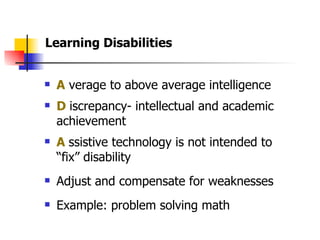
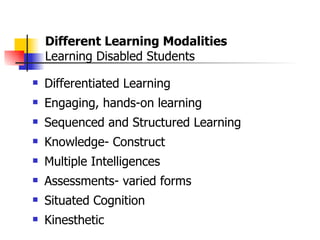
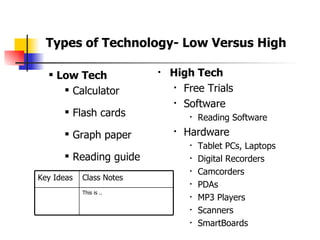
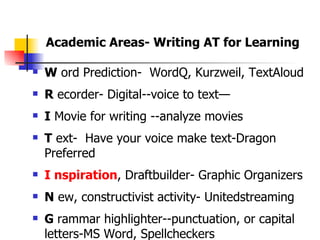
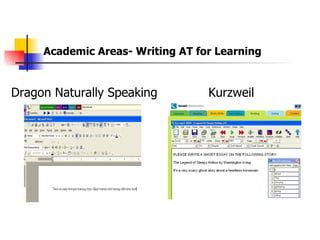
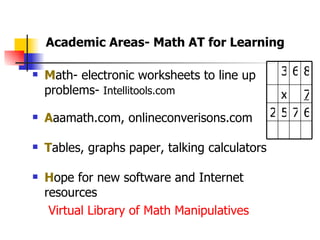
The document is a guide on assistive technology (AT) for parents and teachers of middle school students with learning disabilities, emphasizing the definition of AT as tools and equipment that enhance learning capabilities rather than fix disabilities. It outlines various types of AT resources, including low and high-tech options, and highlights the importance of differentiated instruction to cater to diverse learning styles and modalities. Additionally, it stresses the collaboration between parents and teachers in implementing effective learning strategies and assessments for students with diverse needs.
![Assistive Technology and Learning Guide for Parents and Teachers Assistive Technology (AT) Learning Disabilities (LD)- Middle School Divergent Learning Styles Current or Future Need Academic Areas Barriers Learning Sciences and Technology (LST) Copyright 2005. James Vincent Puglia [Key Source: Driscoll, 2003]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assistive-technology-26190/75/Assistive-Technology-1-2048.jpg)