The document discusses assessing role-plays and simulations in business English training. It proposes that assessments should:
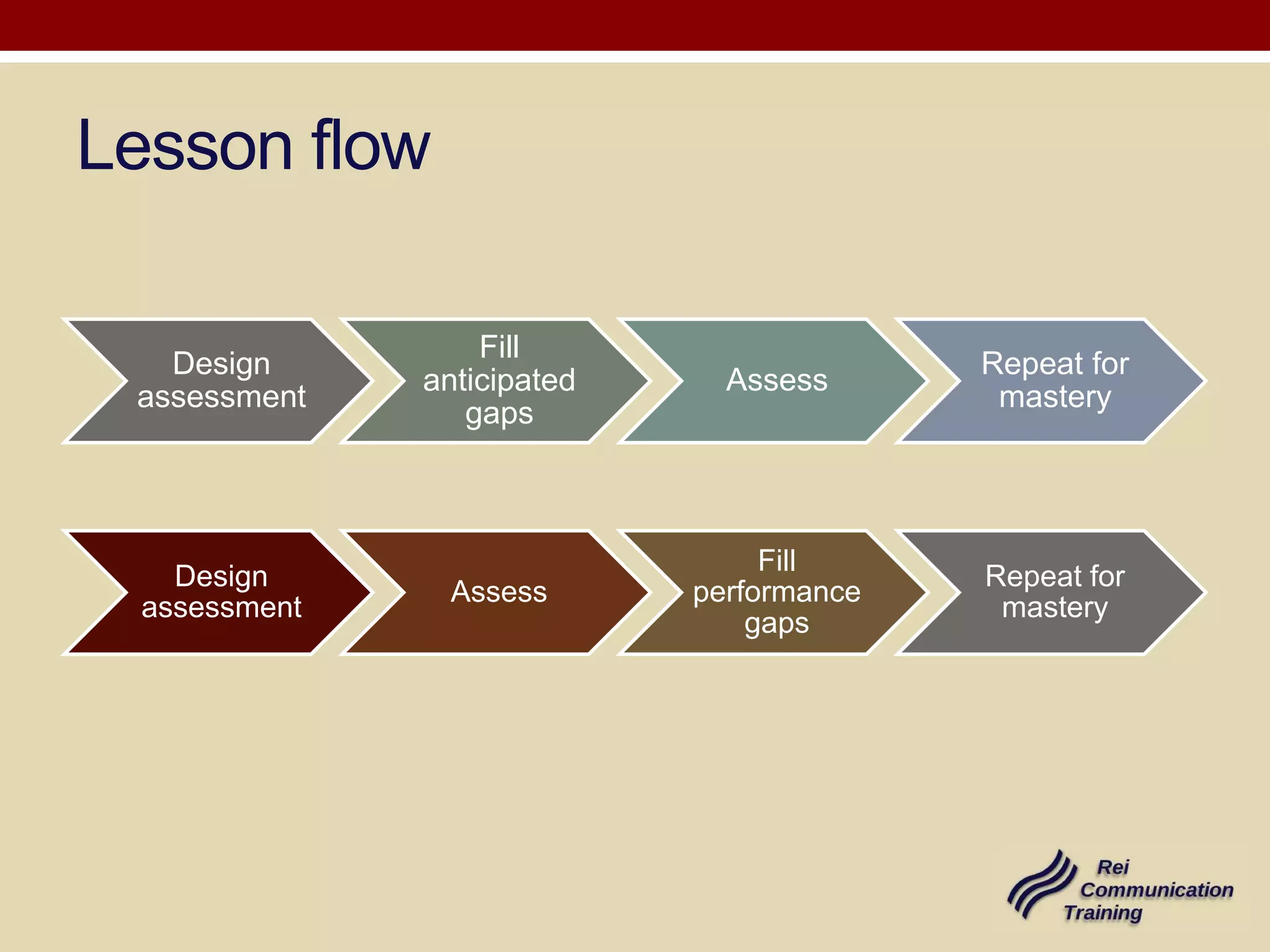
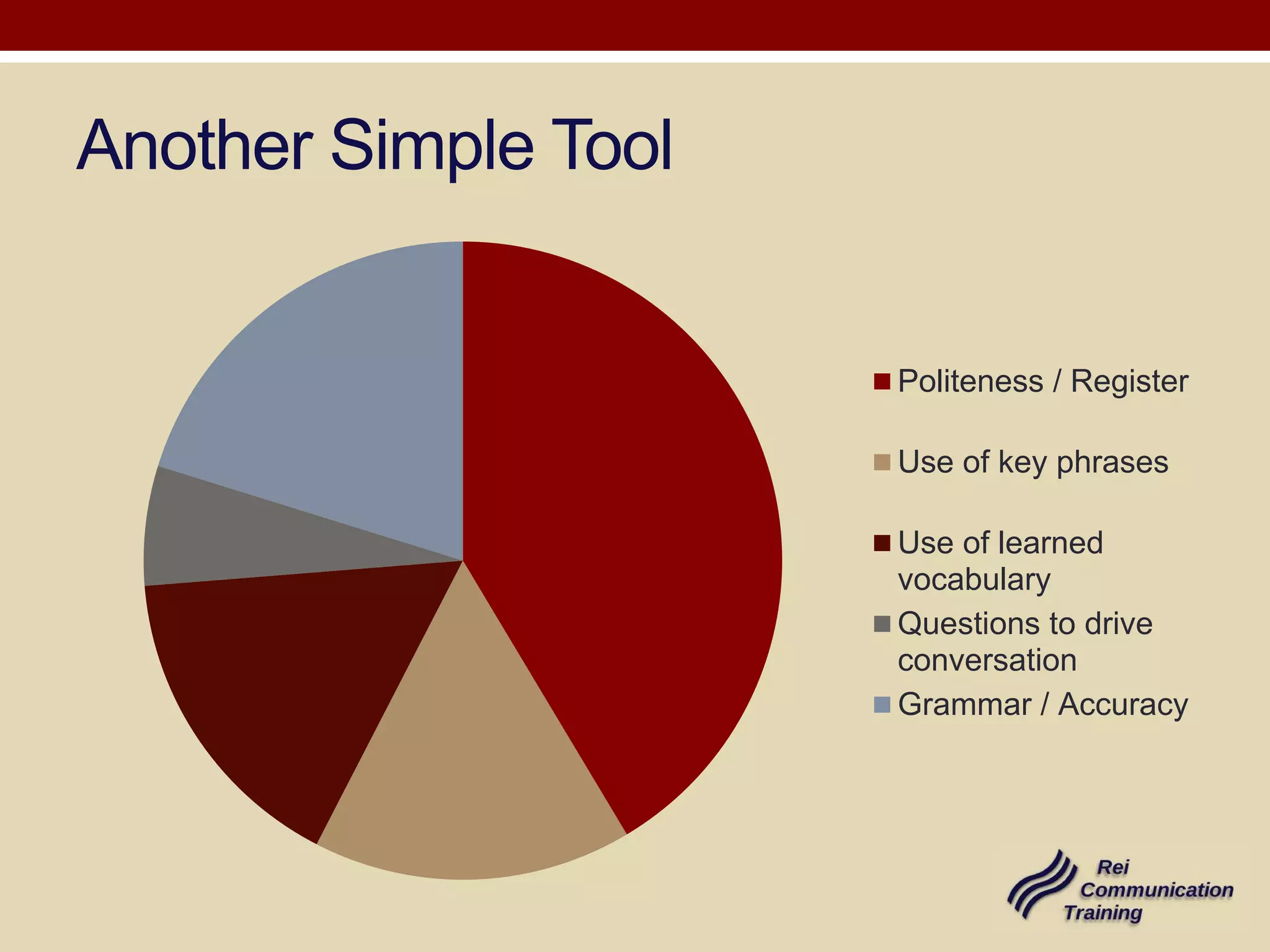
1) Be tailored to the specific discourse community and focus on both language performance and achieving communicative objectives.
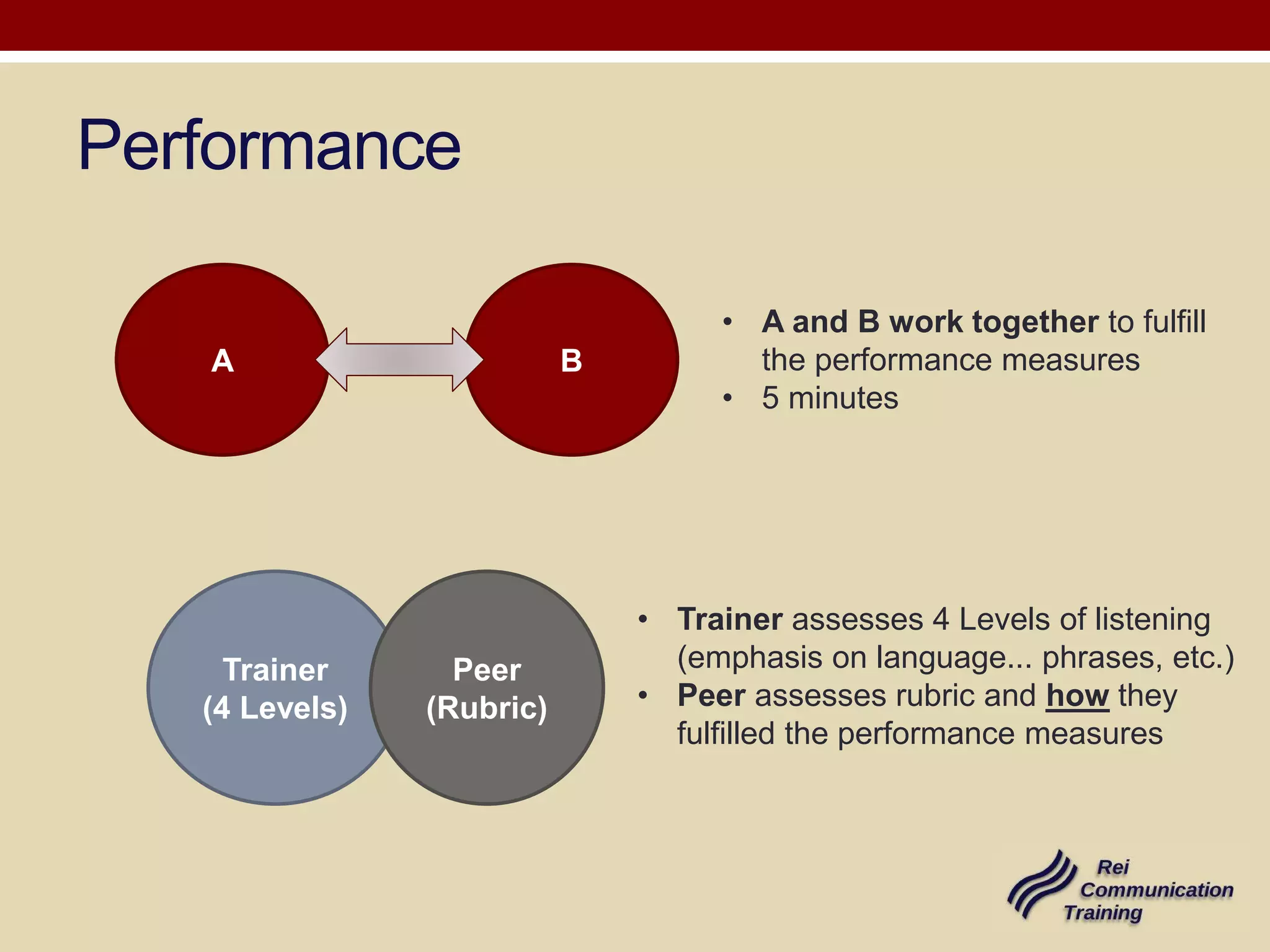
2) Involve peer assessment using rubrics to evaluate how well participants fulfilled expected performance measures.
3) Include trainer assessment of language skills and providing feedback to help close performance gaps.