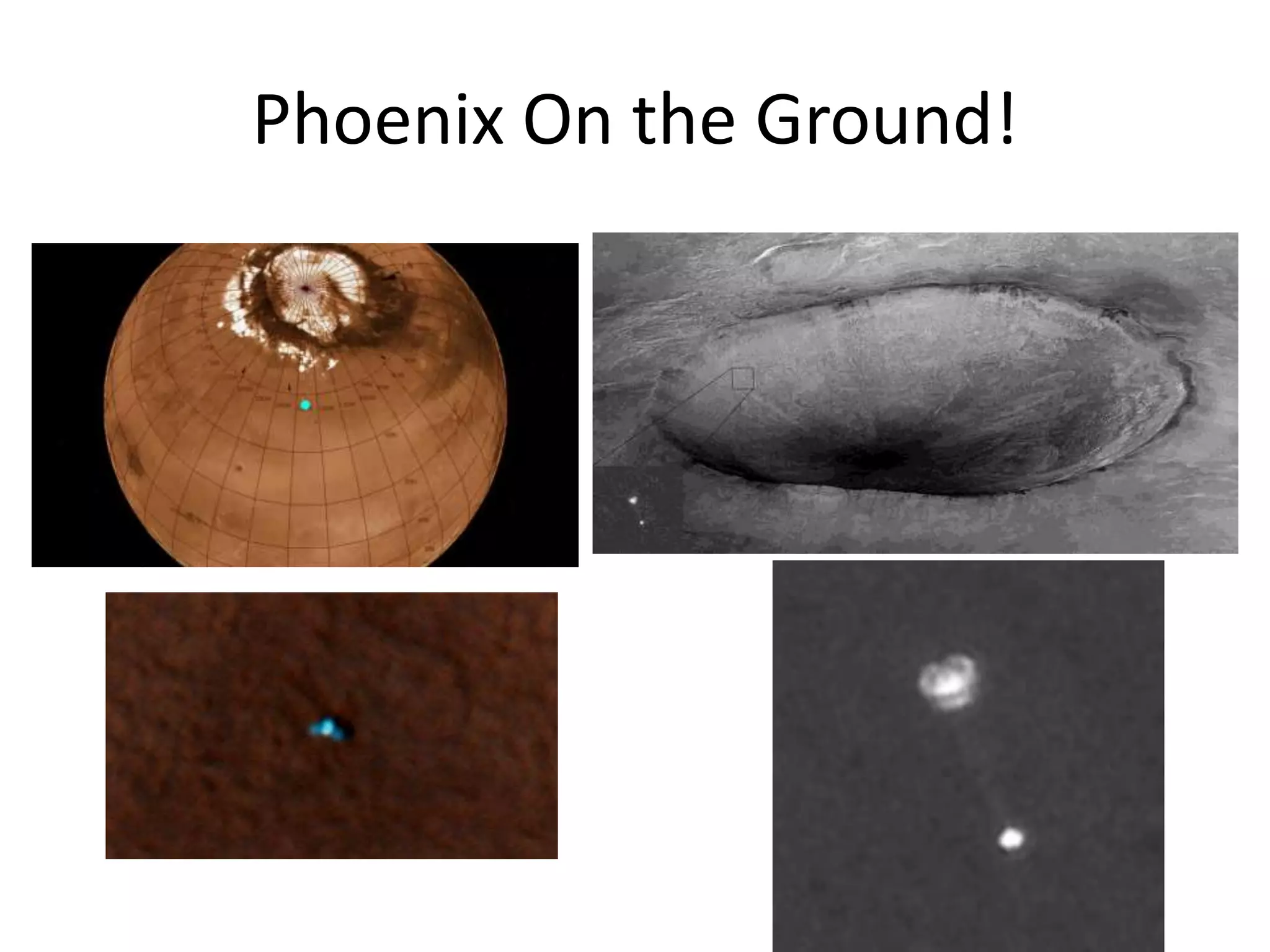
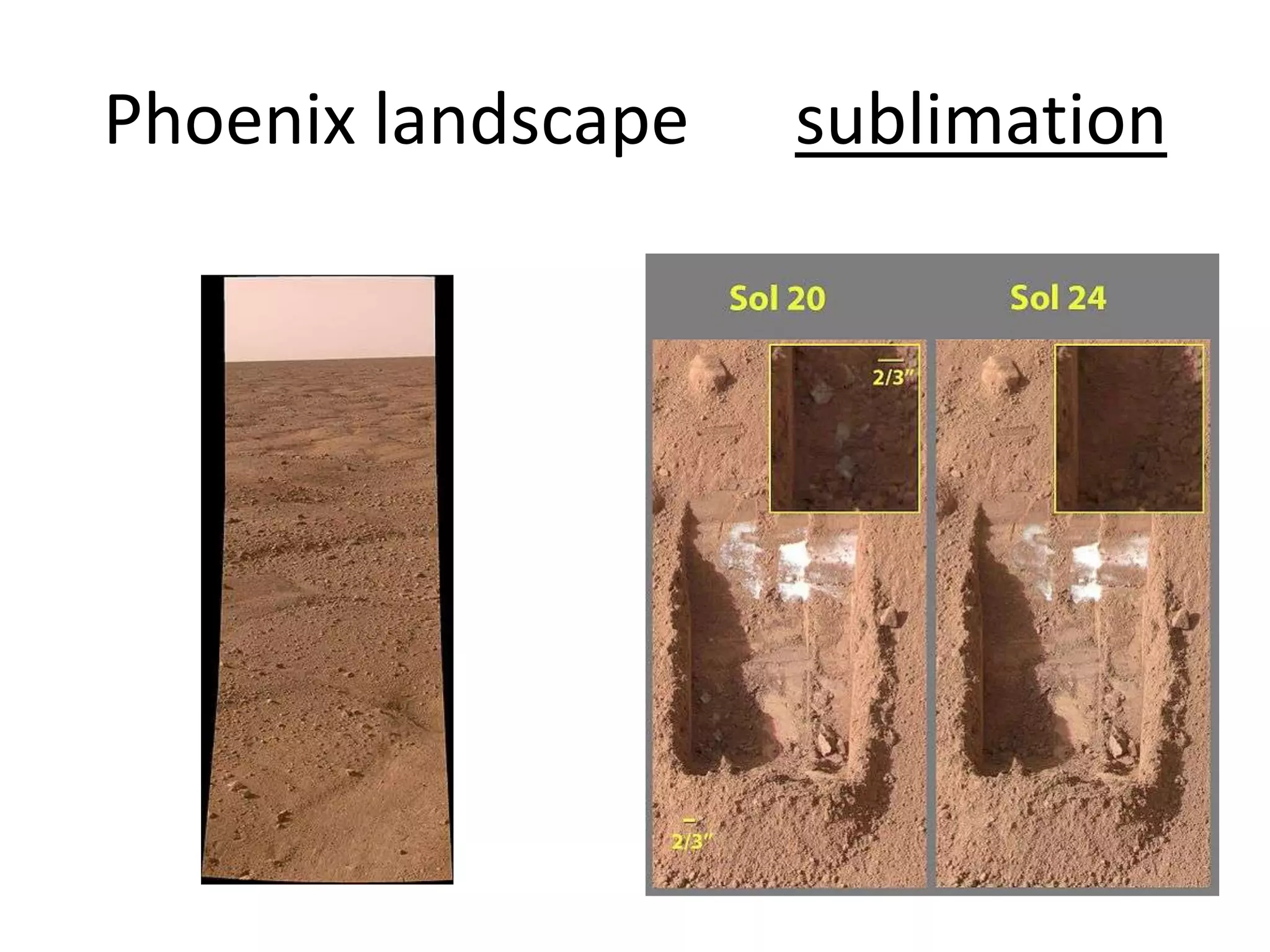
This document provides information on various Mars rovers and landers including Viking 1 and 2 from 1976, Mars Pathfinder and Sojourner rover from 1997, Spirit and Opportunity rovers from 2004, Phoenix lander from 2008, and Curiosity rover. It describes their scientific instruments and key findings such as Viking detecting organic compounds in the soil, Pathfinder determining the atmosphere contains dust particles about 1 micrometer in size, Spirit and Opportunity finding evidence of past water activity, and Phoenix confirming the presence of water ice on Mars.