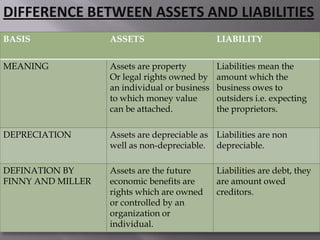
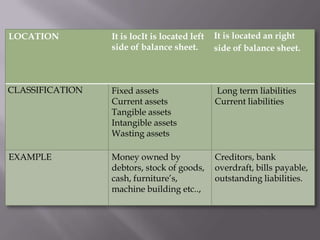
This document discusses assets and liabilities in accounting theory. It defines assets as probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by an entity as a result of past transactions or events. Assets are classified as fixed, current, tangible, and intangible. Liabilities are defined as obligations of an entity to transfer economic benefits in the future. Liabilities are classified as current or long-term. The key difference between assets and liabilities is that assets are resources owned by the entity, while liabilities are amounts owed by the entity.