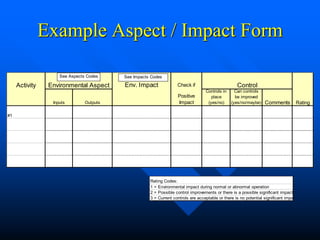
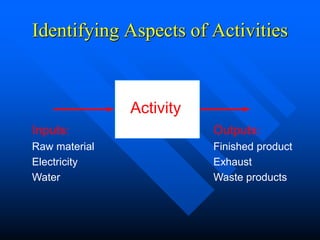
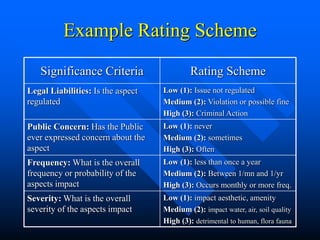
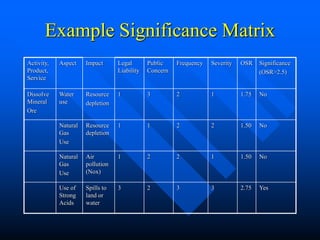
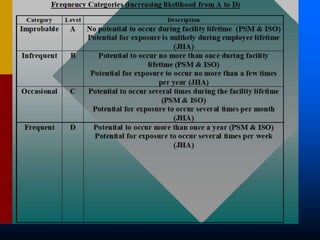
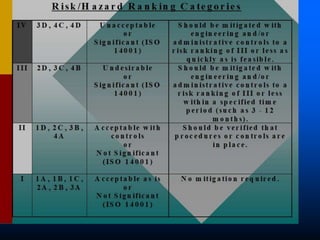
This document provides guidance on identifying environmental aspects and impacts as part of an environmental management system. It discusses establishing a team to identify aspects, educating the team on the purpose and implications, identifying aspects and impacts for each activity, and developing a procedure to determine which aspects have significant impacts. It provides examples of factors to consider for determining significance, such as legal issues, public concern, frequency and severity of impacts. Homework is assigned to complete the identification and ranking of aspects and impacts.