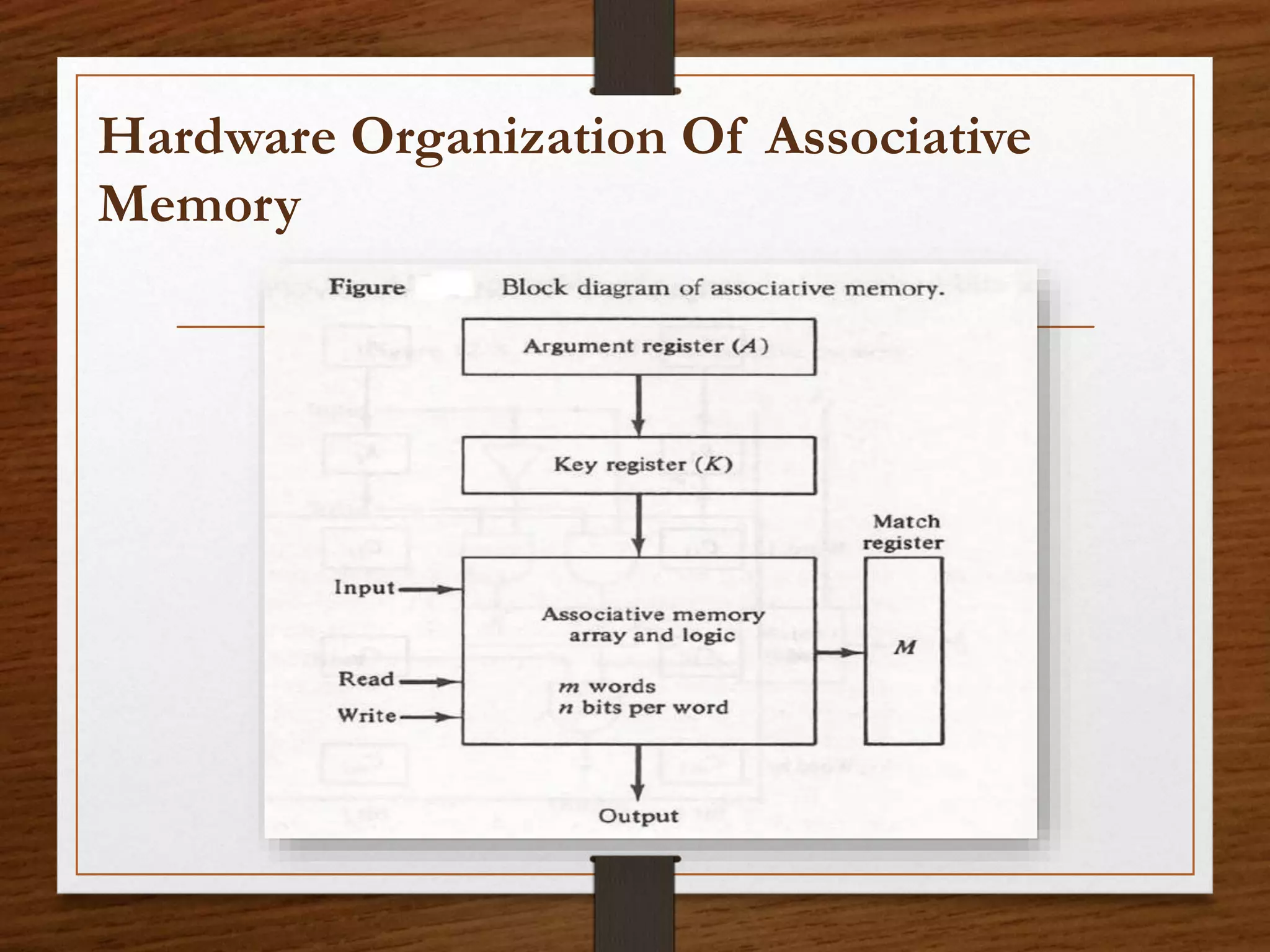
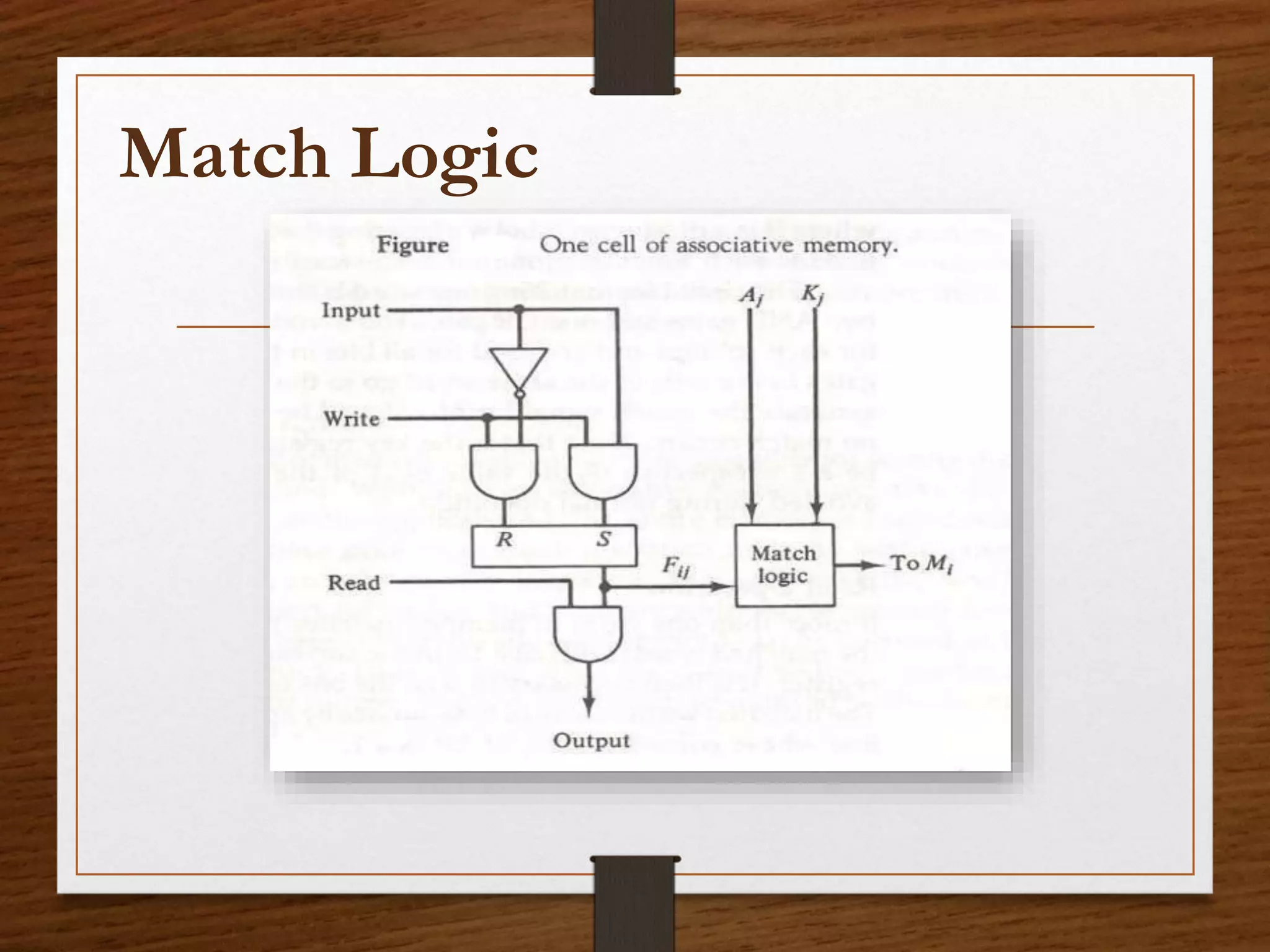
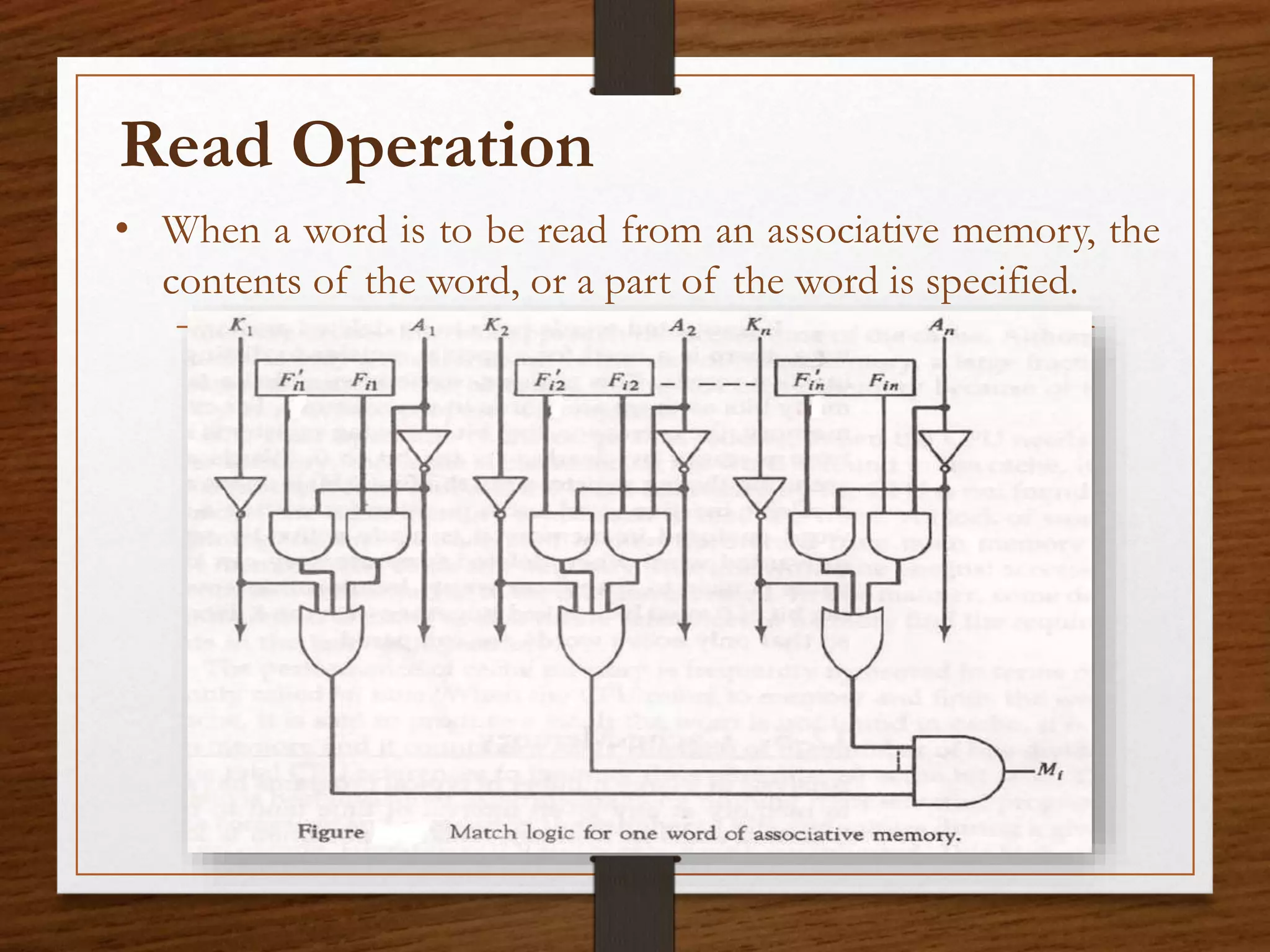
This document summarizes the key aspects of associative memory. It discusses that associative memory allows data to be accessed by content by finding a match rather than an address. The hardware organization involves argument, key, and match registers that are used to specify the data to search for, which bits to compare, and where matches are found. It also describes read and write operations where data can be searched for and stored by content matching rather than addressing. The advantages are parallel searching and speeding up databases, while disadvantages include higher costs than random access memory.