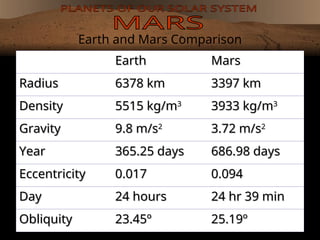
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, known for its red hue due to iron oxide and features like Olympus Mons, the largest volcano, and Valles Marineris, the largest canyon. It has a thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide and experiences seasonal changes similar to Earth, though lasting longer. Mars exploration has revealed its dry terrain and intriguing past, with evidence suggesting it may have once had liquid water and conditions suitable for life.