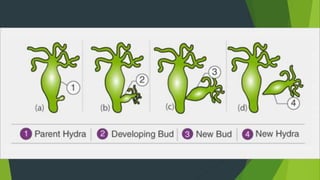
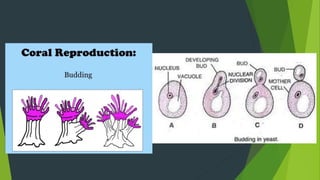
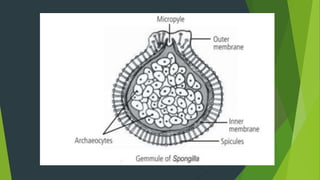
Asexual reproduction allows offspring to form from a single parent without fertilization. It is common in plants, single-celled organisms, and simple animals. There are several mechanisms for asexual reproduction including budding, parthenogenesis, gemmules, and fragmentation. Hydras reproduce through budding where a small bud grows from the parent's body and detaches to form an independent organism. Corals similarly bud but offspring do not detach and instead form groups. Sponges release internal gemmules that develop into new organisms.