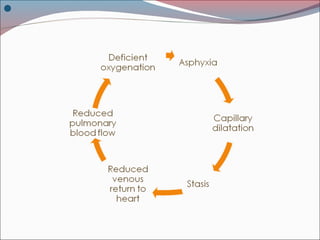
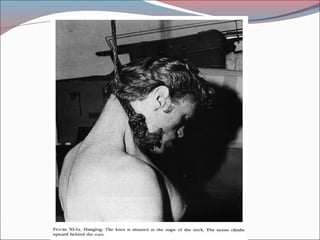
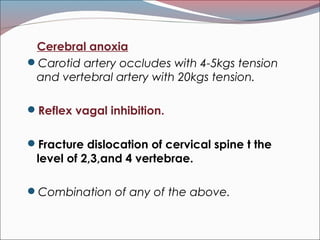
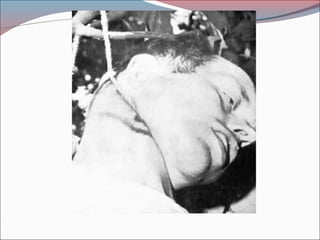
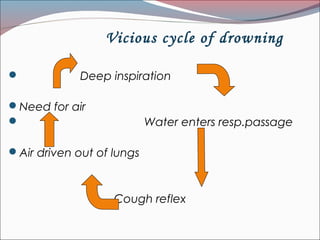
The document provides a comprehensive overview of asphyxia, detailing its causes, features, types of death related to asphyxia (such as hanging, strangulation, and drowning), and the associated postmortem appearances. It discusses the mechanisms of death from asphyxia, the medico-legal implications, and diagnostic criteria, highlighting distinctions between suicidal, homicidal, and accidental cases. The document also covers the nuances of drowning, including typical and atypical drowning, emphasizing the physiological responses and legal considerations in forensic evaluations.