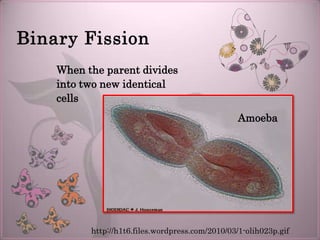
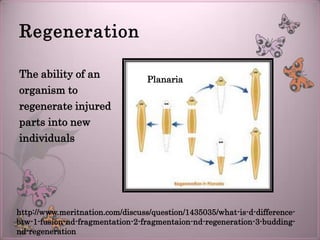
The document discusses the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction, highlighting that sexual reproduction involves two sex cells (egg and sperm) leading to genetically diverse offspring, while asexual reproduction involves one parent producing identical offspring. Various methods of asexual reproduction, such as binary fission, regeneration, budding, and spore formation are explained. It also notes that different kingdoms of life utilize these reproductive methods, including examples like bacteria, fungi, and mammals.